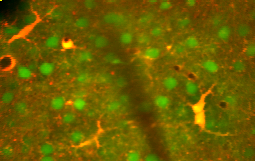
Astrocyte
(Redirected from Protoplasmic astrocyte)
Astrocytes are a type of glial cell that are found in the brain and spinal cord. They are the most abundant cell types in the human brain, playing a critical role in the maintenance of the central nervous system (CNS). Astrocytes are star-shaped cells, a characteristic that gives them their name, derived from the Greek words "astron" meaning star and "kytos" meaning cell.
Functions[edit | edit source]
Astrocytes perform a wide range of functions essential for the proper functioning of the CNS. These include:
- Support and Bracing: Astrocytes provide structural support to neurons, helping to hold them in place.
- Blood-Brain Barrier Maintenance: They are involved in the formation and maintenance of the blood-brain barrier, a selective barrier that prevents certain substances from passing from the blood into the brain.
- Nutrient and Ion Regulation: Astrocytes regulate the concentration of ions and nutrients in the extracellular space, ensuring the optimal environment for neuronal function.
- Neurotransmitter Regulation: They play a role in the uptake and recycling of neurotransmitters, which are chemicals that transmit signals in the brain.
- Neurogenesis: Astrocytes are involved in the process of neurogenesis, the formation of new neurons in the brain.
- Synaptic Support: They are crucial for the formation, maintenance, and modulation of synapses, the points of communication between neurons.
Types of Astrocytes[edit | edit source]
Astrocytes can be broadly classified into two main types based on their location and function:
- Protoplasmic Astrocytes: Found in the gray matter of the brain, these astrocytes have numerous branching processes that make contact with blood vessels and neurons.
- Fibrous Astrocytes: Located in the white matter, fibrous astrocytes have fewer processes than protoplasmic astrocytes and are involved in providing structural support.
Pathology[edit | edit source]
Astrocytes are involved in various pathological conditions affecting the CNS. They can undergo changes in response to injury or disease, a process known as reactive gliosis. In conditions such as Alzheimer's disease, multiple sclerosis, and amyotrophic lateral sclerosis, astrocytes can either contribute to the pathology or play a protective role, depending on the context of the disease.
Research and Clinical Implications[edit | edit source]
Research into astrocytes has expanded our understanding of their roles in the CNS, revealing that they are not just supportive cells but are actively involved in the modulation of neuronal activity and plasticity. This has implications for the development of new therapeutic strategies for neurological disorders, where targeting astrocyte function could offer novel approaches to treatment.
Search WikiMD
Ad.Tired of being Overweight? Try W8MD's physician weight loss program.
Semaglutide (Ozempic / Wegovy and Tirzepatide (Mounjaro / Zepbound) available.
Advertise on WikiMD
|
WikiMD's Wellness Encyclopedia |
| Let Food Be Thy Medicine Medicine Thy Food - Hippocrates |
Translate this page: - East Asian
中文,
日本,
한국어,
South Asian
हिन्दी,
தமிழ்,
తెలుగు,
Urdu,
ಕನ್ನಡ,
Southeast Asian
Indonesian,
Vietnamese,
Thai,
မြန်မာဘာသာ,
বাংলা
European
español,
Deutsch,
français,
Greek,
português do Brasil,
polski,
română,
русский,
Nederlands,
norsk,
svenska,
suomi,
Italian
Middle Eastern & African
عربى,
Turkish,
Persian,
Hebrew,
Afrikaans,
isiZulu,
Kiswahili,
Other
Bulgarian,
Hungarian,
Czech,
Swedish,
മലയാളം,
मराठी,
ਪੰਜਾਬੀ,
ગુજરાતી,
Portuguese,
Ukrainian
Medical Disclaimer: WikiMD is not a substitute for professional medical advice. The information on WikiMD is provided as an information resource only, may be incorrect, outdated or misleading, and is not to be used or relied on for any diagnostic or treatment purposes. Please consult your health care provider before making any healthcare decisions or for guidance about a specific medical condition. WikiMD expressly disclaims responsibility, and shall have no liability, for any damages, loss, injury, or liability whatsoever suffered as a result of your reliance on the information contained in this site. By visiting this site you agree to the foregoing terms and conditions, which may from time to time be changed or supplemented by WikiMD. If you do not agree to the foregoing terms and conditions, you should not enter or use this site. See full disclaimer.
Credits:Most images are courtesy of Wikimedia commons, and templates, categories Wikipedia, licensed under CC BY SA or similar.
Contributors: Prab R. Tumpati, MD