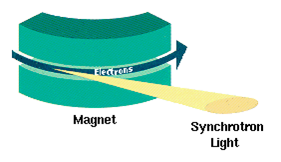
Synchrotron radiation
==Synchrotron Radiation ==
Synchrotron radiation is the electromagnetic radiation emitted when charged particles are accelerated radially. This phenomenon occurs when particles travel at relativistic speeds in magnetic fields, causing them to emit energy in the form of light. Synchrotron radiation is characterized by its broad spectrum, which ranges from infrared to X-rays and even gamma rays.
History[edit | edit source]
The concept of synchrotron radiation was first observed in a synchrotron particle accelerator in 1947 by researchers at the General Electric research laboratory. The radiation was initially considered a nuisance because it caused energy loss in the particle beams. However, it was soon recognized for its potential applications in various scientific fields.
Properties[edit | edit source]
Synchrotron radiation has several unique properties:
- Broad Spectrum: It covers a wide range of wavelengths, from infrared to X-rays.
- High Intensity: The radiation is extremely intense, making it useful for detailed imaging and analysis.
- Polarization: The emitted light is highly polarized.
- Coherence: The radiation can be highly coherent, especially in the X-ray range.
Applications[edit | edit source]
Synchrotron radiation has numerous applications across different scientific disciplines:
- X-ray crystallography: Used to determine the atomic structure of crystals.
- Biology: Helps in understanding the structure of proteins and nucleic acids.
- Materials science: Used to study the properties of materials at the atomic level.
- Medical imaging: Provides high-resolution images for diagnostic purposes.
- Environmental science: Analyzes pollutants and their effects on the environment.
Synchrotron Facilities[edit | edit source]
Several large-scale facilities around the world are dedicated to producing synchrotron radiation for research purposes. Some of the most notable ones include:
- European Synchrotron Radiation Facility (ESRF) in France
- Advanced Photon Source (APS) in the United States
- SPring-8 in Japan
- Diamond Light Source in the United Kingdom
Future Developments[edit | edit source]
Research is ongoing to develop more advanced synchrotron sources, such as free-electron lasers (FELs), which promise even higher brightness and coherence. These advancements are expected to open new frontiers in scientific research and technological innovation.
See Also[edit | edit source]
References[edit | edit source]
External Links[edit | edit source]
Search WikiMD
Ad.Tired of being Overweight? Try W8MD's physician weight loss program.
Semaglutide (Ozempic / Wegovy and Tirzepatide (Mounjaro / Zepbound) available.
Advertise on WikiMD
|
WikiMD's Wellness Encyclopedia |
| Let Food Be Thy Medicine Medicine Thy Food - Hippocrates |
Translate this page: - East Asian
中文,
日本,
한국어,
South Asian
हिन्दी,
தமிழ்,
తెలుగు,
Urdu,
ಕನ್ನಡ,
Southeast Asian
Indonesian,
Vietnamese,
Thai,
မြန်မာဘာသာ,
বাংলা
European
español,
Deutsch,
français,
Greek,
português do Brasil,
polski,
română,
русский,
Nederlands,
norsk,
svenska,
suomi,
Italian
Middle Eastern & African
عربى,
Turkish,
Persian,
Hebrew,
Afrikaans,
isiZulu,
Kiswahili,
Other
Bulgarian,
Hungarian,
Czech,
Swedish,
മലയാളം,
मराठी,
ਪੰਜਾਬੀ,
ગુજરાતી,
Portuguese,
Ukrainian
Medical Disclaimer: WikiMD is not a substitute for professional medical advice. The information on WikiMD is provided as an information resource only, may be incorrect, outdated or misleading, and is not to be used or relied on for any diagnostic or treatment purposes. Please consult your health care provider before making any healthcare decisions or for guidance about a specific medical condition. WikiMD expressly disclaims responsibility, and shall have no liability, for any damages, loss, injury, or liability whatsoever suffered as a result of your reliance on the information contained in this site. By visiting this site you agree to the foregoing terms and conditions, which may from time to time be changed or supplemented by WikiMD. If you do not agree to the foregoing terms and conditions, you should not enter or use this site. See full disclaimer.
Credits:Most images are courtesy of Wikimedia commons, and templates, categories Wikipedia, licensed under CC BY SA or similar.
Contributors: Prab R. Tumpati, MD