Calcifediol
(Redirected from Rayaldee)
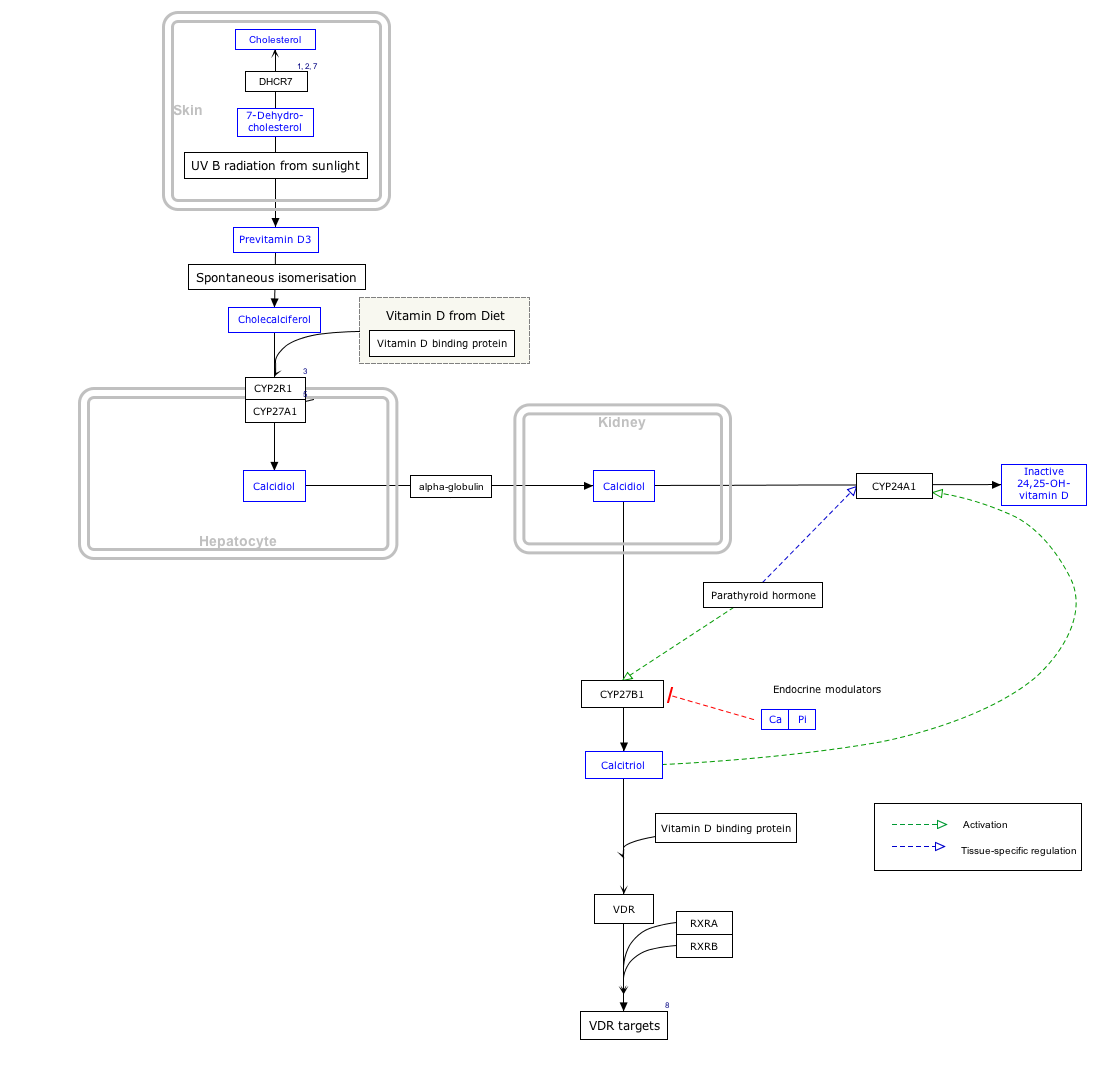
Calcifediol (INN), alternatively known as calcidiol, 25-hydroxycholecalciferol, or 25-hydroxyvitamin D (represented as 25(OH)D), is a significant prehormone generated in the liver. Its synthesis is achieved through the hydroxylation of vitamin D3 (cholecalciferol) by the enzyme named cholecalciferol 25-hydroxylase, an enzyme first isolated by Michael F. Holick. Physicians across the globe utilize this metabolite as a benchmark to gauge a patient's vitamin D status. After its initial formation, calcifediol undergoes further conversion in the kidneys. It can be transformed into calcitriol (1,25-(OH)2D3), which acts as a secosteroid hormone and is identified as the activated form of vitamin D. Another renal conversion results in 24-hydroxycalcidiol through 24-hydroxylation.
Blood test[edit | edit source]
In the realm of medical diagnostics, the 25-hydroxy vitamin D (calcidiol) blood assessment serves as a pivotal tool to ascertain the amount of vitamin D present in a patient's body. The concentration of calcidiol in the blood is upheld as the paramount indicator of a patient's vitamin D levels.
This specific assessment is valuable for identifying vitamin D deficiency. It becomes especially crucial for patients exhibiting a higher vulnerability to such a deficiency. Instances include those suffering from conditions like osteoporosis, chronic kidney disorders, malabsorption syndromes, obesity, or certain infections. Despite the prevalence of vitamin D deficiency in populations residing in higher latitudes or those with diminished sun exposure, this test isn't universally recommended. For patients at a lower risk, physicians might suggest over-the-counter vitamin D supplements as an alternative to screening.
While the test is notably sensitive, there has been a call for heightened standardization across labs to ensure reproducibility. According to MedlinePlus, calcidiol's normal concentration range is from 30.0 to 74.0 ng/mL. However, this normal range can deviate considerably, contingent on numerous variables, such as age or geographical factors. Other studies advocate a more expansive reference range (20–150 nmol/L or 8-60 ng/ml), even pinpointing levels below 80 nmol/L (32 ng/ml) as markers of vitamin D deficiency.
It's noteworthy that US laboratories predominantly report 25(OH)D concentrations in ng/mL, whereas other nations may opt for nmol/L. For conversion between these units, multiplying the ng/mL value by 2.5 yields the equivalent in nmol/L.
Clinical significance[edit | edit source]
An upward trend in calcifediol concentrations correlates with an enhanced fractional absorption of calcium from the digestive system, a relationship observed up to concentrations of 80 nmol/L (32 ng/mL). It's notable that, regardless of increasing calcifediol levels, urinary calcium excretion (which balances with intestinal calcium absorption) does not surge, even with calcifediol levels peaking at around ~400 nmol/L (160 ng/mL).
In a notable research endeavor, Cedric F. Garland and Frank C. Garland of the University of California, San Diego evaluated blood samples from 25,000 individuals in Washington County, Maryland. Their findings indicated a striking observation: participants with elevated calcifediol concentrations exhibited a colon cancer risk that was merely one-fifth of the standard rates. Nonetheless, subsequent randomized controlled trials did not corroborate a significant association between vitamin D supplementation and reduced colon cancer risks.
Interactive pathway map[edit | edit source]
See also[edit | edit source]
References[edit | edit source]
| This article is a medical stub. You can help WikiMD by expanding it! | |
|---|---|
Vitamins[edit source]A[edit source]B[edit source]
C[edit source]D[edit source] |
E[edit source]F[edit source]I[edit source]K[edit source] |
M[edit source]N[edit source]P[edit source]R[edit source] |
S[edit source]T[edit source]V[edit source]
Z[edit source] |
Search WikiMD
Ad.Tired of being Overweight? Try W8MD's physician weight loss program.
Semaglutide (Ozempic / Wegovy and Tirzepatide (Mounjaro / Zepbound) available.
Advertise on WikiMD
|
WikiMD's Wellness Encyclopedia |
| Let Food Be Thy Medicine Medicine Thy Food - Hippocrates |
Translate this page: - East Asian
中文,
日本,
한국어,
South Asian
हिन्दी,
தமிழ்,
తెలుగు,
Urdu,
ಕನ್ನಡ,
Southeast Asian
Indonesian,
Vietnamese,
Thai,
မြန်မာဘာသာ,
বাংলা
European
español,
Deutsch,
français,
Greek,
português do Brasil,
polski,
română,
русский,
Nederlands,
norsk,
svenska,
suomi,
Italian
Middle Eastern & African
عربى,
Turkish,
Persian,
Hebrew,
Afrikaans,
isiZulu,
Kiswahili,
Other
Bulgarian,
Hungarian,
Czech,
Swedish,
മലയാളം,
मराठी,
ਪੰਜਾਬੀ,
ગુજરાતી,
Portuguese,
Ukrainian
Medical Disclaimer: WikiMD is not a substitute for professional medical advice. The information on WikiMD is provided as an information resource only, may be incorrect, outdated or misleading, and is not to be used or relied on for any diagnostic or treatment purposes. Please consult your health care provider before making any healthcare decisions or for guidance about a specific medical condition. WikiMD expressly disclaims responsibility, and shall have no liability, for any damages, loss, injury, or liability whatsoever suffered as a result of your reliance on the information contained in this site. By visiting this site you agree to the foregoing terms and conditions, which may from time to time be changed or supplemented by WikiMD. If you do not agree to the foregoing terms and conditions, you should not enter or use this site. See full disclaimer.
Credits:Most images are courtesy of Wikimedia commons, and templates, categories Wikipedia, licensed under CC BY SA or similar.
Contributors: Prab R. Tumpati, MD