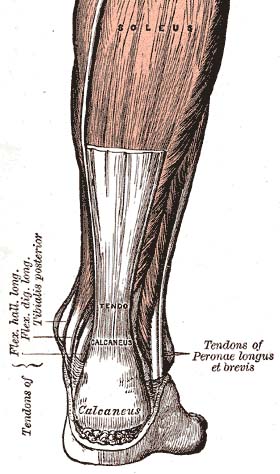
Tendon
(Redirected from Sinew)
Tendon is a flexible yet inelastic cord of strong fibrous collagen tissue attaching a muscle to a bone. Tendons are similar to ligaments and fasciae as they are all made of collagen. Ligaments join one bone to another bone, while fasciae connect muscles to other muscles. Tendons and muscles work together to move bones.
Structure[edit | edit source]
Tendons are composed of collagen fibers, ground substance, elastin, proteoglycans, and inorganic components. The majority of the tendon consists of densely packed collagen fibers. These fibers are arranged in a parallel fashion to one another, which provides the tendon with its strength and stiffness.
Function[edit | edit source]
The primary function of a tendon is to transmit the force generated by the muscle to the bone, which allows for movement of the joint. Tendons can also store energy, as in the tendons of the leg, which store energy for jumping.
Clinical significance[edit | edit source]
Tendons can be damaged by injury or overuse, resulting in tendinitis or tendon rupture. Tendinitis is inflammation of the tendon, which can cause pain and loss of function. Tendon rupture is a more serious condition, where the tendon is completely or partially torn.
See also[edit | edit source]
Search WikiMD
Ad.Tired of being Overweight? Try W8MD's physician weight loss program.
Semaglutide (Ozempic / Wegovy and Tirzepatide (Mounjaro / Zepbound) available.
Advertise on WikiMD
|
WikiMD's Wellness Encyclopedia |
| Let Food Be Thy Medicine Medicine Thy Food - Hippocrates |
Translate this page: - East Asian
中文,
日本,
한국어,
South Asian
हिन्दी,
தமிழ்,
తెలుగు,
Urdu,
ಕನ್ನಡ,
Southeast Asian
Indonesian,
Vietnamese,
Thai,
မြန်မာဘာသာ,
বাংলা
European
español,
Deutsch,
français,
Greek,
português do Brasil,
polski,
română,
русский,
Nederlands,
norsk,
svenska,
suomi,
Italian
Middle Eastern & African
عربى,
Turkish,
Persian,
Hebrew,
Afrikaans,
isiZulu,
Kiswahili,
Other
Bulgarian,
Hungarian,
Czech,
Swedish,
മലയാളം,
मराठी,
ਪੰਜਾਬੀ,
ગુજરાતી,
Portuguese,
Ukrainian
Medical Disclaimer: WikiMD is not a substitute for professional medical advice. The information on WikiMD is provided as an information resource only, may be incorrect, outdated or misleading, and is not to be used or relied on for any diagnostic or treatment purposes. Please consult your health care provider before making any healthcare decisions or for guidance about a specific medical condition. WikiMD expressly disclaims responsibility, and shall have no liability, for any damages, loss, injury, or liability whatsoever suffered as a result of your reliance on the information contained in this site. By visiting this site you agree to the foregoing terms and conditions, which may from time to time be changed or supplemented by WikiMD. If you do not agree to the foregoing terms and conditions, you should not enter or use this site. See full disclaimer.
Credits:Most images are courtesy of Wikimedia commons, and templates, categories Wikipedia, licensed under CC BY SA or similar.
Contributors: Prab R. Tumpati, MD