External globus pallidus
(Redirected from Lateral globus pallidus)
== External Globus Pallidus ==
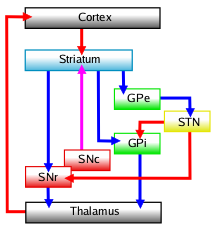
The external globus pallidus (GPe) is a subregion of the globus pallidus, which is part of the basal ganglia in the brain. The basal ganglia are a group of nuclei in the brain associated with a variety of functions, including the regulation of voluntary motor movements, procedural learning, routine behaviors or "habits", eye movements, cognition, and emotion.
Anatomy[edit | edit source]
The external globus pallidus is located lateral to the internal globus pallidus (GPi) and medial to the putamen. It is part of the lentiform nucleus, which also includes the putamen. The GPe is separated from the GPi by the medial medullary lamina, a thin layer of white matter.
Function[edit | edit source]
The external globus pallidus plays a crucial role in the indirect pathway of the basal ganglia circuitry. It receives inhibitory input from the striatum and sends inhibitory output to the subthalamic nucleus (STN). This pathway is essential for the regulation of movement and the suppression of involuntary movements.
Pathways[edit | edit source]
The GPe is involved in several important neural pathways:
- **Indirect Pathway**: In this pathway, the GPe receives input from the striatum and projects to the STN. The STN then projects to the GPi and the substantia nigra pars reticulata (SNr), which in turn project to the thalamus and then to the cerebral cortex.
- **Projections to the Subthalamic Nucleus**: The GPe sends inhibitory signals to the STN, which is a critical component of the indirect pathway. This interaction helps modulate the activity of the GPi and SNr.
Clinical Significance[edit | edit source]
Dysfunction in the external globus pallidus is associated with several neurological disorders, including Parkinson's disease, Huntington's disease, and dystonia. In Parkinson's disease, the loss of dopaminergic neurons in the substantia nigra pars compacta leads to increased activity in the GPe, which disrupts the normal balance of the basal ganglia circuitry and results in motor symptoms such as tremors, rigidity, and bradykinesia.
Research[edit | edit source]
Ongoing research is focused on understanding the precise role of the GPe in the basal ganglia circuitry and its involvement in various neurological disorders. Advances in neuroimaging and electrophysiological techniques are providing new insights into the function and dysfunction of the GPe.
See Also[edit | edit source]
- Basal ganglia
- Globus pallidus
- Internal globus pallidus
- Subthalamic nucleus
- Parkinson's disease
- Huntington's disease
- Dystonia
References[edit | edit source]
External Links[edit | edit source]
Search WikiMD
Ad.Tired of being Overweight? Try W8MD's physician weight loss program.
Semaglutide (Ozempic / Wegovy and Tirzepatide (Mounjaro / Zepbound) available.
Advertise on WikiMD
|
WikiMD's Wellness Encyclopedia |
| Let Food Be Thy Medicine Medicine Thy Food - Hippocrates |
Translate this page: - East Asian
中文,
日本,
한국어,
South Asian
हिन्दी,
தமிழ்,
తెలుగు,
Urdu,
ಕನ್ನಡ,
Southeast Asian
Indonesian,
Vietnamese,
Thai,
မြန်မာဘာသာ,
বাংলা
European
español,
Deutsch,
français,
Greek,
português do Brasil,
polski,
română,
русский,
Nederlands,
norsk,
svenska,
suomi,
Italian
Middle Eastern & African
عربى,
Turkish,
Persian,
Hebrew,
Afrikaans,
isiZulu,
Kiswahili,
Other
Bulgarian,
Hungarian,
Czech,
Swedish,
മലയാളം,
मराठी,
ਪੰਜਾਬੀ,
ગુજરાતી,
Portuguese,
Ukrainian
Medical Disclaimer: WikiMD is not a substitute for professional medical advice. The information on WikiMD is provided as an information resource only, may be incorrect, outdated or misleading, and is not to be used or relied on for any diagnostic or treatment purposes. Please consult your health care provider before making any healthcare decisions or for guidance about a specific medical condition. WikiMD expressly disclaims responsibility, and shall have no liability, for any damages, loss, injury, or liability whatsoever suffered as a result of your reliance on the information contained in this site. By visiting this site you agree to the foregoing terms and conditions, which may from time to time be changed or supplemented by WikiMD. If you do not agree to the foregoing terms and conditions, you should not enter or use this site. See full disclaimer.
Credits:Most images are courtesy of Wikimedia commons, and templates, categories Wikipedia, licensed under CC BY SA or similar.
Contributors: Prab R. Tumpati, MD