Helicoid
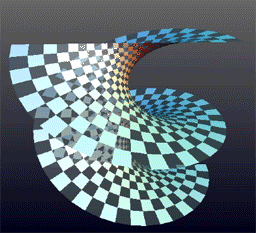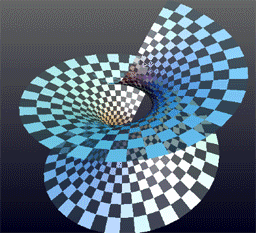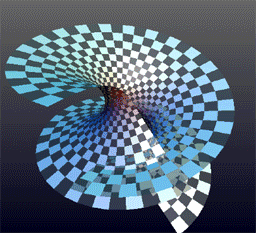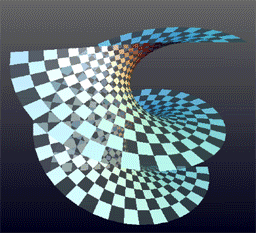
Helicoid is a geometric term that refers to a type of surface in three-dimensional space. It can be visualized as a two-dimensional plane that has been twisted along a straight line axis, creating a spiral-like structure. This concept is significant in various fields such as mathematics, physics, and engineering, due to its unique properties and applications.
Definition[edit | edit source]
A helicoid is generated by a straight line, also known as a generator, which moves along a helical path around a fixed axis, at a constant angle to the axis. Mathematically, it can be described using parametric equations in terms of parameters u and v:
- x(u,v) = v*cos(u),
- y(u,v) = v*sin(u),
- z(u,v) = c*u,
where u and v are parameters, and c is a constant that determines the pitch of the helix. The parameter u can vary from -∞ to +∞, while v can take any real value, allowing the surface to extend infinitely in both the direction of the axis and the direction perpendicular to it.
Properties[edit | edit source]
The helicoid has several notable properties. It is a minimal surface, meaning that it has the least surface area among surfaces that span a given boundary. This property makes it a subject of interest in the study of differential geometry. Additionally, the helicoid and the catenoid are unique among minimal surfaces in that they are ruled surfaces (surfaces that can be generated by moving a straight line in space).
Another interesting property of the helicoid is its relation to the catenoid. Through a continuous deformation known as a geometric transformation, a helicoid can be transformed into a catenoid without altering its minimal surface property. This transformation is a striking example of the deep connections between different geometric shapes.
Applications[edit | edit source]
Helicoids find applications in various areas of science and technology. In engineering, the shape of the helicoid is used in the design of screws, propellers, and turbines, where the ability to convert linear motion into rotational motion (or vice versa) is required. In architecture, helicoid structures can be seen in staircases and ramps, where they provide an efficient way to ascend or descend between levels in a compact space.
In biology, the helicoid shape is observed in certain plant structures and microscopic organisms, where it may play a role in strength, flexibility, or fluid dynamics. The study of natural helicoids can inspire biomimetic designs in technology and materials science.
See Also[edit | edit source]
This article is a mathematics-related stub. You can help WikiMD by expanding it!
Search WikiMD
Ad.Tired of being Overweight? Try W8MD's physician weight loss program.
Semaglutide (Ozempic / Wegovy and Tirzepatide (Mounjaro / Zepbound) available.
Advertise on WikiMD
|
WikiMD's Wellness Encyclopedia |
| Let Food Be Thy Medicine Medicine Thy Food - Hippocrates |
Translate this page: - East Asian
中文,
日本,
한국어,
South Asian
हिन्दी,
தமிழ்,
తెలుగు,
Urdu,
ಕನ್ನಡ,
Southeast Asian
Indonesian,
Vietnamese,
Thai,
မြန်မာဘာသာ,
বাংলা
European
español,
Deutsch,
français,
Greek,
português do Brasil,
polski,
română,
русский,
Nederlands,
norsk,
svenska,
suomi,
Italian
Middle Eastern & African
عربى,
Turkish,
Persian,
Hebrew,
Afrikaans,
isiZulu,
Kiswahili,
Other
Bulgarian,
Hungarian,
Czech,
Swedish,
മലയാളം,
मराठी,
ਪੰਜਾਬੀ,
ગુજરાતી,
Portuguese,
Ukrainian
Medical Disclaimer: WikiMD is not a substitute for professional medical advice. The information on WikiMD is provided as an information resource only, may be incorrect, outdated or misleading, and is not to be used or relied on for any diagnostic or treatment purposes. Please consult your health care provider before making any healthcare decisions or for guidance about a specific medical condition. WikiMD expressly disclaims responsibility, and shall have no liability, for any damages, loss, injury, or liability whatsoever suffered as a result of your reliance on the information contained in this site. By visiting this site you agree to the foregoing terms and conditions, which may from time to time be changed or supplemented by WikiMD. If you do not agree to the foregoing terms and conditions, you should not enter or use this site. See full disclaimer.
Credits:Most images are courtesy of Wikimedia commons, and templates, categories Wikipedia, licensed under CC BY SA or similar.
Contributors: Prab R. Tumpati, MD