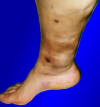
Necrosis
(Redirected from Myonecrosis)
Necrosis is the premature death of cells or tissues in a living organism, typically as a result of injury, infection, disease, or lack of blood supply. Necrosis is distinct from apoptosis, which is a regulated form of cell death that occurs as a natural part of an organism's growth and development.
Types of Necrosis[edit | edit source]
There are several types of necrosis, each with distinct characteristics and underlying causes:
- Coagulative necrosis: This is the most common form of necrosis, typically occurring in solid organs such as the heart, kidneys, and liver. Coagulative necrosis is characterized by the denaturation of cellular proteins, leading to the preservation of cellular architecture.
- Liquefactive necrosis: This type of necrosis is characterized by the rapid dissolution of dead tissue, resulting in a viscous, liquid mass. Liquefactive necrosis is commonly observed in the central nervous system (CNS) and in abscesses caused by bacterial infections.
- Caseous necrosis: Often associated with tuberculosis, caseous necrosis is characterized by a cheese-like appearance of the dead tissue. The affected tissue is soft, white, and granular, with a mixture of both coagulative and liquefactive necrosis.
- Fat necrosis: This form of necrosis occurs primarily in adipose tissue, as a result of the action of lipases that break down triglycerides, releasing free fatty acids. Fat necrosis is often seen in acute pancreatitis or following traumatic injury to fatty tissue.
- Fibrinoid necrosis: Commonly observed in immune-mediated vasculitis and malignant hypertension, fibrinoid necrosis is characterized by the deposition of fibrin-like material within blood vessel walls, leading to their destruction and subsequent tissue damage.
- Gangrenous necrosis: A type of coagulative necrosis that occurs when there is severe ischemia (lack of blood supply), usually affecting the extremities or bowel. Gangrenous necrosis can be further classified as dry, wet, or gas gangrene, depending on the presence of bacterial infection and the production of gas within the affected tissue.
Causes and Risk Factors[edit | edit source]
Necrosis can be caused by a variety of factors, including:
- Ischemia: Lack of blood supply to tissues, often due to obstruction of blood vessels, can lead to tissue death.
- Trauma: Physical injury or mechanical damage to tissues can result in necrosis.
- Infection: Bacterial, viral, fungal, or parasitic infections can cause localized tissue destruction and necrosis.
- Toxins: Exposure to chemicals, venom, or radiation can induce cell death and necrosis.
- Immune-mediated damage: Autoimmune diseases or hypersensitivity reactions can cause targeted destruction of specific tissues, leading to necrosis.
- Thermal injury: Extreme heat or cold can cause cell death and necrosis.
Pathophysiology[edit | edit source]
Necrosis is a complex process that involves several cellular and molecular events. The initial insult to the cell leads to a disruption of cellular integrity, causing an influx of calcium ions and the activation of destructive enzymes, such as proteases, lipases, and nucleases. These enzymes degrade cellular components, leading to the loss of cell membrane integrity and the release of intracellular contents into the extracellular space. The release of these contents can trigger an inflammatory response, attracting immune cells to the site of injury and exacerbating tissue damage.
As necrotic tissue accumulates, it can impair the normal function of the affected organ or tissue, leading to a range of clinical manifestations depending on the location and extent of the necrosis.
Diagnosis[edit | edit source]
The diagnosis of necrosis is typically based on a combination of clinical history, physical examination, and diagnostic tests, which may include:
- Imaging studies: X-rays, ultrasound, computed tomography (CT), or magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) may be used to visualize areas of tissue necrosis and to evaluate the extent of tissue damage.
- Laboratory tests: Blood tests may be used to detect markers of tissue damage or inflammation, as well as to identify potential underlying causes, such as infection or autoimmune disease.
- Biopsy: In some cases, a tissue sample may be obtained through biopsy to confirm the presence of necrosis and to determine the underlying cause. Histological examination of the biopsy sample can reveal the specific type of necrosis present and provide important diagnostic information.
Treatment[edit | edit source]
Treatment for necrosis depends on the underlying cause, the extent of tissue damage, and the presence of any associated complications. Common treatment strategies include:
- Addressing the underlying cause: Identifying and treating the underlying cause of necrosis, such as infection, autoimmune disease, or vascular obstruction, is crucial for preventing further tissue damage.
- Wound care and debridement: Proper wound care, including the removal of dead tissue (debridement), is essential for promoting healing and preventing infection.
- Antibiotics or antifungal medications: If an infection is present or suspected, appropriate antimicrobial therapy may be initiated to control the infection and prevent further tissue damage.
- Surgery: In some cases, surgical intervention may be necessary to remove necrotic tissue, reestablish blood flow to ischemic areas, or repair damaged organs.
- Hyperbaric oxygen therapy: For certain types of necrosis, such as gas gangrene, hyperbaric oxygen therapy may be used to increase oxygen delivery to affected tissues and promote healing.
Complications[edit | edit source]
Untreated or improperly managed necrosis can lead to a range of complications, including:
- Infection: Dead tissue can serve as a breeding ground for bacteria and other pathogens, increasing the risk of infection.
- Sepsis: Severe or widespread infection can lead to sepsis, a life-threatening condition characterized by a dysregulated immune response to infection.
- Loss of organ function: Extensive necrosis can impair the normal function of affected organs, leading to organ failure or dysfunction.
- Amputation: In cases of severe necrosis involving the extremities, amputation may be necessary to prevent the spread of infection or to address irreversible tissue damage.
Prevention[edit | edit source]
Preventing necrosis primarily involves addressing the risk factors and underlying causes of tissue damage. Strategies for prevention include:
- Prompt treatment of infections, injuries, or other conditions that may lead to tissue damage
- Regular monitoring and management of chronic medical conditions, such as diabetes, peripheral artery disease, or autoimmune diseases
- Avoiding exposure to toxins, radiation, and extreme temperatures
- Practicing good hygiene and wound care to reduce the risk of infection
Search WikiMD
Ad.Tired of being Overweight? Try W8MD's physician weight loss program.
Semaglutide (Ozempic / Wegovy and Tirzepatide (Mounjaro / Zepbound) available.
Advertise on WikiMD
|
WikiMD's Wellness Encyclopedia |
| Let Food Be Thy Medicine Medicine Thy Food - Hippocrates |
Translate this page: - East Asian
中文,
日本,
한국어,
South Asian
हिन्दी,
தமிழ்,
తెలుగు,
Urdu,
ಕನ್ನಡ,
Southeast Asian
Indonesian,
Vietnamese,
Thai,
မြန်မာဘာသာ,
বাংলা
European
español,
Deutsch,
français,
Greek,
português do Brasil,
polski,
română,
русский,
Nederlands,
norsk,
svenska,
suomi,
Italian
Middle Eastern & African
عربى,
Turkish,
Persian,
Hebrew,
Afrikaans,
isiZulu,
Kiswahili,
Other
Bulgarian,
Hungarian,
Czech,
Swedish,
മലയാളം,
मराठी,
ਪੰਜਾਬੀ,
ગુજરાતી,
Portuguese,
Ukrainian
Medical Disclaimer: WikiMD is not a substitute for professional medical advice. The information on WikiMD is provided as an information resource only, may be incorrect, outdated or misleading, and is not to be used or relied on for any diagnostic or treatment purposes. Please consult your health care provider before making any healthcare decisions or for guidance about a specific medical condition. WikiMD expressly disclaims responsibility, and shall have no liability, for any damages, loss, injury, or liability whatsoever suffered as a result of your reliance on the information contained in this site. By visiting this site you agree to the foregoing terms and conditions, which may from time to time be changed or supplemented by WikiMD. If you do not agree to the foregoing terms and conditions, you should not enter or use this site. See full disclaimer.
Credits:Most images are courtesy of Wikimedia commons, and templates, categories Wikipedia, licensed under CC BY SA or similar.
Contributors: Prab R. Tumpati, MD