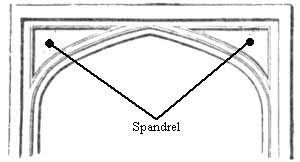
Spandrel
Spandrel is an architectural term referring to the space between two arches or between an arch and a rectangular enclosure. In the context of architecture, spandrels can be found in a variety of structures, including bridges, domes, and archways. They often contain decorative elements and have been utilized in both historical and modern architecture to fill the triangular space that arises from the intersection of two rounded or pointed structures. The concept of a spandrel highlights the intersection of functionality and aesthetics in architectural design.
History and Development[edit | edit source]
The use of spandrels dates back to ancient architecture, where they were primarily structural elements before evolving into spaces for artistic and decorative expression. In Gothic architecture, spandrels are prominently featured in cathedrals and churches, adorned with sculptures, carvings, and stained glass that contribute to the narrative and thematic elements of the building. The Renaissance period saw a further evolution in the use of spandrels, with artists and architects like Michelangelo and Brunelleschi incorporating them into their work as canvases for artistic expression.
Types of Spandrels[edit | edit source]
There are several types of spandrels in architecture, including:
- Architectural Spandrels: These are the most common type, found between arches or between an arch and a rectangular boundary. They can be purely decorative or serve as structural supports.
- Bridge Spandrels: Found in arch bridges, these spandrels support the deck of the bridge and can be solid or open, depending on the design and structural requirements.
- Decorative Spandrels: These are primarily used for ornamental purposes, featuring intricate designs, carvings, and artworks.
Material and Construction[edit | edit source]
Spandrels can be constructed from a variety of materials, including stone, brick, concrete, and metal. The choice of material often depends on the structural requirements, aesthetic considerations, and the overall design of the architecture. In modern construction, glass and steel are also used, especially in skyscrapers and commercial buildings, to create visually appealing and light-filled spaces.
Significance in Architecture[edit | edit source]
Spandrels play a crucial role in the aesthetics of architectural design. They offer architects and designers an opportunity to integrate decorative elements into the structure, enhancing the visual appeal and thematic coherence of the building. Beyond their decorative function, spandrels also serve practical purposes, such as reducing the weight of a structure, providing insulation, and concealing structural elements.
Contemporary Use[edit | edit source]
In contemporary architecture, spandrels continue to be an important element, especially in the design of skyscrapers and large buildings. Modern techniques have expanded the possibilities for spandrel design, allowing for the integration of energy-efficient materials and innovative decorative techniques. Glass spandrels, for example, can be used to create seamless transitions between windows, contributing to the sleek and modern aesthetic of many urban buildings.
Conclusion[edit | edit source]
Spandrels represent a fascinating aspect of architectural design, bridging the gap between form and function. From their origins in ancient and Gothic architecture to their contemporary applications, spandrels illustrate the evolving nature of architectural innovation and the continuous interplay between structural necessity and artistic expression.
Search WikiMD
Ad.Tired of being Overweight? Try W8MD's physician weight loss program.
Semaglutide (Ozempic / Wegovy and Tirzepatide (Mounjaro / Zepbound) available.
Advertise on WikiMD
|
WikiMD's Wellness Encyclopedia |
| Let Food Be Thy Medicine Medicine Thy Food - Hippocrates |
Translate this page: - East Asian
中文,
日本,
한국어,
South Asian
हिन्दी,
தமிழ்,
తెలుగు,
Urdu,
ಕನ್ನಡ,
Southeast Asian
Indonesian,
Vietnamese,
Thai,
မြန်မာဘာသာ,
বাংলা
European
español,
Deutsch,
français,
Greek,
português do Brasil,
polski,
română,
русский,
Nederlands,
norsk,
svenska,
suomi,
Italian
Middle Eastern & African
عربى,
Turkish,
Persian,
Hebrew,
Afrikaans,
isiZulu,
Kiswahili,
Other
Bulgarian,
Hungarian,
Czech,
Swedish,
മലയാളം,
मराठी,
ਪੰਜਾਬੀ,
ગુજરાતી,
Portuguese,
Ukrainian
Medical Disclaimer: WikiMD is not a substitute for professional medical advice. The information on WikiMD is provided as an information resource only, may be incorrect, outdated or misleading, and is not to be used or relied on for any diagnostic or treatment purposes. Please consult your health care provider before making any healthcare decisions or for guidance about a specific medical condition. WikiMD expressly disclaims responsibility, and shall have no liability, for any damages, loss, injury, or liability whatsoever suffered as a result of your reliance on the information contained in this site. By visiting this site you agree to the foregoing terms and conditions, which may from time to time be changed or supplemented by WikiMD. If you do not agree to the foregoing terms and conditions, you should not enter or use this site. See full disclaimer.
Credits:Most images are courtesy of Wikimedia commons, and templates Wikipedia, licensed under CC BY SA or similar.
Contributors: Prab R. Tumpati, MD