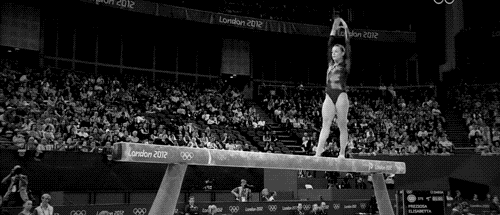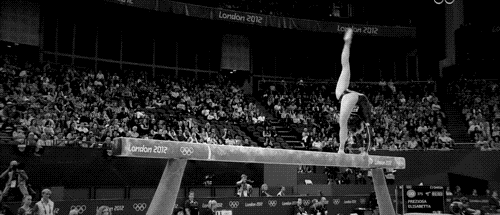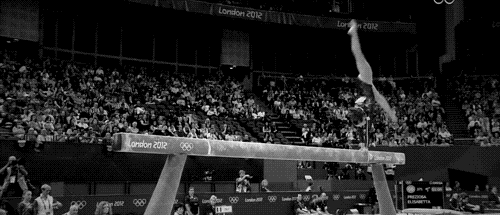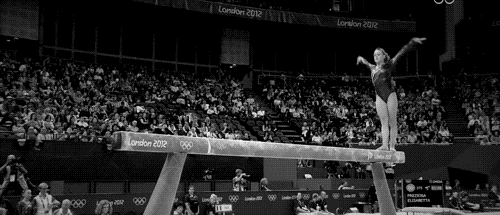Balance beam
A gymnastic apparatus used by women gymnasts.
Introduction[edit | edit source]
The balance beam is an apparatus used primarily in women's artistic gymnastics. Gymnasts perform routines combining acrobatic skills, dance elements, and athletic feats of balance and strength.
History[edit | edit source]
The balance beam dates back to the early days of gymnastics, where it began as a log suspended off the ground. It has evolved significantly since then, becoming a staple event in women's gymnastics competitions.
Design[edit | edit source]
A standard balance beam is 5 meters long, 10 centimeters wide, and set at a height of 1.25 meters above the gymnastics mat. The beam is typically made of a metal or wooden base covered with a foam layer and a non-slip, suede-like material.
Disciplines[edit | edit source]
Balance beam routines are a mix of various disciplines:
- Acrobatic skills - flips and handsprings
- Dance elements - leaps, turns, and dance sequences
- Strength moves - handstands and jumps
Rules and Scoring[edit | edit source]
Balance beam routines are subject to strict rules and scoring guidelines, as outlined by the International Gymnastics Federation (FIG). Judges evaluate routines based on difficulty, execution, and artistry.
Competitions[edit | edit source]
Balance beam is featured in various levels of gymnastic competition, from local meets to the Olympic Games. It is one of the four women's artistic gymnastics events, alongside the vault, uneven bars, and floor exercise.
Training[edit | edit source]
Gymnasts train for years to master balance beam routines. They work on building balance, strength, and flexibility, along with perfecting their routines to minimize deductions during competition.
Notable Gymnasts[edit | edit source]
Many gymnasts have become well-known for their performances on the balance beam:
- Nadia Comăneci, renowned for scoring the first perfect 10.0 at the Olympics
- Shannon Miller, one of the most decorated gymnasts in U.S. history
- Simone Biles, noted for her complex and high-difficulty routines
In Popular Culture[edit | edit source]
The balance beam has been depicted in movies, television shows, and books, often symbolizing the precision and grace of gymnastics.
Safety Considerations[edit | edit source]
While the balance beam is less than a foot wide, safety is paramount. Gymnasts utilize safety mats, spotter assistance, and progressively learn difficult skills to prevent injuries.
See Also[edit | edit source]
- Gymnastics at the Summer Olympics
- World Artistic Gymnastics Championships
- European Women's Artistic Gymnastics Championships
- USA Gymnastics National Championships
External Links[edit | edit source]
Search WikiMD
Ad.Tired of being Overweight? Try W8MD's NYC physician weight loss.
Semaglutide (Ozempic / Wegovy and Tirzepatide (Mounjaro / Zepbound) available. Call 718 946 5500.
Advertise on WikiMD
|
WikiMD's Wellness Encyclopedia |
| Let Food Be Thy Medicine Medicine Thy Food - Hippocrates |
Translate this page: - East Asian
中文,
日本,
한국어,
South Asian
हिन्दी,
தமிழ்,
తెలుగు,
Urdu,
ಕನ್ನಡ,
Southeast Asian
Indonesian,
Vietnamese,
Thai,
မြန်မာဘာသာ,
বাংলা
European
español,
Deutsch,
français,
Greek,
português do Brasil,
polski,
română,
русский,
Nederlands,
norsk,
svenska,
suomi,
Italian
Middle Eastern & African
عربى,
Turkish,
Persian,
Hebrew,
Afrikaans,
isiZulu,
Kiswahili,
Other
Bulgarian,
Hungarian,
Czech,
Swedish,
മലയാളം,
मराठी,
ਪੰਜਾਬੀ,
ગુજરાતી,
Portuguese,
Ukrainian
Medical Disclaimer: WikiMD is not a substitute for professional medical advice. The information on WikiMD is provided as an information resource only, may be incorrect, outdated or misleading, and is not to be used or relied on for any diagnostic or treatment purposes. Please consult your health care provider before making any healthcare decisions or for guidance about a specific medical condition. WikiMD expressly disclaims responsibility, and shall have no liability, for any damages, loss, injury, or liability whatsoever suffered as a result of your reliance on the information contained in this site. By visiting this site you agree to the foregoing terms and conditions, which may from time to time be changed or supplemented by WikiMD. If you do not agree to the foregoing terms and conditions, you should not enter or use this site. See full disclaimer.
Credits:Most images are courtesy of Wikimedia commons, and templates, categories Wikipedia, licensed under CC BY SA or similar.
Contributors: Prab R. Tumpati, MD