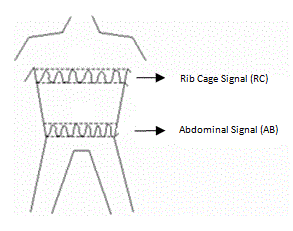
Respiratory inductance plethysmography
Respiratory Inductance Plethysmography[edit | edit source]
Respiratory inductance plethysmography (RIP) is a non-invasive method used to measure respiratory parameters such as tidal volume, respiratory rate, and breathing patterns. It is widely used in both clinical and research settings to monitor respiratory function in patients and study respiratory physiology.
Principles of Operation[edit | edit source]
RIP operates on the principle of inductance, which is the property of an electrical conductor by which a change in current through it induces an electromotive force (voltage) in both the conductor itself and in any nearby conductors. In RIP, elastic bands embedded with wire coils are placed around the thorax and abdomen. As the subject breathes, the expansion and contraction of the chest and abdominal walls alter the inductance of the coils. These changes in inductance are converted into electrical signals that can be analyzed to determine respiratory parameters.
Components of RIP[edit | edit source]
The main components of a respiratory inductance plethysmography system include:
- RIP Bands: These are elastic bands containing wire coils that are placed around the thorax and abdomen. They detect changes in the cross-sectional area of the body as the subject breathes.
- Signal Processing Unit: This unit receives the electrical signals from the RIP bands and processes them to extract respiratory parameters.
- Data Display and Analysis Software: The processed signals are displayed and analyzed using specialized software, which can provide real-time feedback on respiratory function.
Applications[edit | edit source]
RIP is used in various applications, including:
- Sleep Studies: RIP is commonly used in polysomnography to monitor breathing patterns during sleep and diagnose sleep disorders such as sleep apnea.
- Pulmonary Function Testing: It provides a non-invasive way to assess lung function and can be used in conjunction with other tests such as spirometry.
- Research: RIP is used in research to study respiratory physiology and the effects of various interventions on breathing.
Advantages and Limitations[edit | edit source]
Advantages[edit | edit source]
- Non-Invasive: RIP does not require any invasive procedures, making it suitable for continuous monitoring.
- Comfortable: The elastic bands are comfortable to wear, allowing for long-term monitoring without significant discomfort.
- Real-Time Monitoring: Provides real-time data on respiratory parameters, which is useful in both clinical and research settings.
Limitations[edit | edit source]
- Calibration: Accurate measurement requires proper calibration of the system, which can be complex.
- Motion Artifacts: Movement of the subject can introduce artifacts into the data, affecting accuracy.
- Limited to Surface Measurements: RIP measures changes in the surface area of the thorax and abdomen, which may not fully represent lung volume changes.
Related Pages[edit | edit source]
Conclusion[edit | edit source]
Respiratory inductance plethysmography is a valuable tool in the assessment and monitoring of respiratory function. Its non-invasive nature and ability to provide real-time data make it an essential component in both clinical diagnostics and physiological research. Despite its limitations, RIP continues to be a widely used method for understanding and evaluating respiratory health.
Search WikiMD
Ad.Tired of being Overweight? Try W8MD's physician weight loss program.
Semaglutide (Ozempic / Wegovy and Tirzepatide (Mounjaro / Zepbound) available.
Advertise on WikiMD
|
WikiMD's Wellness Encyclopedia |
| Let Food Be Thy Medicine Medicine Thy Food - Hippocrates |
Translate this page: - East Asian
中文,
日本,
한국어,
South Asian
हिन्दी,
தமிழ்,
తెలుగు,
Urdu,
ಕನ್ನಡ,
Southeast Asian
Indonesian,
Vietnamese,
Thai,
မြန်မာဘာသာ,
বাংলা
European
español,
Deutsch,
français,
Greek,
português do Brasil,
polski,
română,
русский,
Nederlands,
norsk,
svenska,
suomi,
Italian
Middle Eastern & African
عربى,
Turkish,
Persian,
Hebrew,
Afrikaans,
isiZulu,
Kiswahili,
Other
Bulgarian,
Hungarian,
Czech,
Swedish,
മലയാളം,
मराठी,
ਪੰਜਾਬੀ,
ગુજરાતી,
Portuguese,
Ukrainian
Medical Disclaimer: WikiMD is not a substitute for professional medical advice. The information on WikiMD is provided as an information resource only, may be incorrect, outdated or misleading, and is not to be used or relied on for any diagnostic or treatment purposes. Please consult your health care provider before making any healthcare decisions or for guidance about a specific medical condition. WikiMD expressly disclaims responsibility, and shall have no liability, for any damages, loss, injury, or liability whatsoever suffered as a result of your reliance on the information contained in this site. By visiting this site you agree to the foregoing terms and conditions, which may from time to time be changed or supplemented by WikiMD. If you do not agree to the foregoing terms and conditions, you should not enter or use this site. See full disclaimer.
Credits:Most images are courtesy of Wikimedia commons, and templates, categories Wikipedia, licensed under CC BY SA or similar.
Contributors: Prab R. Tumpati, MD