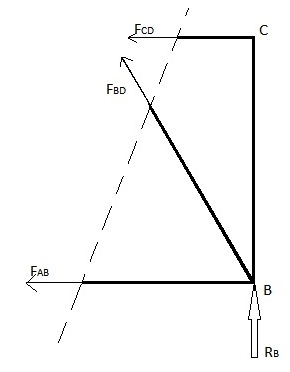
Structural analysis
Structural analysis is a branch of civil engineering and mechanical engineering that involves the determination of the effects of loads on physical structures and their components. The results of the analysis are used to verify a structure's fitness for use, often precluding physical tests.
History[edit | edit source]
The history of structural analysis dates back to ancient times when early engineers and builders used empirical methods to design structures. The development of the theory of elasticity in the 19th century provided a scientific basis for structural analysis. The advent of computers in the 20th century revolutionized the field, allowing for more complex and accurate analyses.
Methods[edit | edit source]
Structural analysis can be performed using various methods, including:
- Analytical methods: These involve solving equations derived from the principles of mechanics and material science.
- Numerical methods: These include techniques such as the finite element method (FEM), which approximates solutions to complex problems.
- Experimental methods: These involve physical testing of structures or models to observe their behavior under loads.
Types of Loads[edit | edit source]
Structures are subjected to different types of loads, including:
- Dead load: The weight of the structure itself.
- Live load: The weight of movable objects, such as people and furniture.
- Environmental load: Loads due to environmental factors like wind, snow, and earthquakes.
Applications[edit | edit source]
Structural analysis is crucial in the design and assessment of various structures, including:
Software[edit | edit source]
Several software programs are used in structural analysis, including:
Related Pages[edit | edit source]
- Civil engineering
- Mechanical engineering
- Finite element method
- Theory of elasticity
- Structural engineering
Categories[edit | edit source]
Search WikiMD
Ad.Tired of being Overweight? Try W8MD's physician weight loss program.
Semaglutide (Ozempic / Wegovy and Tirzepatide (Mounjaro / Zepbound) available.
Advertise on WikiMD
|
WikiMD's Wellness Encyclopedia |
| Let Food Be Thy Medicine Medicine Thy Food - Hippocrates |
Translate this page: - East Asian
中文,
日本,
한국어,
South Asian
हिन्दी,
தமிழ்,
తెలుగు,
Urdu,
ಕನ್ನಡ,
Southeast Asian
Indonesian,
Vietnamese,
Thai,
မြန်မာဘာသာ,
বাংলা
European
español,
Deutsch,
français,
Greek,
português do Brasil,
polski,
română,
русский,
Nederlands,
norsk,
svenska,
suomi,
Italian
Middle Eastern & African
عربى,
Turkish,
Persian,
Hebrew,
Afrikaans,
isiZulu,
Kiswahili,
Other
Bulgarian,
Hungarian,
Czech,
Swedish,
മലയാളം,
मराठी,
ਪੰਜਾਬੀ,
ગુજરાતી,
Portuguese,
Ukrainian
Medical Disclaimer: WikiMD is not a substitute for professional medical advice. The information on WikiMD is provided as an information resource only, may be incorrect, outdated or misleading, and is not to be used or relied on for any diagnostic or treatment purposes. Please consult your health care provider before making any healthcare decisions or for guidance about a specific medical condition. WikiMD expressly disclaims responsibility, and shall have no liability, for any damages, loss, injury, or liability whatsoever suffered as a result of your reliance on the information contained in this site. By visiting this site you agree to the foregoing terms and conditions, which may from time to time be changed or supplemented by WikiMD. If you do not agree to the foregoing terms and conditions, you should not enter or use this site. See full disclaimer.
Credits:Most images are courtesy of Wikimedia commons, and templates, categories Wikipedia, licensed under CC BY SA or similar.
Contributors: Prab R. Tumpati, MD