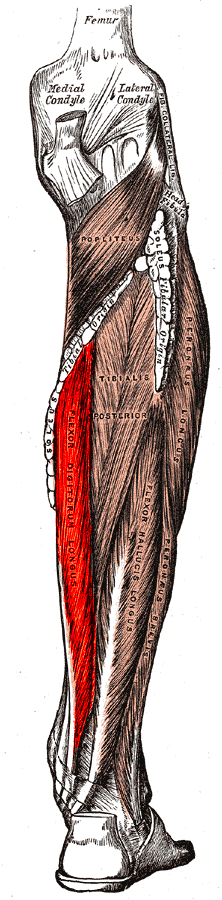
Flexor digitorum longus muscle
The flexor digitorum longus muscle is a muscle located on the posterior aspect of the leg. It is one of the deep muscles of the posterior compartment of the leg and plays a crucial role in the movement of the foot and toes.
Anatomy[edit | edit source]
The flexor digitorum longus muscle originates from the posterior surface of the body of the tibia. It travels down the leg, passing behind the medial malleolus of the ankle, and divides into four tendons. These tendons insert into the bases of the distal phalanges of the four lesser toes (second to fifth toes).
Innervation[edit | edit source]
The muscle is innervated by the tibial nerve, which is a branch of the sciatic nerve.
Blood Supply[edit | edit source]
The blood supply to the flexor digitorum longus muscle is provided by the posterior tibial artery.
Function[edit | edit source]
The primary function of the flexor digitorum longus muscle is to flex the toes. It also assists in plantar flexion of the ankle and inversion of the foot. This muscle is essential for activities such as walking, running, and gripping objects with the toes.
Clinical Significance[edit | edit source]
Injuries or conditions affecting the flexor digitorum longus muscle can lead to difficulties in toe flexion and overall foot movement. Conditions such as tendinitis or tendon rupture can impair the function of this muscle.
See Also[edit | edit source]
References[edit | edit source]
External Links[edit | edit source]
Translate: - East Asian
中文,
日本,
한국어,
South Asian
हिन्दी,
தமிழ்,
తెలుగు,
Urdu,
ಕನ್ನಡ,
Southeast Asian
Indonesian,
Vietnamese,
Thai,
မြန်မာဘာသာ,
বাংলা
European
español,
Deutsch,
français,
Greek,
português do Brasil,
polski,
română,
русский,
Nederlands,
norsk,
svenska,
suomi,
Italian
Middle Eastern & African
عربى,
Turkish,
Persian,
Hebrew,
Afrikaans,
isiZulu,
Kiswahili,
Other
Bulgarian,
Hungarian,
Czech,
Swedish,
മലയാളം,
मराठी,
ਪੰਜਾਬੀ,
ગુજરાતી,
Portuguese,
Ukrainian
Navigation: Wellness - Encyclopedia - Health topics - Disease Index - Drugs - World Directory - Gray's Anatomy - Keto diet - Recipes
Search WikiMD
Ad.Tired of being Overweight? Try W8MD's physician weight loss program.
Semaglutide (Ozempic / Wegovy and Tirzepatide (Mounjaro / Zepbound) available.
Advertise on WikiMD
WikiMD is not a substitute for professional medical advice. See full disclaimer.
Credits:Most images are courtesy of Wikimedia commons, and templates Wikipedia, licensed under CC BY SA or similar.Contributors: Prab R. Tumpati, MD