Adenine phosphoribosyltransferase
Adenine phosphoribosyltransferase[edit | edit source]
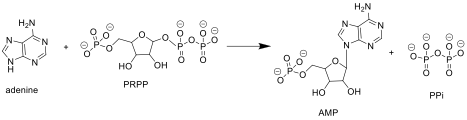
Adenine phosphoribosyltransferase (APRT) is an enzyme that plays a crucial role in the purine salvage pathway, which is essential for the recycling of purines to synthesize nucleotides. This enzyme catalyzes the conversion of adenine and phosphoribosyl pyrophosphate (PRPP) into adenosine monophosphate (AMP).
Function[edit | edit source]
APRT is responsible for the salvage of adenine, a purine base, by converting it into AMP. This reaction is important for maintaining the balance of purine nucleotides in the cell and for conserving energy by recycling purines rather than synthesizing them de novo.
Mechanism[edit | edit source]
The reaction catalyzed by APRT involves the transfer of a phosphoribosyl group from PRPP to adenine, forming AMP and pyrophosphate. This reaction is facilitated by the enzyme's active site, which binds both substrates and stabilizes the transition state.
Structure[edit | edit source]
APRT is a homodimeric enzyme, meaning it consists of two identical subunits. Each subunit contains a flexible loop and a hood domain that are important for substrate binding and catalysis.
Active Site[edit | edit source]
The active site of APRT is where adenine and PRPP bind. The enzyme undergoes conformational changes upon substrate binding, which facilitates the catalytic process. The binding site is highly specific for adenine, ensuring the correct substrate is utilized.
Genetic Implications[edit | edit source]
Mutations in the APRT gene can lead to a deficiency in the enzyme, resulting in the accumulation of adenine and its conversion to 2,8-dihydroxyadenine, which can cause kidney stones and renal failure. This condition is known as APRT deficiency.
Clinical Significance[edit | edit source]
APRT deficiency is a rare genetic disorder that can lead to the formation of kidney stones composed of 2,8-dihydroxyadenine. Early diagnosis and treatment are important to prevent kidney damage. Treatment typically involves a low-purine diet and medications that reduce adenine production.
Related pages[edit | edit source]
Gallery[edit | edit source]
Search WikiMD
Ad.Tired of being Overweight? Try W8MD's physician weight loss program.
Semaglutide (Ozempic / Wegovy and Tirzepatide (Mounjaro / Zepbound) available.
Advertise on WikiMD
|
WikiMD's Wellness Encyclopedia |
| Let Food Be Thy Medicine Medicine Thy Food - Hippocrates |
Translate this page: - East Asian
中文,
日本,
한국어,
South Asian
हिन्दी,
தமிழ்,
తెలుగు,
Urdu,
ಕನ್ನಡ,
Southeast Asian
Indonesian,
Vietnamese,
Thai,
မြန်မာဘာသာ,
বাংলা
European
español,
Deutsch,
français,
Greek,
português do Brasil,
polski,
română,
русский,
Nederlands,
norsk,
svenska,
suomi,
Italian
Middle Eastern & African
عربى,
Turkish,
Persian,
Hebrew,
Afrikaans,
isiZulu,
Kiswahili,
Other
Bulgarian,
Hungarian,
Czech,
Swedish,
മലയാളം,
मराठी,
ਪੰਜਾਬੀ,
ગુજરાતી,
Portuguese,
Ukrainian
Medical Disclaimer: WikiMD is not a substitute for professional medical advice. The information on WikiMD is provided as an information resource only, may be incorrect, outdated or misleading, and is not to be used or relied on for any diagnostic or treatment purposes. Please consult your health care provider before making any healthcare decisions or for guidance about a specific medical condition. WikiMD expressly disclaims responsibility, and shall have no liability, for any damages, loss, injury, or liability whatsoever suffered as a result of your reliance on the information contained in this site. By visiting this site you agree to the foregoing terms and conditions, which may from time to time be changed or supplemented by WikiMD. If you do not agree to the foregoing terms and conditions, you should not enter or use this site. See full disclaimer.
Credits:Most images are courtesy of Wikimedia commons, and templates, categories Wikipedia, licensed under CC BY SA or similar.
Contributors: Prab R. Tumpati, MD