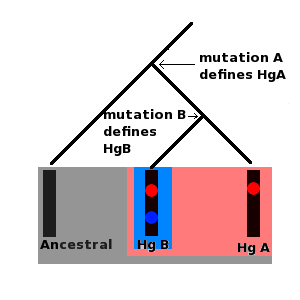
Haplogroup
Haplogroup refers to a group of similar haplotypes that share a common ancestor with a single-nucleotide polymorphism (SNP) mutation. In the study of genetic genealogy, haplogroups are essential for understanding the historical and geographical distribution of human populations. Haplogroups are often used in anthropology, archaeology, and forensic science to trace human evolution, migration patterns, and to identify ancient human remains.
Overview[edit | edit source]
A haplogroup is categorized in both Y-chromosome DNA (Y-DNA) and mitochondrial DNA (mtDNA), which are passed down from father to son and from mother to offspring, respectively. This inheritance pattern makes Y-DNA and mtDNA ideal for tracing lineage and ancestry because they do not recombine, and thus mutations accumulate at a relatively steady rate over time, forming distinct haplogroups.
Y-Chromosome DNA Haplogroups[edit | edit source]
Y-DNA haplogroups are particularly useful for tracing paternal lineage. They are identified by specific SNP mutations on the Y-chromosome, which is passed from father to son. Y-DNA haplogroups are often used in studies related to human migration patterns, identifying ancient tribes and civilizations, and understanding the spread of languages and cultures.
Mitochondrial DNA Haplogroups[edit | edit source]
Mitochondrial DNA haplogroups trace maternal ancestry since mtDNA is passed from mothers to their children. mtDNA mutations accumulate over generations, allowing scientists to categorize different lineages into specific haplogroups. mtDNA haplogroups provide insights into ancient human migrations, maternal lineage, and the historical distribution of populations.
Classification and Nomenclature[edit | edit source]
Haplogroups are classified into major groups denoted by letters of the alphabet. Each major group is further divided into subgroups represented by combinations of letters and numbers, indicating a more precise lineage. This hierarchical classification system allows for a detailed understanding of human genetic diversity and evolutionary history.
Applications[edit | edit source]
Haplogroup analysis has a wide range of applications, including:
- **Anthropology and Archaeology**: Understanding the migration and settlement patterns of ancient human populations. - **Forensic Science**: Identifying remains by comparing DNA samples to known haplogroups. - **Genealogy**: Tracing paternal and maternal lineages to understand familial roots and connections. - **Medical Research**: Identifying genetic predispositions to certain diseases that may be more prevalent in specific haplogroups.
Challenges and Limitations[edit | edit source]
While haplogroup analysis provides valuable insights, it also has limitations. The interpretation of haplogroup data can be complex, and the conclusions drawn from such analyses can sometimes be speculative. Additionally, the focus on Y-DNA and mtDNA excludes the vast majority of an individual's genome, which is recombined in each generation.
Conclusion[edit | edit source]
Haplogroups offer a fascinating glimpse into human history, migration, and evolution. By studying these genetic lineages, scientists can uncover patterns and connections that are not visible through other means. As genetic sequencing technologies improve and databases grow, our understanding of haplogroups and their implications for human history and health will continue to expand.
Search WikiMD
Ad.Tired of being Overweight? Try W8MD's physician weight loss program.
Semaglutide (Ozempic / Wegovy and Tirzepatide (Mounjaro / Zepbound) available.
Advertise on WikiMD
|
WikiMD's Wellness Encyclopedia |
| Let Food Be Thy Medicine Medicine Thy Food - Hippocrates |
Translate this page: - East Asian
中文,
日本,
한국어,
South Asian
हिन्दी,
தமிழ்,
తెలుగు,
Urdu,
ಕನ್ನಡ,
Southeast Asian
Indonesian,
Vietnamese,
Thai,
မြန်မာဘာသာ,
বাংলা
European
español,
Deutsch,
français,
Greek,
português do Brasil,
polski,
română,
русский,
Nederlands,
norsk,
svenska,
suomi,
Italian
Middle Eastern & African
عربى,
Turkish,
Persian,
Hebrew,
Afrikaans,
isiZulu,
Kiswahili,
Other
Bulgarian,
Hungarian,
Czech,
Swedish,
മലയാളം,
मराठी,
ਪੰਜਾਬੀ,
ગુજરાતી,
Portuguese,
Ukrainian
Medical Disclaimer: WikiMD is not a substitute for professional medical advice. The information on WikiMD is provided as an information resource only, may be incorrect, outdated or misleading, and is not to be used or relied on for any diagnostic or treatment purposes. Please consult your health care provider before making any healthcare decisions or for guidance about a specific medical condition. WikiMD expressly disclaims responsibility, and shall have no liability, for any damages, loss, injury, or liability whatsoever suffered as a result of your reliance on the information contained in this site. By visiting this site you agree to the foregoing terms and conditions, which may from time to time be changed or supplemented by WikiMD. If you do not agree to the foregoing terms and conditions, you should not enter or use this site. See full disclaimer.
Credits:Most images are courtesy of Wikimedia commons, and templates, categories Wikipedia, licensed under CC BY SA or similar.
Contributors: Prab R. Tumpati, MD