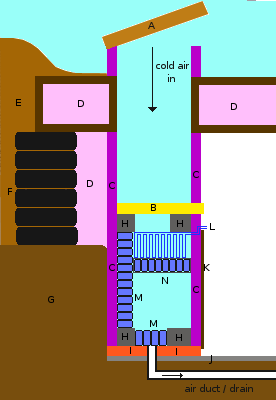
Thermal mass refrigerator
A thermal mass refrigerator is a type of refrigeration system that utilizes the concept of thermal mass to store and release cold energy, allowing for the preservation of food and other perishable items without the need for continuous electrical power. This technology is particularly beneficial in areas with limited or unreliable access to electricity, and it represents a sustainable alternative to traditional refrigeration methods.
Overview[edit | edit source]
The principle behind a thermal mass refrigerator is to use a large mass, often water or a phase-change material, that is capable of absorbing and storing a significant amount of cold energy during periods when electricity is available or when ambient temperatures are naturally low. This stored energy is then used to maintain a cool internal environment within the refrigerator, keeping its contents at a safe and stable temperature even during power outages or periods of high ambient temperatures.
Components and Functioning[edit | edit source]
The key components of a thermal mass refrigerator include:
- The thermal mass itself, which is the core element responsible for storing cold energy.
- An insulation system, which is critical for minimizing thermal exchange between the inside of the refrigerator and the external environment.
- A cooling mechanism, which may involve conventional refrigeration techniques or alternative methods such as evaporative cooling, to initially lower the temperature of the thermal mass.
The functioning of a thermal mass refrigerator involves several steps: 1. **Cooling Phase**: During periods of electricity availability or cooler ambient temperatures, the thermal mass is cooled down using the chosen cooling mechanism. 2. **Storage Phase**: The cold energy is stored within the thermal mass, thanks to the insulating properties of the refrigerator's design. 3. **Release Phase**: When the external temperature rises or when electrical power is not available, the cold energy stored in the thermal mass is gradually released, maintaining a cool internal temperature.
Advantages[edit | edit source]
Thermal mass refrigerators offer several advantages over traditional electric refrigerators, including:
- Reduced dependence on continuous electrical power, making them ideal for off-grid applications or regions with unreliable power supply.
- Potential for lower operational costs, as they can take advantage of off-peak electricity rates or natural cooling sources.
- Enhanced sustainability, by reducing the need for fossil fuel-based power and utilizing natural or recycled materials for thermal mass.
Challenges[edit | edit source]
Despite their benefits, thermal mass refrigerators also face challenges:
- The initial cooling of the thermal mass requires access to a cooling source, which may still involve electricity or other energy inputs.
- The size and weight of the thermal mass can make these refrigerators larger and heavier than conventional models, potentially limiting their applicability in certain settings.
- Achieving optimal performance requires careful design and insulation, which can increase upfront costs.
Applications[edit | edit source]
Thermal mass refrigerators are particularly suited for:
- Remote or off-grid locations where electrical power is scarce or expensive.
- Sustainable living environments aiming to reduce energy consumption and carbon footprint.
- Emergency preparedness, providing a means to preserve food during power outages.
Conclusion[edit | edit source]
While not a universal solution, thermal mass refrigerators offer a promising alternative for sustainable refrigeration in specific contexts. Their ability to leverage thermal mass for energy storage and release can contribute significantly to reducing reliance on continuous electrical power, enhancing food security, and promoting environmental sustainability.
Search WikiMD
Ad.Tired of being Overweight? Try W8MD's physician weight loss program.
Semaglutide (Ozempic / Wegovy and Tirzepatide (Mounjaro / Zepbound) available.
Advertise on WikiMD
|
WikiMD's Wellness Encyclopedia |
| Let Food Be Thy Medicine Medicine Thy Food - Hippocrates |
Translate this page: - East Asian
中文,
日本,
한국어,
South Asian
हिन्दी,
தமிழ்,
తెలుగు,
Urdu,
ಕನ್ನಡ,
Southeast Asian
Indonesian,
Vietnamese,
Thai,
မြန်မာဘာသာ,
বাংলা
European
español,
Deutsch,
français,
Greek,
português do Brasil,
polski,
română,
русский,
Nederlands,
norsk,
svenska,
suomi,
Italian
Middle Eastern & African
عربى,
Turkish,
Persian,
Hebrew,
Afrikaans,
isiZulu,
Kiswahili,
Other
Bulgarian,
Hungarian,
Czech,
Swedish,
മലയാളം,
मराठी,
ਪੰਜਾਬੀ,
ગુજરાતી,
Portuguese,
Ukrainian
Medical Disclaimer: WikiMD is not a substitute for professional medical advice. The information on WikiMD is provided as an information resource only, may be incorrect, outdated or misleading, and is not to be used or relied on for any diagnostic or treatment purposes. Please consult your health care provider before making any healthcare decisions or for guidance about a specific medical condition. WikiMD expressly disclaims responsibility, and shall have no liability, for any damages, loss, injury, or liability whatsoever suffered as a result of your reliance on the information contained in this site. By visiting this site you agree to the foregoing terms and conditions, which may from time to time be changed or supplemented by WikiMD. If you do not agree to the foregoing terms and conditions, you should not enter or use this site. See full disclaimer.
Credits:Most images are courtesy of Wikimedia commons, and templates Wikipedia, licensed under CC BY SA or similar.
Contributors: Prab R. Tumpati, MD