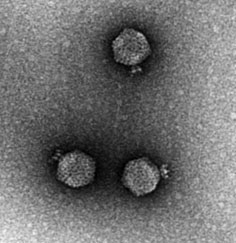
Bacteriophage
(Redirected from Phage)
Bacteriophage, often abbreviated as phage, are viruses that infect and replicate within bacteria and archaea. The term "bacteriophage" literally means "bacteria eater," derived from the Greek bakterion, meaning "little staff," and phagein, meaning "to eat." Bacteriophages play a critical role in the regulation of microbial populations in natural environments and have been used in various applications, from biotechnology to medicine.
History[edit | edit source]
The discovery of bacteriophages dates back to the early 20th century, with independent observations made by Frederick Twort in 1915 and Félix d'Hérelle in 1917. D'Hérelle was the first to propose the idea that bacteriophages could be used as a therapeutic agent against bacterial infections, a practice now known as phage therapy.
Classification[edit | edit source]
Bacteriophages can be classified into a number of families, such as Myoviridae, Siphoviridae, and Podoviridae, based on their morphology and genetic material. They can contain either DNA or RNA as their genetic material, which can be either single-stranded or double-stranded.
Life Cycle[edit | edit source]
Bacteriophages have two main life cycles: the lytic cycle and the lysogenic cycle. In the lytic cycle, phages infect a bacterial cell, use the cell's machinery to replicate, and ultimately cause the cell to lyse, releasing new phage particles. In the lysogenic cycle, the phage integrates its genome into the host cell's genome, replicating along with the cell until a trigger causes it to enter the lytic cycle.
Applications[edit | edit source]
- Phage Therapy###
Phage therapy is the use of bacteriophages to treat bacterial infections. It offers an alternative to traditional antibiotics, especially in the face of increasing antibiotic resistance.
- Biotechnology###
In biotechnology, bacteriophages are used for various applications, including the development of bacteriophage display techniques for the discovery and engineering of proteins and peptides, and the use of phage enzymes in molecular biology, such as restriction enzymes and ligases.
- Food Safety###
Bacteriophages are also applied in food safety, where they are used to detect and control pathogenic bacteria in food products.
Challenges and Future Directions[edit | edit source]
While the potential of bacteriophages in medicine and biotechnology is significant, there are challenges to their widespread adoption. These include the specificity of phages to their bacterial hosts, the potential for bacterial resistance to phages, and regulatory hurdles. Ongoing research aims to overcome these challenges, exploring ways to engineer phages for broader host ranges, prevent resistance, and ensure safety and efficacy in therapeutic applications.
Search WikiMD
Ad.Tired of being Overweight? Try W8MD's physician weight loss program.
Semaglutide (Ozempic / Wegovy and Tirzepatide (Mounjaro / Zepbound) available.
Advertise on WikiMD
|
WikiMD's Wellness Encyclopedia |
| Let Food Be Thy Medicine Medicine Thy Food - Hippocrates |
Translate this page: - East Asian
中文,
日本,
한국어,
South Asian
हिन्दी,
தமிழ்,
తెలుగు,
Urdu,
ಕನ್ನಡ,
Southeast Asian
Indonesian,
Vietnamese,
Thai,
မြန်မာဘာသာ,
বাংলা
European
español,
Deutsch,
français,
Greek,
português do Brasil,
polski,
română,
русский,
Nederlands,
norsk,
svenska,
suomi,
Italian
Middle Eastern & African
عربى,
Turkish,
Persian,
Hebrew,
Afrikaans,
isiZulu,
Kiswahili,
Other
Bulgarian,
Hungarian,
Czech,
Swedish,
മലയാളം,
मराठी,
ਪੰਜਾਬੀ,
ગુજરાતી,
Portuguese,
Ukrainian
Medical Disclaimer: WikiMD is not a substitute for professional medical advice. The information on WikiMD is provided as an information resource only, may be incorrect, outdated or misleading, and is not to be used or relied on for any diagnostic or treatment purposes. Please consult your health care provider before making any healthcare decisions or for guidance about a specific medical condition. WikiMD expressly disclaims responsibility, and shall have no liability, for any damages, loss, injury, or liability whatsoever suffered as a result of your reliance on the information contained in this site. By visiting this site you agree to the foregoing terms and conditions, which may from time to time be changed or supplemented by WikiMD. If you do not agree to the foregoing terms and conditions, you should not enter or use this site. See full disclaimer.
Credits:Most images are courtesy of Wikimedia commons, and templates, categories Wikipedia, licensed under CC BY SA or similar.
Contributors: Prab R. Tumpati, MD