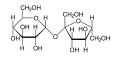
Hydrolysis
Hydrolysis means using water to split or dissolve a compound. (hydro means water and lysis means split).
The Chemistry of Breaking Compounds with Water[edit]
Hydrolysis is a fundamental chemical reaction where water is utilized to cleave or dissolve a compound. Derived from the Greek words hydro, meaning water, and lysis, which translates to split, the term aptly describes the process where water molecules are used to break chemical bonds in another molecule.
Understanding the Basics[edit]
At the heart of a hydrolysis reaction lies the water molecule (H2O). This molecule interacts with a compound, facilitating the breakage of its chemical bonds. During this process, the water molecule itself is split into a hydrogen cation (H+) and a hydroxide anion (OH−), which then react with the compound.
Types and Examples of Hydrolysis[edit]
Hydrolysis reactions can be seen in various chemical contexts:
- Ester Hydrolysis: When an ester reacts with water, it produces an alcohol and a carboxylic acid. This type of hydrolysis is the basis for the process of saponification, where fats are converted into soap.
- Peptide Hydrolysis: Proteins, which are essentially long chains of amino acids linked by peptide bonds, undergo hydrolysis to yield individual amino acids.
- Glycosidic Hydrolysis: Polysaccharides, like starch or glycogen, can be broken down into simpler sugars through hydrolysis.
- ATP Hydrolysis: The energy-rich molecule adenosine triphosphate (ATP) can be hydrolyzed to produce adenosine diphosphate (ADP) and an inorganic phosphate. This reaction releases energy utilized by cells for various functions.
Factors Influencing Hydrolysis[edit]
The rate and efficiency of hydrolysis can be influenced by multiple factors:
- pH: Many hydrolysis reactions are pH-dependent, requiring either an acidic or alkaline environment.
- Temperature: Raising the temperature generally accelerates the rate of hydrolysis.
- Enzymatic Activity: In biological systems, enzymes often act as catalysts to facilitate and speed up hydrolysis reactions. For instance, enzymes like amylase and lipase assist in the hydrolysis of carbohydrates and lipids, respectively.
Hydrolysis in Daily Life[edit]
Hydrolysis isn't just a laboratory phenomenon; it plays a critical role in our daily lives:
- Digestion: The process of digestion heavily relies on hydrolysis, where large food molecules are broken down into absorbable units.
- Soap-making: As mentioned, the saponification process involves the hydrolysis of fats to produce soap.
- Water Treatment: In certain water purification processes, hydrolysis reactions help in the removal of contaminants.
Environmental Significance[edit]
Hydrolysis is also pivotal in environmental chemistry. Pesticides, herbicides, and other chemicals, when released into the environment, may undergo hydrolysis, influencing their persistence, bioavailability, and toxicity.
Summary[edit]
Hydrolysis is a versatile and fundamental chemical reaction with a broad spectrum of applications, from biochemistry to industrial processes. Understanding this reaction provides insights into various biological, environmental, and industrial phenomena, emphasizing its significance in the interconnected web of chemical processes.
See Also[edit]
Ad. Transform your life with W8MD's Budget GLP-1 injections from $75


W8MD offers a medical weight loss program to lose weight in Philadelphia. Our physician-supervised medical weight loss provides:
- Weight loss injections in NYC (generic and brand names):
- Zepbound / Mounjaro, Wegovy / Ozempic, Saxenda
- Most insurances accepted or discounted self-pay rates. We will obtain insurance prior authorizations if needed.
- Generic GLP1 weight loss injections from $75 for the starting dose.
- Also offer prescription weight loss medications including Phentermine, Qsymia, Diethylpropion, Contrave etc.
NYC weight loss doctor appointmentsNYC weight loss doctor appointments
Start your NYC weight loss journey today at our NYC medical weight loss and Philadelphia medical weight loss clinics.
- Call 718-946-5500 to lose weight in NYC or for medical weight loss in Philadelphia 215-676-2334.
- Tags:NYC medical weight loss, Philadelphia lose weight Zepbound NYC, Budget GLP1 weight loss injections, Wegovy Philadelphia, Wegovy NYC, Philadelphia medical weight loss, Brookly weight loss and Wegovy NYC
|
WikiMD's Wellness Encyclopedia |
| Let Food Be Thy Medicine Medicine Thy Food - Hippocrates |
Medical Disclaimer: WikiMD is not a substitute for professional medical advice. The information on WikiMD is provided as an information resource only, may be incorrect, outdated or misleading, and is not to be used or relied on for any diagnostic or treatment purposes. Please consult your health care provider before making any healthcare decisions or for guidance about a specific medical condition. WikiMD expressly disclaims responsibility, and shall have no liability, for any damages, loss, injury, or liability whatsoever suffered as a result of your reliance on the information contained in this site. By visiting this site you agree to the foregoing terms and conditions, which may from time to time be changed or supplemented by WikiMD. If you do not agree to the foregoing terms and conditions, you should not enter or use this site. See full disclaimer.
Credits:Most images are courtesy of Wikimedia commons, and templates, categories Wikipedia, licensed under CC BY SA or similar.
Translate this page: - East Asian
中文,
日本,
한국어,
South Asian
हिन्दी,
தமிழ்,
తెలుగు,
Urdu,
ಕನ್ನಡ,
Southeast Asian
Indonesian,
Vietnamese,
Thai,
မြန်မာဘာသာ,
বাংলা
European
español,
Deutsch,
français,
Greek,
português do Brasil,
polski,
română,
русский,
Nederlands,
norsk,
svenska,
suomi,
Italian
Middle Eastern & African
عربى,
Turkish,
Persian,
Hebrew,
Afrikaans,
isiZulu,
Kiswahili,
Other
Bulgarian,
Hungarian,
Czech,
Swedish,
മലയാളം,
मराठी,
ਪੰਜਾਬੀ,
ગુજરાતી,
Portuguese,
Ukrainian