Acid dissociation constant
(Redirected from PKa)
Acid Dissociation Constant[edit | edit source]
The acid dissociation constant, denoted as Ka, is a quantitative measure of the strength of an acid in solution. It is the equilibrium constant for a chemical reaction known as dissociation in the context of acid-base reactions. The equilibrium is represented as:
- HA _ H+ + A-
where HA is a generic acid that dissociates into a proton (H+) and its conjugate base (A-). The larger the value of Ka, the more the acid dissociates, and the stronger the acid.
Definition and Expression[edit | edit source]
The acid dissociation constant is defined by the equation:
- Ka = \( \frac{[\text{H}^+][\text{A}^-]}{[\text{HA}]} \)
where [H+], [A-], and [HA] are the molar concentrations of the hydrogen ion, the conjugate base, and the undissociated acid, respectively.
pKa[edit | edit source]
The pKa is the negative logarithm (base 10) of the acid dissociation constant:
- pKa = -log10Ka
A lower pKa value indicates a stronger acid, which means it more fully dissociates in solution.
Factors Affecting Acid Strength[edit | edit source]
Several factors influence the strength of an acid, including:
- Electronegativity: More electronegative atoms can stabilize the negative charge on the conjugate base, increasing acid strength.
- Resonance: Delocalization of charge through resonance can stabilize the conjugate base.
- Inductive Effect: Electron-withdrawing groups can stabilize the conjugate base through the inductive effect.
- Hybridization: The s-character of the hybrid orbitals can affect acidity; more s-character can lead to stronger acids.
Examples of Acid Dissociation Constants[edit | edit source]
Acetic Acid[edit | edit source]
Acetic acid (CH3COOH) is a weak acid with a pKa of approximately 4.76. It partially dissociates in water to form acetate ions (CH3COO-) and hydrogen ions (H+).
Phosphoric Acid[edit | edit source]
Phosphoric acid (H3PO4) is a triprotic acid with three dissociation constants, corresponding to the loss of each proton.
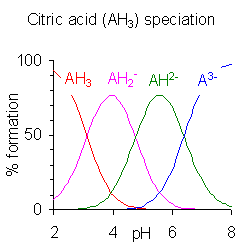
Citric Acid[edit | edit source]
Citric acid (C6H8O7) is a weak organic acid with three carboxyl groups, each with its own dissociation constant.
Related Concepts[edit | edit source]
Related Pages[edit | edit source]
Gallery[edit | edit source]
Search WikiMD
Ad.Tired of being Overweight? Try W8MD's physician weight loss program.
Semaglutide (Ozempic / Wegovy and Tirzepatide (Mounjaro / Zepbound) available.
Advertise on WikiMD
|
WikiMD's Wellness Encyclopedia |
| Let Food Be Thy Medicine Medicine Thy Food - Hippocrates |
Translate this page: - East Asian
中文,
日本,
한국어,
South Asian
हिन्दी,
தமிழ்,
తెలుగు,
Urdu,
ಕನ್ನಡ,
Southeast Asian
Indonesian,
Vietnamese,
Thai,
မြန်မာဘာသာ,
বাংলা
European
español,
Deutsch,
français,
Greek,
português do Brasil,
polski,
română,
русский,
Nederlands,
norsk,
svenska,
suomi,
Italian
Middle Eastern & African
عربى,
Turkish,
Persian,
Hebrew,
Afrikaans,
isiZulu,
Kiswahili,
Other
Bulgarian,
Hungarian,
Czech,
Swedish,
മലയാളം,
मराठी,
ਪੰਜਾਬੀ,
ગુજરાતી,
Portuguese,
Ukrainian
Medical Disclaimer: WikiMD is not a substitute for professional medical advice. The information on WikiMD is provided as an information resource only, may be incorrect, outdated or misleading, and is not to be used or relied on for any diagnostic or treatment purposes. Please consult your health care provider before making any healthcare decisions or for guidance about a specific medical condition. WikiMD expressly disclaims responsibility, and shall have no liability, for any damages, loss, injury, or liability whatsoever suffered as a result of your reliance on the information contained in this site. By visiting this site you agree to the foregoing terms and conditions, which may from time to time be changed or supplemented by WikiMD. If you do not agree to the foregoing terms and conditions, you should not enter or use this site. See full disclaimer.
Credits:Most images are courtesy of Wikimedia commons, and templates, categories Wikipedia, licensed under CC BY SA or similar.
Contributors: Prab R. Tumpati, MD