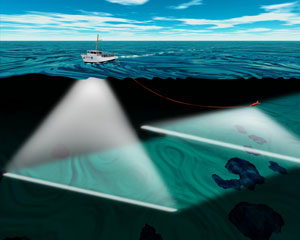
Underwater survey
Underwater survey is a method used to collect data and information about underwater environments. This process is essential for various fields such as marine biology, archaeology, geology, and engineering. Underwater surveys can be conducted using different techniques and equipment, depending on the objectives and the environment being studied.
Techniques[edit | edit source]
Underwater surveys employ a variety of techniques, including:
- Diver-based surveys: Divers equipped with underwater cameras, measuring tools, and other instruments manually collect data. This method is often used for detailed inspections and small-scale surveys.
- Remote sensing: This includes the use of sonar, LiDAR, and satellite imagery to gather data from a distance. These methods are useful for large-scale surveys and areas that are difficult to access.
- ROVs (Remotely Operated Vehicles): These are unmanned, remotely controlled vehicles equipped with cameras and sensors. ROVs are used for deep-water surveys and hazardous environments.
- AUVs (Autonomous Underwater Vehicles): These are robotic vehicles that operate independently, following pre-programmed paths to collect data. AUVs are used for extensive and repetitive surveys.
Applications[edit | edit source]
Underwater surveys have a wide range of applications, including:
- Marine biology: Studying marine ecosystems, habitats, and species distribution.
- Archaeology: Locating and documenting underwater cultural heritage sites such as shipwrecks and submerged settlements.
- Geology: Mapping the seafloor, studying underwater geological formations, and assessing natural hazards like underwater landslides.
- Engineering: Inspecting underwater infrastructure such as pipelines, cables, and offshore platforms.
Equipment[edit | edit source]
The equipment used in underwater surveys varies based on the technique and the specific requirements of the survey. Common equipment includes:
- Sonar systems: Used for mapping the seafloor and detecting objects underwater.
- Underwater cameras: High-resolution cameras for capturing images and videos.
- GPS and navigation systems: Essential for accurate positioning and mapping.
- Diving gear: For diver-based surveys, including scuba gear and underwater communication devices.
Challenges[edit | edit source]
Conducting underwater surveys presents several challenges, such as:
- Visibility: Poor visibility due to water turbidity can hinder data collection.
- Depth: Deep-water surveys require specialized equipment and techniques.
- Environmental conditions: Currents, waves, and weather conditions can affect the survey process.
- Safety: Ensuring the safety of divers and equipment in hazardous environments.
Related Pages[edit | edit source]
 This surveying related article is a stub. You can help WikiMD by expanding it.
This surveying related article is a stub. You can help WikiMD by expanding it.
Search WikiMD
Ad.Tired of being Overweight? Try W8MD's physician weight loss program.
Semaglutide (Ozempic / Wegovy and Tirzepatide (Mounjaro / Zepbound) available.
Advertise on WikiMD
|
WikiMD's Wellness Encyclopedia |
| Let Food Be Thy Medicine Medicine Thy Food - Hippocrates |
Translate this page: - East Asian
中文,
日本,
한국어,
South Asian
हिन्दी,
தமிழ்,
తెలుగు,
Urdu,
ಕನ್ನಡ,
Southeast Asian
Indonesian,
Vietnamese,
Thai,
မြန်မာဘာသာ,
বাংলা
European
español,
Deutsch,
français,
Greek,
português do Brasil,
polski,
română,
русский,
Nederlands,
norsk,
svenska,
suomi,
Italian
Middle Eastern & African
عربى,
Turkish,
Persian,
Hebrew,
Afrikaans,
isiZulu,
Kiswahili,
Other
Bulgarian,
Hungarian,
Czech,
Swedish,
മലയാളം,
मराठी,
ਪੰਜਾਬੀ,
ગુજરાતી,
Portuguese,
Ukrainian
Medical Disclaimer: WikiMD is not a substitute for professional medical advice. The information on WikiMD is provided as an information resource only, may be incorrect, outdated or misleading, and is not to be used or relied on for any diagnostic or treatment purposes. Please consult your health care provider before making any healthcare decisions or for guidance about a specific medical condition. WikiMD expressly disclaims responsibility, and shall have no liability, for any damages, loss, injury, or liability whatsoever suffered as a result of your reliance on the information contained in this site. By visiting this site you agree to the foregoing terms and conditions, which may from time to time be changed or supplemented by WikiMD. If you do not agree to the foregoing terms and conditions, you should not enter or use this site. See full disclaimer.
Credits:Most images are courtesy of Wikimedia commons, and templates, categories Wikipedia, licensed under CC BY SA or similar.
Contributors: Prab R. Tumpati, MD