Central sulcus
(Redirected from Sulcus centralis)
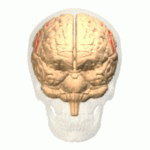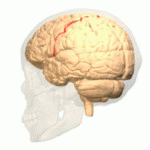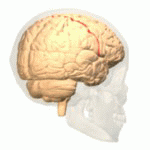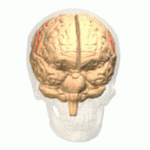
File:Cerebral Hemisphere Demonstration - Sanjoy Sanyal - Neuroscience Lab Fall 2013 1 (from 1m24s to 2m36s) Central sulcus.webm Central Sulcus is a prominent landmark of the brain's surface anatomy, dividing the frontal lobe from the parietal lobe. It is also known as the fissure of Rolando, named after the Italian anatomist Luigi Rolando. The central sulcus is a critical structure in the brain, playing a key role in separating the brain's motor and sensory areas.
Anatomy[edit | edit source]
The central sulcus begins near the top of the brain, just behind the frontal lobe's precentral gyrus, which is responsible for motor control, and extends downward towards the Sylvian fissure. Anterior to the central sulcus is the precentral gyrus, involved in motor functions, and posterior to it is the postcentral gyrus, involved in sensory functions. This anatomical arrangement is crucial for the brain's division of labor between motor and sensory tasks.
Function[edit | edit source]
The central sulcus is a vital anatomical feature in the understanding of the brain's functional organization. It demarcates the boundary between the frontal lobe's motor cortex, which is responsible for controlling voluntary muscle movements, and the parietal lobe's sensory cortex, which processes sensory information from the body. The precise localization of motor and sensory functions in these adjacent cortical areas is known as somatotopy. This organization allows for detailed mapping of the body's motor and sensory functions onto the brain's surface.
Clinical Significance[edit | edit source]
The central sulcus is of significant clinical interest due to its role in various neurological conditions. Its identification is crucial in neurosurgery for avoiding damage to critical motor and sensory areas during operations. Conditions such as stroke, epilepsy, and traumatic brain injury can affect areas around the central sulcus, leading to deficits in movement, sensation, or both, depending on the specific location and extent of the damage.
Imaging[edit | edit source]
In neuroimaging, the central sulcus is a key landmark for orienting the brain's anatomy. Techniques such as MRI (Magnetic Resonance Imaging) and CT scans (Computed Tomography) utilize the central sulcus to differentiate between the frontal and parietal lobes. Its identification helps in diagnosing and treating neurological disorders, planning surgical interventions, and conducting research on brain function.
Conclusion[edit | edit source]
The central sulcus is a fundamental feature of the brain's anatomy and function, serving as a critical landmark for dividing motor and sensory regions. Its significance extends beyond basic anatomy to clinical applications in diagnosis, treatment, and research of neurological conditions.
Search WikiMD
Ad.Tired of being Overweight? Try W8MD's physician weight loss program.
Semaglutide (Ozempic / Wegovy and Tirzepatide (Mounjaro / Zepbound) available.
Advertise on WikiMD
|
WikiMD's Wellness Encyclopedia |
| Let Food Be Thy Medicine Medicine Thy Food - Hippocrates |
Translate this page: - East Asian
中文,
日本,
한국어,
South Asian
हिन्दी,
தமிழ்,
తెలుగు,
Urdu,
ಕನ್ನಡ,
Southeast Asian
Indonesian,
Vietnamese,
Thai,
မြန်မာဘာသာ,
বাংলা
European
español,
Deutsch,
français,
Greek,
português do Brasil,
polski,
română,
русский,
Nederlands,
norsk,
svenska,
suomi,
Italian
Middle Eastern & African
عربى,
Turkish,
Persian,
Hebrew,
Afrikaans,
isiZulu,
Kiswahili,
Other
Bulgarian,
Hungarian,
Czech,
Swedish,
മലയാളം,
मराठी,
ਪੰਜਾਬੀ,
ગુજરાતી,
Portuguese,
Ukrainian
Medical Disclaimer: WikiMD is not a substitute for professional medical advice. The information on WikiMD is provided as an information resource only, may be incorrect, outdated or misleading, and is not to be used or relied on for any diagnostic or treatment purposes. Please consult your health care provider before making any healthcare decisions or for guidance about a specific medical condition. WikiMD expressly disclaims responsibility, and shall have no liability, for any damages, loss, injury, or liability whatsoever suffered as a result of your reliance on the information contained in this site. By visiting this site you agree to the foregoing terms and conditions, which may from time to time be changed or supplemented by WikiMD. If you do not agree to the foregoing terms and conditions, you should not enter or use this site. See full disclaimer.
Credits:Most images are courtesy of Wikimedia commons, and templates, categories Wikipedia, licensed under CC BY SA or similar.
Contributors: Prab R. Tumpati, MD