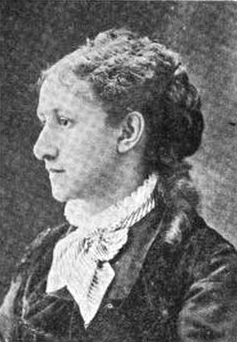Alice Walbridge Gulick
Alice Walbridge Gulick (1847–1903) was an influential American educator and missionary who played a pivotal role in the advancement of women's education in Spain. She is best known for founding the International Institute for Girls in Spain, an institution that aimed to provide comprehensive education to Spanish women, which was a significant departure from the traditional educational opportunities available to them at the time.
Early Life and Education[edit | edit source]
Alice Walbridge Gulick was born in 1847 in Boston, Massachusetts, to a family with a strong commitment to education and missionary work. From a young age, Gulick was exposed to the importance of education and the need for educational reform. She pursued her education with the intention of making a significant contribution to society.
Missionary Work and Education Reform[edit | edit source]
In the late 19th century, Gulick and her husband, William H. Gulick, who was also a missionary, moved to Spain. At the time, Spain offered limited educational opportunities for women, mostly confined to basic literacy and domestic skills. Recognizing the need for comprehensive educational reform, Alice Gulick embarked on a mission to establish an institution that would offer a broad curriculum to Spanish women, including subjects such as science, mathematics, and the arts, which were largely inaccessible to them.
Founding of the International Institute for Girls in Spain[edit | edit source]
In 1877, Alice Gulick founded the International Institute for Girls in Spain. The institute was revolutionary in its approach to women's education in Spain, providing students with an education that was comparable to that offered to men. The curriculum was designed not only to educate but to empower students, encouraging them to pursue careers and participate actively in society.
The institute quickly gained recognition for its high standards of education and its role in promoting gender equality in education. It attracted students from across Spain and played a crucial role in shaping the future of women's education in the country.
Legacy[edit | edit source]
Alice Walbridge Gulick's work had a profound impact on women's education in Spain. Through her efforts, she helped to break down barriers to education for women and laid the foundation for future educational reforms. The International Institute for Girls in Spain continues to operate, now as part of a larger educational organization, and remains a testament to Gulick's vision and dedication to women's education.
Gulick's legacy extends beyond the walls of the institute. She is remembered as a pioneer of women's education and a key figure in the history of educational reform in Spain. Her work has inspired generations of educators and activists to continue the fight for equal educational opportunities for all.
Death and Memoriam[edit | edit source]
Alice Walbridge Gulick passed away in 1903. Her death was mourned by many who recognized her contributions to education and society. Today, she is commemorated through various memorials and the ongoing work of the International Institute for Girls in Spain, which continues to embody her commitment to education and equality.
This educator-related article is a stub. You can help WikiMD by expanding it.
Search WikiMD
Ad.Tired of being Overweight? Try W8MD's physician weight loss program.
Semaglutide (Ozempic / Wegovy and Tirzepatide (Mounjaro / Zepbound) available.
Advertise on WikiMD
|
WikiMD's Wellness Encyclopedia |
| Let Food Be Thy Medicine Medicine Thy Food - Hippocrates |
Translate this page: - East Asian
中文,
日本,
한국어,
South Asian
हिन्दी,
தமிழ்,
తెలుగు,
Urdu,
ಕನ್ನಡ,
Southeast Asian
Indonesian,
Vietnamese,
Thai,
မြန်မာဘာသာ,
বাংলা
European
español,
Deutsch,
français,
Greek,
português do Brasil,
polski,
română,
русский,
Nederlands,
norsk,
svenska,
suomi,
Italian
Middle Eastern & African
عربى,
Turkish,
Persian,
Hebrew,
Afrikaans,
isiZulu,
Kiswahili,
Other
Bulgarian,
Hungarian,
Czech,
Swedish,
മലയാളം,
मराठी,
ਪੰਜਾਬੀ,
ગુજરાતી,
Portuguese,
Ukrainian
Medical Disclaimer: WikiMD is not a substitute for professional medical advice. The information on WikiMD is provided as an information resource only, may be incorrect, outdated or misleading, and is not to be used or relied on for any diagnostic or treatment purposes. Please consult your health care provider before making any healthcare decisions or for guidance about a specific medical condition. WikiMD expressly disclaims responsibility, and shall have no liability, for any damages, loss, injury, or liability whatsoever suffered as a result of your reliance on the information contained in this site. By visiting this site you agree to the foregoing terms and conditions, which may from time to time be changed or supplemented by WikiMD. If you do not agree to the foregoing terms and conditions, you should not enter or use this site. See full disclaimer.
Credits:Most images are courtesy of Wikimedia commons, and templates Wikipedia, licensed under CC BY SA or similar.
Contributors: Prab R. Tumpati, MD