Rotameter
Rotameter
A rotameter is a device that measures the flow rate of liquid or gas in a closed tube. It belongs to a class of meters called variable area flow meters, which measure flow rate by allowing the cross-sectional area the fluid travels through to vary, causing a measurable change.
Design and Operation[edit | edit source]
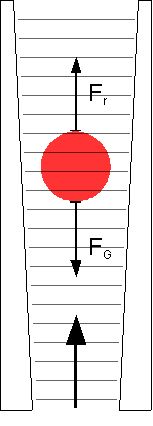
The rotameter consists of a tapered tube, typically made of glass, with a float inside that is pushed up by the flow of the fluid and pulled down by gravity. The position of the float is an indication of the flow rate. The tube is wider at the top than at the bottom, which means that as the float rises, the area between the float and the tube wall increases, allowing more fluid to pass around the float.
The float reaches a stable position when the upward force exerted by the fluid flow equals the downward gravitational force on the float. The height of the float is then read off a scale on the tube, which is calibrated to the flow rate.
Applications[edit | edit source]
Rotameters are widely used in various industries, including chemical, pharmaceutical, and water treatment industries. They are used for applications such as monitoring the flow of gases in laboratory experiments, controlling the flow of liquids in industrial processes, and measuring the flow rate of water in water treatment plants.
Advantages and Disadvantages[edit | edit source]
Advantages[edit | edit source]
- Simple and reliable design
- No external power required
- Can be used for both liquids and gases
- Provides a visual indication of flow rate
Disadvantages[edit | edit source]
- Limited to low-pressure systems
- Glass tubes can be fragile
- Accuracy can be affected by changes in fluid density and viscosity
Related Pages[edit | edit source]
See Also[edit | edit source]
Search WikiMD
Ad.Tired of being Overweight? Try W8MD's physician weight loss program.
Semaglutide (Ozempic / Wegovy and Tirzepatide (Mounjaro / Zepbound) available.
Advertise on WikiMD
|
WikiMD's Wellness Encyclopedia |
| Let Food Be Thy Medicine Medicine Thy Food - Hippocrates |
Translate this page: - East Asian
中文,
日本,
한국어,
South Asian
हिन्दी,
தமிழ்,
తెలుగు,
Urdu,
ಕನ್ನಡ,
Southeast Asian
Indonesian,
Vietnamese,
Thai,
မြန်မာဘာသာ,
বাংলা
European
español,
Deutsch,
français,
Greek,
português do Brasil,
polski,
română,
русский,
Nederlands,
norsk,
svenska,
suomi,
Italian
Middle Eastern & African
عربى,
Turkish,
Persian,
Hebrew,
Afrikaans,
isiZulu,
Kiswahili,
Other
Bulgarian,
Hungarian,
Czech,
Swedish,
മലയാളം,
मराठी,
ਪੰਜਾਬੀ,
ગુજરાતી,
Portuguese,
Ukrainian
Medical Disclaimer: WikiMD is not a substitute for professional medical advice. The information on WikiMD is provided as an information resource only, may be incorrect, outdated or misleading, and is not to be used or relied on for any diagnostic or treatment purposes. Please consult your health care provider before making any healthcare decisions or for guidance about a specific medical condition. WikiMD expressly disclaims responsibility, and shall have no liability, for any damages, loss, injury, or liability whatsoever suffered as a result of your reliance on the information contained in this site. By visiting this site you agree to the foregoing terms and conditions, which may from time to time be changed or supplemented by WikiMD. If you do not agree to the foregoing terms and conditions, you should not enter or use this site. See full disclaimer.
Credits:Most images are courtesy of Wikimedia commons, and templates Wikipedia, licensed under CC BY SA or similar.
Contributors: Prab R. Tumpati, MD