Coccyx
(Redirected from Tail bone)
Coccyx, commonly referred to as the tailbone, is the final segment of the vertebral column in humans and certain other animals. Comprising three to five separate or fused vertebrae below the sacrum, the coccyx is a vestigial structure that remains as a remnant of a lost tail. Despite its reduced size and function in humans, the coccyx plays a significant role in the support and stability of the pelvic region, serving as an attachment site for various muscles, tendons, and ligaments.
Anatomy[edit | edit source]
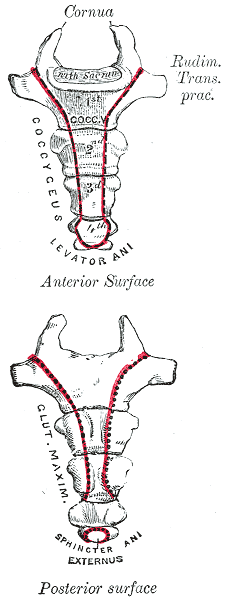
The coccyx is typically made up of four vertebrae in humans, named the coccygeal vertebrae, which can be partially or completely fused. The number of coccygeal vertebrae can vary from three to five, with four being the most common configuration. The coccyx articulates superiorly with the sacral bone at the sacrococcygeal symphysis, a cartilaginous joint that allows for limited movement, primarily during childbirth.
Function[edit | edit source]
Although often considered a vestigial structure, the coccyx has several important functions. It serves as an attachment point for various muscles, ligaments, and tendons. Among these are the gluteus maximus, which extends the thigh at the hip; the levator ani, which supports the pelvic organs; and the coccygeus muscle, which assists in supporting the pelvic floor. The coccyx also plays a role in supporting the body when sitting, especially in a leaning back position.
Clinical Significance[edit | edit source]
Injury to the coccyx, commonly known as a coccyx or tailbone injury, can occur due to direct trauma, such as a fall onto the tailbone, or as a result of childbirth. Symptoms of a coccygeal injury include pain and tenderness at the base of the spine, which can be exacerbated by sitting or by any pressure on the area. Treatment for coccygeal injuries typically involves pain management, the use of cushions or pillows designed to relieve pressure on the coccyx, and, in rare cases, surgery.
Coccydynia is a condition characterized by chronic pain in the coccyx area. The pain associated with coccydynia can be severe and is often aggravated by sitting. The exact cause of coccydynia is not always clear, but it may arise from trauma, abnormal mobility of the coccyx, or the degeneration of the coccygeal vertebrae.
Evolutionary Perspective[edit | edit source]
The coccyx is considered a vestigial structure, a remnant of a longer tail present in our evolutionary ancestors. In some animals, the tail serves various functions, such as balance and communication. However, as humans evolved to walk upright, the need for a tail diminished, leading to the reduced form of the coccyx observed today.
See Also[edit | edit source]
Search WikiMD
Ad.Tired of being Overweight? Try W8MD's physician weight loss program.
Semaglutide (Ozempic / Wegovy and Tirzepatide (Mounjaro / Zepbound) available.
Advertise on WikiMD
|
WikiMD's Wellness Encyclopedia |
| Let Food Be Thy Medicine Medicine Thy Food - Hippocrates |
Translate this page: - East Asian
中文,
日本,
한국어,
South Asian
हिन्दी,
தமிழ்,
తెలుగు,
Urdu,
ಕನ್ನಡ,
Southeast Asian
Indonesian,
Vietnamese,
Thai,
မြန်မာဘာသာ,
বাংলা
European
español,
Deutsch,
français,
Greek,
português do Brasil,
polski,
română,
русский,
Nederlands,
norsk,
svenska,
suomi,
Italian
Middle Eastern & African
عربى,
Turkish,
Persian,
Hebrew,
Afrikaans,
isiZulu,
Kiswahili,
Other
Bulgarian,
Hungarian,
Czech,
Swedish,
മലയാളം,
मराठी,
ਪੰਜਾਬੀ,
ગુજરાતી,
Portuguese,
Ukrainian
Medical Disclaimer: WikiMD is not a substitute for professional medical advice. The information on WikiMD is provided as an information resource only, may be incorrect, outdated or misleading, and is not to be used or relied on for any diagnostic or treatment purposes. Please consult your health care provider before making any healthcare decisions or for guidance about a specific medical condition. WikiMD expressly disclaims responsibility, and shall have no liability, for any damages, loss, injury, or liability whatsoever suffered as a result of your reliance on the information contained in this site. By visiting this site you agree to the foregoing terms and conditions, which may from time to time be changed or supplemented by WikiMD. If you do not agree to the foregoing terms and conditions, you should not enter or use this site. See full disclaimer.
Credits:Most images are courtesy of Wikimedia commons, and templates, categories Wikipedia, licensed under CC BY SA or similar.
Contributors: Prab R. Tumpati, MD