Bronchiole
(Redirected from Terminal bronchiole)
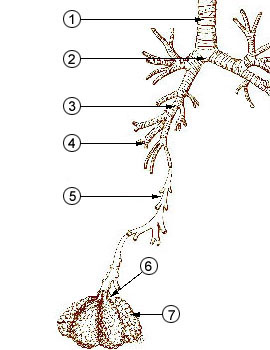
Bronchioles are small airways in the respiratory system that extend from the bronchi and connect to the alveolar ducts, leading directly to the alveoli, where gas exchange occurs. They are a crucial part of the lung anatomy, facilitating the movement of air in and out of the lungs. Unlike the larger bronchi, bronchioles do not contain cartilage in their wall structure. This absence allows them to be more flexible but also more susceptible to collapse and obstruction.
Structure[edit | edit source]
Bronchioles are typically less than 1 mm in diameter and are composed of smooth muscle and elastic fibers. They are lined with a simple columnar to cuboidal epithelium, which includes ciliated cells and club cells (formerly known as Clara cells). Club cells serve several functions, including detoxifying harmful substances inhaled into the lungs, secreting components of surfactant which reduces surface tension in the alveoli, and acting as progenitor cells to regenerate the bronchiolar epithelium.
The bronchioles divide further into smaller tubes, known as terminal bronchioles, which in turn give rise to the respiratory bronchioles. These then lead to the alveolar ducts and eventually the alveolar sacs. This branching structure is often referred to as the bronchial tree.
Function[edit | edit source]
The primary function of the bronchioles is to carry air from the bronchi to the alveoli, ensuring that oxygen reaches the bloodstream and carbon dioxide is expelled. The smooth muscle in their walls helps regulate airflow through the lungs by contracting or relaxing, a process known as bronchoconstriction and bronchodilation, respectively. This regulation is crucial for maintaining proper air distribution and gas exchange efficiency in the lungs.
Clinical Significance[edit | edit source]
Several conditions can affect the bronchioles, leading to respiratory issues. One of the most common is Asthma, a chronic inflammatory disease that causes bronchoconstriction, making breathing difficult. Another condition is Bronchiolitis, often caused by viral infections in infants, leading to inflammation and obstruction of the bronchioles. Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD), which includes chronic bronchitis and emphysema, also affects the bronchioles and alveoli, leading to decreased airflow and difficulty breathing.
Treatment and Management[edit | edit source]
Treatment for conditions affecting the bronchioles depends on the underlying cause. In the case of asthma, management often involves the use of inhaled corticosteroids to reduce inflammation and bronchodilators to open the airways. For bronchiolitis, treatment is primarily supportive, including hydration and sometimes oxygen therapy. COPD management may include bronchodilators, corticosteroids, and lifestyle changes such as smoking cessation to slow the progression of the disease.
Search WikiMD
Ad.Tired of being Overweight? Try W8MD's physician weight loss program.
Semaglutide (Ozempic / Wegovy and Tirzepatide (Mounjaro / Zepbound) available.
Advertise on WikiMD
|
WikiMD's Wellness Encyclopedia |
| Let Food Be Thy Medicine Medicine Thy Food - Hippocrates |
Translate this page: - East Asian
中文,
日本,
한국어,
South Asian
हिन्दी,
தமிழ்,
తెలుగు,
Urdu,
ಕನ್ನಡ,
Southeast Asian
Indonesian,
Vietnamese,
Thai,
မြန်မာဘာသာ,
বাংলা
European
español,
Deutsch,
français,
Greek,
português do Brasil,
polski,
română,
русский,
Nederlands,
norsk,
svenska,
suomi,
Italian
Middle Eastern & African
عربى,
Turkish,
Persian,
Hebrew,
Afrikaans,
isiZulu,
Kiswahili,
Other
Bulgarian,
Hungarian,
Czech,
Swedish,
മലയാളം,
मराठी,
ਪੰਜਾਬੀ,
ગુજરાતી,
Portuguese,
Ukrainian
Medical Disclaimer: WikiMD is not a substitute for professional medical advice. The information on WikiMD is provided as an information resource only, may be incorrect, outdated or misleading, and is not to be used or relied on for any diagnostic or treatment purposes. Please consult your health care provider before making any healthcare decisions or for guidance about a specific medical condition. WikiMD expressly disclaims responsibility, and shall have no liability, for any damages, loss, injury, or liability whatsoever suffered as a result of your reliance on the information contained in this site. By visiting this site you agree to the foregoing terms and conditions, which may from time to time be changed or supplemented by WikiMD. If you do not agree to the foregoing terms and conditions, you should not enter or use this site. See full disclaimer.
Credits:Most images are courtesy of Wikimedia commons, and templates, categories Wikipedia, licensed under CC BY SA or similar.
Contributors: Prab R. Tumpati, MD