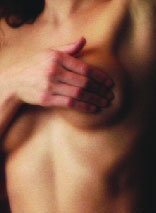
Breast self-examination
Breast Self-Examination[edit | edit source]
Breast self-examination (BSE) is a method by which individuals can check their own breasts for breast cancer or other abnormalities. It is a simple procedure that can be performed at home and is intended to help individuals become familiar with the normal state of their breasts, so that they can detect any changes early.
Purpose[edit | edit source]
The primary purpose of breast self-examination is to increase awareness of the normal condition of one's breasts and to detect any unusual changes as early as possible. While BSE is not a substitute for professional medical screening, such as mammography, it can be a useful tool for early detection of breast abnormalities.
Procedure[edit | edit source]
Breast self-examination involves a few simple steps that can be performed in front of a mirror, in the shower, or lying down. The examination typically includes visual inspection and manual palpation.
Visual Inspection[edit | edit source]
1. Stand in front of a mirror with shoulders straight and arms on hips. 2. Look for any changes in the shape, size, or symmetry of the breasts. 3. Check for any visible distortion or swelling. 4. Raise arms and look for the same changes. 5. Look for any signs of fluid coming out of one or both nipples.
Manual Palpation[edit | edit source]
1. Lie down and use the right hand to feel the left breast and vice versa. 2. Use a firm, smooth touch with the first few fingers of the hand, keeping the fingers flat and together. 3. Cover the entire breast from top to bottom, side to side. 4. Follow a pattern to ensure that the entire breast is covered, such as circular, vertical, or wedge patterns. 5. Feel for any lumps, thickening, or hardened knots.
Importance of Regular Examination[edit | edit source]
Regular breast self-examinations can help individuals become familiar with the normal look and feel of their breasts. This familiarity can make it easier to notice any changes, such as lumps or thickenings, which should be reported to a healthcare professional promptly.
Limitations[edit | edit source]
While breast self-examination can be a useful tool for early detection, it is not a replacement for regular screening by a healthcare professional. BSE does not detect all breast cancers, and not all detected lumps are cancerous. Therefore, it is important to combine BSE with other screening methods, such as clinical breast exams and mammograms.
Related Pages[edit | edit source]
Search WikiMD
Ad.Tired of being Overweight? Try W8MD's physician weight loss program.
Semaglutide (Ozempic / Wegovy and Tirzepatide (Mounjaro / Zepbound) available.
Advertise on WikiMD
|
WikiMD's Wellness Encyclopedia |
| Let Food Be Thy Medicine Medicine Thy Food - Hippocrates |
Translate this page: - East Asian
中文,
日本,
한국어,
South Asian
हिन्दी,
தமிழ்,
తెలుగు,
Urdu,
ಕನ್ನಡ,
Southeast Asian
Indonesian,
Vietnamese,
Thai,
မြန်မာဘာသာ,
বাংলা
European
español,
Deutsch,
français,
Greek,
português do Brasil,
polski,
română,
русский,
Nederlands,
norsk,
svenska,
suomi,
Italian
Middle Eastern & African
عربى,
Turkish,
Persian,
Hebrew,
Afrikaans,
isiZulu,
Kiswahili,
Other
Bulgarian,
Hungarian,
Czech,
Swedish,
മലയാളം,
मराठी,
ਪੰਜਾਬੀ,
ગુજરાતી,
Portuguese,
Ukrainian
Medical Disclaimer: WikiMD is not a substitute for professional medical advice. The information on WikiMD is provided as an information resource only, may be incorrect, outdated or misleading, and is not to be used or relied on for any diagnostic or treatment purposes. Please consult your health care provider before making any healthcare decisions or for guidance about a specific medical condition. WikiMD expressly disclaims responsibility, and shall have no liability, for any damages, loss, injury, or liability whatsoever suffered as a result of your reliance on the information contained in this site. By visiting this site you agree to the foregoing terms and conditions, which may from time to time be changed or supplemented by WikiMD. If you do not agree to the foregoing terms and conditions, you should not enter or use this site. See full disclaimer.
Credits:Most images are courtesy of Wikimedia commons, and templates, categories Wikipedia, licensed under CC BY SA or similar.
Contributors: Prab R. Tumpati, MD