Diffusion-weighted magnetic resonance imaging
(Redirected from Diffusion MRI)
Medical imaging technique
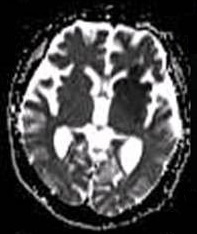
Diffusion-weighted magnetic resonance imaging (DW-MRI or DWI) is a specialized form of magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) that is particularly sensitive to the random Brownian motion of water molecules within a voxel of tissue. This technique is widely used in the field of neuroimaging and has applications in the diagnosis and monitoring of various medical conditions, particularly in the detection of acute ischemic stroke.
Principles of Diffusion-weighted Imaging[edit | edit source]
Diffusion-weighted imaging exploits the diffusion properties of water molecules to generate contrast in MR images. In biological tissues, water diffusion is not free but is restricted by cellular structures such as membranes and macromolecules. DWI measures the apparent diffusion coefficient (ADC), which reflects the degree of water diffusion within tissue.
The basic principle involves applying a pair of diffusion-sensitizing gradients in the MRI sequence. These gradients dephase and then rephase the spins of water protons. If water molecules have moved between the application of the gradients, the rephasing is incomplete, resulting in signal attenuation. The degree of attenuation is proportional to the amount of diffusion.
Applications in Medicine[edit | edit source]
DWI is particularly useful in the early detection of stroke, as it can identify ischemic changes within minutes of onset. In acute ischemic stroke, the diffusion of water is restricted due to cytotoxic edema, leading to a high signal on DWI and a low ADC value.
Beyond stroke, DWI is used in the evaluation of brain tumors, abscesses, and traumatic brain injury. It is also valuable in assessing the integrity of white matter tracts through diffusion tensor imaging (DTI), a related technique that provides information about the directionality of water diffusion.
Technical Considerations[edit | edit source]
The quality of DWI can be affected by several factors, including the strength and timing of the diffusion gradients, the choice of b-value (a parameter that reflects the sensitivity of the sequence to diffusion), and the presence of artifacts such as eddy currents and susceptibility effects.
Advanced techniques such as echo-planar imaging (EPI) are often used to acquire DWI data rapidly, minimizing motion artifacts. However, EPI is sensitive to magnetic field inhomogeneities, which can lead to geometric distortions.
Diffusion Tensor Imaging[edit | edit source]
Diffusion tensor imaging (DTI) is an extension of DWI that models the diffusion process as a tensor, allowing for the characterization of anisotropic diffusion. This is particularly useful in mapping the orientation of white matter tracts in the brain, providing insights into the structural connectivity of the brain.
Related Pages[edit | edit source]
Search WikiMD
Ad.Tired of being Overweight? Try W8MD's NYC physician weight loss.
Semaglutide (Ozempic / Wegovy and Tirzepatide (Mounjaro / Zepbound) available. Call 718 946 5500.
Advertise on WikiMD
|
WikiMD's Wellness Encyclopedia |
| Let Food Be Thy Medicine Medicine Thy Food - Hippocrates |
Translate this page: - East Asian
中文,
日本,
한국어,
South Asian
हिन्दी,
தமிழ்,
తెలుగు,
Urdu,
ಕನ್ನಡ,
Southeast Asian
Indonesian,
Vietnamese,
Thai,
မြန်မာဘာသာ,
বাংলা
European
español,
Deutsch,
français,
Greek,
português do Brasil,
polski,
română,
русский,
Nederlands,
norsk,
svenska,
suomi,
Italian
Middle Eastern & African
عربى,
Turkish,
Persian,
Hebrew,
Afrikaans,
isiZulu,
Kiswahili,
Other
Bulgarian,
Hungarian,
Czech,
Swedish,
മലയാളം,
मराठी,
ਪੰਜਾਬੀ,
ગુજરાતી,
Portuguese,
Ukrainian
Medical Disclaimer: WikiMD is not a substitute for professional medical advice. The information on WikiMD is provided as an information resource only, may be incorrect, outdated or misleading, and is not to be used or relied on for any diagnostic or treatment purposes. Please consult your health care provider before making any healthcare decisions or for guidance about a specific medical condition. WikiMD expressly disclaims responsibility, and shall have no liability, for any damages, loss, injury, or liability whatsoever suffered as a result of your reliance on the information contained in this site. By visiting this site you agree to the foregoing terms and conditions, which may from time to time be changed or supplemented by WikiMD. If you do not agree to the foregoing terms and conditions, you should not enter or use this site. See full disclaimer.
Credits:Most images are courtesy of Wikimedia commons, and templates, categories Wikipedia, licensed under CC BY SA or similar.
Contributors: Prab R. Tumpati, MD