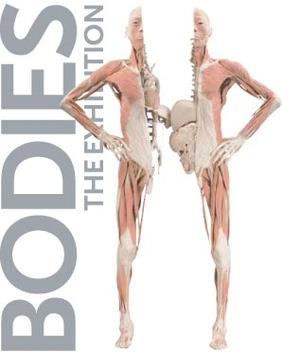
Bodies: The Exhibition
Bodies: The Exhibition[edit | edit source]
Bodies: The Exhibition is a controversial exhibition showcasing preserved human bodies and anatomical specimens. The exhibition aims to educate the public about the complexities of the human body and promote health awareness. It features real human bodies that have been dissected and preserved through a process called plastination.
History[edit | edit source]
Bodies: The Exhibition was first opened in 2005 and has since toured various cities around the world. The exhibition is produced by Premier Exhibitions, a company known for creating educational and entertaining exhibitions. The bodies displayed in the exhibition are sourced from unclaimed bodies in China, which has led to ethical debates and controversies.
Exhibition Content[edit | edit source]
The exhibition is divided into several galleries, each focusing on different systems of the human body. These include the muscular system, skeletal system, nervous system, circulatory system, and digestive system. Each gallery provides detailed views of the human anatomy, allowing visitors to see the intricate structures and functions of the body.
Muscular System[edit | edit source]
The muscular system gallery displays the muscles of the human body in various poses, demonstrating how muscles work together to facilitate movement. Visitors can observe the layers of muscles and understand their role in maintaining posture and generating force.
Skeletal System[edit | edit source]
In the skeletal system gallery, the bones of the human body are showcased, highlighting their structure and function. The exhibition provides insights into how bones support the body, protect internal organs, and enable movement.
Nervous System[edit | edit source]
The nervous system gallery features the brain, spinal cord, and nerves, illustrating how the body processes information and coordinates actions. This section emphasizes the complexity of the nervous system and its critical role in controlling bodily functions.
Circulatory System[edit | edit source]
The circulatory system gallery presents the heart, blood vessels, and blood, explaining how they work together to transport oxygen and nutrients throughout the body. Visitors can learn about the importance of maintaining cardiovascular health.
Digestive System[edit | edit source]
The digestive system gallery explores the organs involved in digestion, such as the stomach, intestines, and liver. This section educates visitors on how the body processes food and absorbs nutrients.
Ethical Controversies[edit | edit source]
Bodies: The Exhibition has faced criticism and ethical concerns regarding the sourcing of the bodies. Critics argue that the exhibition exploits human remains and lacks proper consent from the deceased individuals. The producers claim that the bodies are legally obtained and used for educational purposes.
Educational Impact[edit | edit source]
Despite the controversies, Bodies: The Exhibition has been praised for its educational value. It provides a unique opportunity for the public to learn about human anatomy in a direct and engaging manner. The exhibition encourages visitors to appreciate the complexity of the human body and promotes discussions about health and wellness.
Related Pages[edit | edit source]
Search WikiMD
Ad.Tired of being Overweight? Try W8MD's physician weight loss program.
Semaglutide (Ozempic / Wegovy and Tirzepatide (Mounjaro / Zepbound) available.
Advertise on WikiMD
|
WikiMD's Wellness Encyclopedia |
| Let Food Be Thy Medicine Medicine Thy Food - Hippocrates |
Translate this page: - East Asian
中文,
日本,
한국어,
South Asian
हिन्दी,
தமிழ்,
తెలుగు,
Urdu,
ಕನ್ನಡ,
Southeast Asian
Indonesian,
Vietnamese,
Thai,
မြန်မာဘာသာ,
বাংলা
European
español,
Deutsch,
français,
Greek,
português do Brasil,
polski,
română,
русский,
Nederlands,
norsk,
svenska,
suomi,
Italian
Middle Eastern & African
عربى,
Turkish,
Persian,
Hebrew,
Afrikaans,
isiZulu,
Kiswahili,
Other
Bulgarian,
Hungarian,
Czech,
Swedish,
മലയാളം,
मराठी,
ਪੰਜਾਬੀ,
ગુજરાતી,
Portuguese,
Ukrainian
Medical Disclaimer: WikiMD is not a substitute for professional medical advice. The information on WikiMD is provided as an information resource only, may be incorrect, outdated or misleading, and is not to be used or relied on for any diagnostic or treatment purposes. Please consult your health care provider before making any healthcare decisions or for guidance about a specific medical condition. WikiMD expressly disclaims responsibility, and shall have no liability, for any damages, loss, injury, or liability whatsoever suffered as a result of your reliance on the information contained in this site. By visiting this site you agree to the foregoing terms and conditions, which may from time to time be changed or supplemented by WikiMD. If you do not agree to the foregoing terms and conditions, you should not enter or use this site. See full disclaimer.
Credits:Most images are courtesy of Wikimedia commons, and templates, categories Wikipedia, licensed under CC BY SA or similar.
Contributors: Prab R. Tumpati, MD