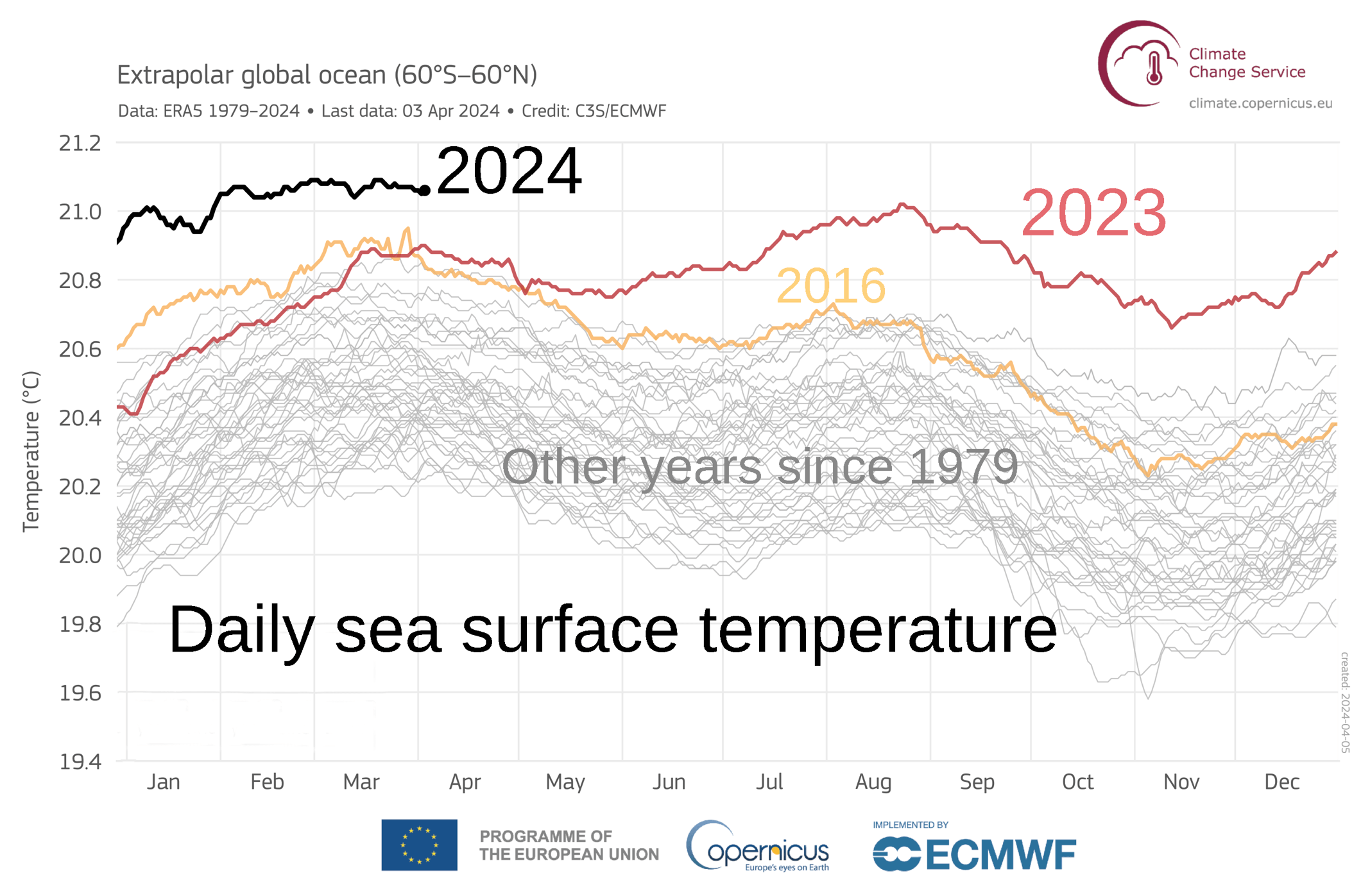
Marine heatwave
|1979- Daily sea surface temperatures 60S-60N latitudes.png|left]]|thumb]]
Marine heatwave (MHW) is a phenomenon where the water temperature in an ocean or sea is significantly higher than average for a prolonged period, typically ranging from days to months. Marine heatwaves can have profound impacts on marine ecosystems, affecting species distribution, biodiversity, and the services these ecosystems provide to humans, such as fisheries and carbon sequestration. The study of marine heatwaves is a critical area of research within the fields of marine biology, oceanography, and climate science.
Causes[edit | edit source]
Marine heatwaves can be caused by a variety of factors, including atmospheric pressure anomalies, ocean currents, and global warming. Atmospheric high-pressure systems can lead to calm and clear conditions, reducing the mixing of surface water and allowing it to warm up. Changes in ocean currents can transport warm water masses to cooler regions. Additionally, the increasing levels of greenhouse gases in the atmosphere are warming the oceans globally, making marine heatwaves more frequent and intense.
Impacts[edit | edit source]
The impacts of marine heatwaves are wide-ranging and can be devastating for marine environments. They can lead to coral bleaching, where corals lose the algae that live in their tissues, causing them to turn white and often leading to coral death. This has significant consequences for reef ecosystems, which are home to a large proportion of marine biodiversity. Marine heatwaves can also cause shifts in species distributions, with some species moving to cooler waters, thereby altering food webs and ecosystem dynamics. Fisheries can suffer as a result of these changes, affecting food security and livelihoods in human communities.
Detection and Monitoring[edit | edit source]
Detecting and monitoring marine heatwaves involves the use of satellite observations, ocean buoys, and climate models to track sea surface temperatures and identify anomalies. Researchers use a variety of metrics to define and categorize marine heatwaves, including intensity, duration, and spatial extent. Early detection and understanding of these events can help in mitigating their impacts through better management of marine resources and adaptation strategies.
Research and Future Challenges[edit | edit source]
Research on marine heatwaves is focused on understanding their causes, impacts, and predicting their occurrence. Scientists are also investigating the role of climate change in increasing the frequency and severity of marine heatwaves. One of the major challenges in this field is improving the accuracy of predictions, which is crucial for the development of adaptation and mitigation strategies. As marine heatwaves become more common, there is an urgent need for global cooperation in research and monitoring to protect marine ecosystems and the human communities that depend on them.
See Also[edit | edit source]
Search WikiMD
Ad.Tired of being Overweight? Try W8MD's physician weight loss program.
Semaglutide (Ozempic / Wegovy and Tirzepatide (Mounjaro / Zepbound) available.
Advertise on WikiMD
|
WikiMD's Wellness Encyclopedia |
| Let Food Be Thy Medicine Medicine Thy Food - Hippocrates |
Translate this page: - East Asian
中文,
日本,
한국어,
South Asian
हिन्दी,
தமிழ்,
తెలుగు,
Urdu,
ಕನ್ನಡ,
Southeast Asian
Indonesian,
Vietnamese,
Thai,
မြန်မာဘာသာ,
বাংলা
European
español,
Deutsch,
français,
Greek,
português do Brasil,
polski,
română,
русский,
Nederlands,
norsk,
svenska,
suomi,
Italian
Middle Eastern & African
عربى,
Turkish,
Persian,
Hebrew,
Afrikaans,
isiZulu,
Kiswahili,
Other
Bulgarian,
Hungarian,
Czech,
Swedish,
മലയാളം,
मराठी,
ਪੰਜਾਬੀ,
ગુજરાતી,
Portuguese,
Ukrainian
Medical Disclaimer: WikiMD is not a substitute for professional medical advice. The information on WikiMD is provided as an information resource only, may be incorrect, outdated or misleading, and is not to be used or relied on for any diagnostic or treatment purposes. Please consult your health care provider before making any healthcare decisions or for guidance about a specific medical condition. WikiMD expressly disclaims responsibility, and shall have no liability, for any damages, loss, injury, or liability whatsoever suffered as a result of your reliance on the information contained in this site. By visiting this site you agree to the foregoing terms and conditions, which may from time to time be changed or supplemented by WikiMD. If you do not agree to the foregoing terms and conditions, you should not enter or use this site. See full disclaimer.
Credits:Most images are courtesy of Wikimedia commons, and templates, categories Wikipedia, licensed under CC BY SA or similar.
Contributors: Prab R. Tumpati, MD