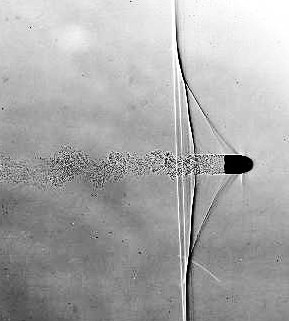
Shadowgraph
Shadowgraph is a technique used to visualize fluid flow patterns, heat currents, and other phenomena that affect the density of a medium. It is a simple and ancient method that relies on the interaction between light and the material being studied. The shadowgraph technique is widely used in various fields, including aerodynamics, thermodynamics, and optics, due to its simplicity and effectiveness in providing qualitative information about the phenomena under observation.
Principle[edit | edit source]
The principle behind the shadowgraph technique is based on the deflection of light rays as they pass through a medium with varying density. When light travels through a medium, its speed changes according to the medium's density; this is known as the refraction of light. In areas where the density of the medium changes, such as in the presence of thermal gradients or fluid flow patterns, the light rays are bent. By projecting these light rays onto a screen, the shadowgraph technique creates visual patterns that correspond to the density variations within the medium. These patterns can be captured and analyzed to study the physical phenomena causing the density changes.
Setup[edit | edit source]
A typical shadowgraph setup involves a coherent light source, such as a laser or a collimated light beam, the test section containing the medium under study, and a screen or detector to capture the resulting shadowgraph image. The light source illuminates the test section, and the screen captures the shadows and patterns formed by the deflection of light rays due to density variations in the medium.
Applications[edit | edit source]
Shadowgraphy has a wide range of applications in scientific research and industry. Some of the key applications include:
- **Aerodynamics**: Visualization of shock waves around supersonic aircraft and in wind tunnel tests. - **Combustion Research**: Study of flame fronts and combustion processes. - **Heat Transfer**: Visualization of convection patterns and heat transfer phenomena. - **Fluid Mechanics**: Observation of flow patterns, turbulence, and vortices in fluids.
Advantages and Limitations[edit | edit source]
The shadowgraph technique offers several advantages, including simplicity, low cost, and the ability to visualize large areas of the test section simultaneously. However, it also has limitations, such as providing only qualitative information and being less sensitive than other optical methods like schlieren photography and interferometry.
Conclusion[edit | edit source]
The shadowgraph technique remains a valuable tool in the visualization of fluid flow and thermal phenomena. Its simplicity and effectiveness make it an essential method in the fields of aerodynamics, thermodynamics, and optics. Despite its limitations, the shadowgraph continues to be used alongside more advanced techniques to provide a comprehensive understanding of complex physical phenomena.
Search WikiMD
Ad.Tired of being Overweight? Try W8MD's physician weight loss program.
Semaglutide (Ozempic / Wegovy and Tirzepatide (Mounjaro / Zepbound) available.
Advertise on WikiMD
|
WikiMD's Wellness Encyclopedia |
| Let Food Be Thy Medicine Medicine Thy Food - Hippocrates |
Translate this page: - East Asian
中文,
日本,
한국어,
South Asian
हिन्दी,
தமிழ்,
తెలుగు,
Urdu,
ಕನ್ನಡ,
Southeast Asian
Indonesian,
Vietnamese,
Thai,
မြန်မာဘာသာ,
বাংলা
European
español,
Deutsch,
français,
Greek,
português do Brasil,
polski,
română,
русский,
Nederlands,
norsk,
svenska,
suomi,
Italian
Middle Eastern & African
عربى,
Turkish,
Persian,
Hebrew,
Afrikaans,
isiZulu,
Kiswahili,
Other
Bulgarian,
Hungarian,
Czech,
Swedish,
മലയാളം,
मराठी,
ਪੰਜਾਬੀ,
ગુજરાતી,
Portuguese,
Ukrainian
Medical Disclaimer: WikiMD is not a substitute for professional medical advice. The information on WikiMD is provided as an information resource only, may be incorrect, outdated or misleading, and is not to be used or relied on for any diagnostic or treatment purposes. Please consult your health care provider before making any healthcare decisions or for guidance about a specific medical condition. WikiMD expressly disclaims responsibility, and shall have no liability, for any damages, loss, injury, or liability whatsoever suffered as a result of your reliance on the information contained in this site. By visiting this site you agree to the foregoing terms and conditions, which may from time to time be changed or supplemented by WikiMD. If you do not agree to the foregoing terms and conditions, you should not enter or use this site. See full disclaimer.
Credits:Most images are courtesy of Wikimedia commons, and templates, categories Wikipedia, licensed under CC BY SA or similar.
Contributors: Prab R. Tumpati, MD