Intercapitular veins of the hand
(Redirected from Intercapitular vein)
Intercapitular veins of the hand[edit | edit source]
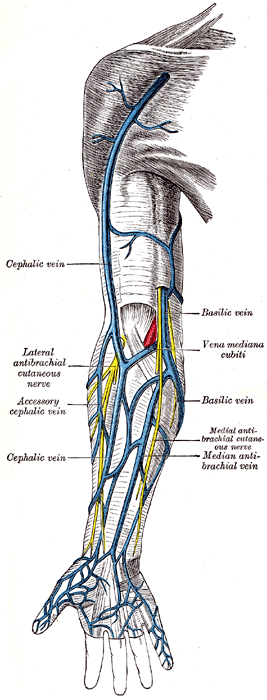
The intercapitular veins of the hand are small veins that play a crucial role in the venous drainage of the hand. These veins are part of the superficial venous system and are located in the dorsum of the hand. They connect the dorsal digital veins with the dorsal venous network of the hand.
Anatomy[edit | edit source]
The intercapitular veins are situated between the metacarpal bones and are responsible for draining blood from the fingers into the larger venous structures of the hand. They are typically found in the spaces between the heads of the metacarpal bones, hence the name "intercapitular," which means "between the heads."
Function[edit | edit source]
The primary function of the intercapitular veins is to facilitate the return of deoxygenated blood from the fingers back to the heart. They achieve this by connecting the smaller dorsal digital veins with the larger dorsal venous network of the hand, which eventually drains into the cephalic vein and the basilic vein.
Clinical significance[edit | edit source]
The intercapitular veins, while small, can be significant in certain medical conditions. For instance, they may become engorged or varicose in conditions that affect venous return, such as chronic venous insufficiency. Additionally, they may be involved in the formation of venous thrombosis in the hand, although this is relatively rare.
Related pages[edit | edit source]
Search WikiMD
Ad.Tired of being Overweight? Try W8MD's physician weight loss program.
Semaglutide (Ozempic / Wegovy and Tirzepatide (Mounjaro / Zepbound) available.
Advertise on WikiMD
|
WikiMD's Wellness Encyclopedia |
| Let Food Be Thy Medicine Medicine Thy Food - Hippocrates |
Translate this page: - East Asian
中文,
日本,
한국어,
South Asian
हिन्दी,
தமிழ்,
తెలుగు,
Urdu,
ಕನ್ನಡ,
Southeast Asian
Indonesian,
Vietnamese,
Thai,
မြန်မာဘာသာ,
বাংলা
European
español,
Deutsch,
français,
Greek,
português do Brasil,
polski,
română,
русский,
Nederlands,
norsk,
svenska,
suomi,
Italian
Middle Eastern & African
عربى,
Turkish,
Persian,
Hebrew,
Afrikaans,
isiZulu,
Kiswahili,
Other
Bulgarian,
Hungarian,
Czech,
Swedish,
മലയാളം,
मराठी,
ਪੰਜਾਬੀ,
ગુજરાતી,
Portuguese,
Ukrainian
Medical Disclaimer: WikiMD is not a substitute for professional medical advice. The information on WikiMD is provided as an information resource only, may be incorrect, outdated or misleading, and is not to be used or relied on for any diagnostic or treatment purposes. Please consult your health care provider before making any healthcare decisions or for guidance about a specific medical condition. WikiMD expressly disclaims responsibility, and shall have no liability, for any damages, loss, injury, or liability whatsoever suffered as a result of your reliance on the information contained in this site. By visiting this site you agree to the foregoing terms and conditions, which may from time to time be changed or supplemented by WikiMD. If you do not agree to the foregoing terms and conditions, you should not enter or use this site. See full disclaimer.
Credits:Most images are courtesy of Wikimedia commons, and templates, categories Wikipedia, licensed under CC BY SA or similar.
Contributors: Prab R. Tumpati, MD