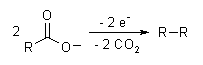Electrosynthesis
Electrosynthesis is a method in chemistry and electrochemistry where chemical compounds are synthesized by the application of electrical energy. This technique is particularly significant in the field of organic chemistry and industrial chemistry, where it offers a green alternative to traditional synthesis methods that often require hazardous chemicals and conditions. Electrosynthesis can be used to produce a wide range of products, including but not limited to, organic compounds, polymers, and inorganic materials.
Overview[edit | edit source]
Electrosynthesis involves the use of an electrochemical cell that consists of two electrodes (an anode and a cathode) immersed in an electrolyte solution. When electrical current is applied, redox reactions occur at the electrodes, leading to the formation of desired products. The process can be tailored to produce specific compounds by adjusting various parameters such as the type of electrolyte, the nature of the electrodes, the applied voltage, and the current density.
Advantages[edit | edit source]
The advantages of electrosynthesis over conventional chemical synthesis methods include:
- Environmental Friendliness: Electrosynthesis often uses water as a solvent and electricity as a reagent, which are cleaner alternatives to organic solvents and chemical reagents.
- Energy Efficiency: It can be more energy-efficient, as it allows for direct conversion of electrical energy into chemical energy.
- Selectivity and Yield: The process can be highly selective, leading to higher yields and purity of the final product.
- Safety: Electrosynthesis can be safer, as it often operates at room temperature and pressure, reducing the risk associated with high temperature and pressure conditions.
Applications[edit | edit source]
Electrosynthesis has a wide range of applications in various fields:
- In organic synthesis, it is used for the production of complex organic molecules, including pharmaceuticals and agrochemicals.
- In the production of polymers, electrosynthesis can be employed to polymerize monomers in a controlled manner.
- In material science, it is used for the deposition of metals and the synthesis of nanomaterials and semiconductors.
- In environmental chemistry, electrosynthesis can be applied in the degradation of pollutants and the recovery of valuable metals from waste.
Challenges and Future Directions[edit | edit source]
Despite its advantages, electrosynthesis faces several challenges that limit its widespread application. These include the need for specialized equipment, the cost of electricity, and the development of more efficient and selective catalysts. Future research in electrosynthesis is likely to focus on overcoming these challenges, developing new catalysts, and expanding the range of reactions that can be efficiently performed using this method.
Search WikiMD
Ad.Tired of being Overweight? Try W8MD's physician weight loss program.
Semaglutide (Ozempic / Wegovy and Tirzepatide (Mounjaro / Zepbound) available.
Advertise on WikiMD
|
WikiMD's Wellness Encyclopedia |
| Let Food Be Thy Medicine Medicine Thy Food - Hippocrates |
Translate this page: - East Asian
中文,
日本,
한국어,
South Asian
हिन्दी,
தமிழ்,
తెలుగు,
Urdu,
ಕನ್ನಡ,
Southeast Asian
Indonesian,
Vietnamese,
Thai,
မြန်မာဘာသာ,
বাংলা
European
español,
Deutsch,
français,
Greek,
português do Brasil,
polski,
română,
русский,
Nederlands,
norsk,
svenska,
suomi,
Italian
Middle Eastern & African
عربى,
Turkish,
Persian,
Hebrew,
Afrikaans,
isiZulu,
Kiswahili,
Other
Bulgarian,
Hungarian,
Czech,
Swedish,
മലയാളം,
मराठी,
ਪੰਜਾਬੀ,
ગુજરાતી,
Portuguese,
Ukrainian
Medical Disclaimer: WikiMD is not a substitute for professional medical advice. The information on WikiMD is provided as an information resource only, may be incorrect, outdated or misleading, and is not to be used or relied on for any diagnostic or treatment purposes. Please consult your health care provider before making any healthcare decisions or for guidance about a specific medical condition. WikiMD expressly disclaims responsibility, and shall have no liability, for any damages, loss, injury, or liability whatsoever suffered as a result of your reliance on the information contained in this site. By visiting this site you agree to the foregoing terms and conditions, which may from time to time be changed or supplemented by WikiMD. If you do not agree to the foregoing terms and conditions, you should not enter or use this site. See full disclaimer.
Credits:Most images are courtesy of Wikimedia commons, and templates Wikipedia, licensed under CC BY SA or similar.
Contributors: Prab R. Tumpati, MD