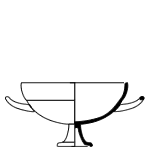
Gordion cup
Gordion cup
The Gordion cup is a type of ancient Greek pottery that dates back to the Archaic period of Greek history. Named after the ancient city of Gordion, located in modern-day Turkey, these cups are notable for their distinctive shape and decorative elements.
Description[edit | edit source]
Gordion cups are characterized by their deep, rounded bowls and high, flaring rims. They typically feature two horizontal handles attached just below the rim. The cups are often decorated with geometric patterns, floral motifs, and sometimes figural scenes. The decoration is usually executed in the black-figure technique, a style of pottery painting that was prevalent during the Archaic period.
Historical Context[edit | edit source]
The city of Gordion was the capital of Phrygia, an ancient kingdom in central Anatolia. The Gordion cup is believed to have been produced during the 7th and 6th centuries BCE, a time when the city was a significant cultural and political center. The cups are often found in archaeological sites in and around Gordion, indicating their local production and use.
Function and Use[edit | edit source]
Gordion cups were primarily used for drinking, likely for consuming wine during symposia, which were social gatherings for drinking and intellectual conversation. The shape and size of the cups made them suitable for holding a moderate amount of liquid, and the handles allowed for easy handling.
Significance[edit | edit source]
The Gordion cup is an important artifact for understanding the cultural and artistic practices of ancient Phrygia. The decorative elements on the cups provide insights into the aesthetic preferences and symbolic motifs of the time. Additionally, the presence of these cups in various archaeological contexts helps scholars trace the trade and cultural interactions between Gordion and other ancient civilizations.
Related Artifacts[edit | edit source]
Other notable types of ancient Greek pottery include the amphora, krater, and kylix. Each of these vessel types had specific functions and decorative styles, contributing to our understanding of ancient Greek daily life and artistic expression.
See Also[edit | edit source]
References[edit | edit source]
External Links[edit | edit source]
Search WikiMD
Ad.Tired of being Overweight? Try W8MD's physician weight loss program.
Semaglutide (Ozempic / Wegovy and Tirzepatide (Mounjaro / Zepbound) available.
Advertise on WikiMD
|
WikiMD's Wellness Encyclopedia |
| Let Food Be Thy Medicine Medicine Thy Food - Hippocrates |
Translate this page: - East Asian
中文,
日本,
한국어,
South Asian
हिन्दी,
தமிழ்,
తెలుగు,
Urdu,
ಕನ್ನಡ,
Southeast Asian
Indonesian,
Vietnamese,
Thai,
မြန်မာဘာသာ,
বাংলা
European
español,
Deutsch,
français,
Greek,
português do Brasil,
polski,
română,
русский,
Nederlands,
norsk,
svenska,
suomi,
Italian
Middle Eastern & African
عربى,
Turkish,
Persian,
Hebrew,
Afrikaans,
isiZulu,
Kiswahili,
Other
Bulgarian,
Hungarian,
Czech,
Swedish,
മലയാളം,
मराठी,
ਪੰਜਾਬੀ,
ગુજરાતી,
Portuguese,
Ukrainian
Medical Disclaimer: WikiMD is not a substitute for professional medical advice. The information on WikiMD is provided as an information resource only, may be incorrect, outdated or misleading, and is not to be used or relied on for any diagnostic or treatment purposes. Please consult your health care provider before making any healthcare decisions or for guidance about a specific medical condition. WikiMD expressly disclaims responsibility, and shall have no liability, for any damages, loss, injury, or liability whatsoever suffered as a result of your reliance on the information contained in this site. By visiting this site you agree to the foregoing terms and conditions, which may from time to time be changed or supplemented by WikiMD. If you do not agree to the foregoing terms and conditions, you should not enter or use this site. See full disclaimer.
Credits:Most images are courtesy of Wikimedia commons, and templates Wikipedia, licensed under CC BY SA or similar.
Contributors: Prab R. Tumpati, MD