Unsupervised learning
Type of machine learning algorithm
| Machine learning and data mining |
|---|
|
|
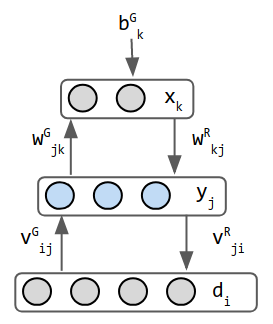
Unsupervised learning is a type of machine learning that involves training a model on data without explicit instructions on what to do with it. The model attempts to learn the underlying structure of the data by identifying patterns and relationships. Unlike supervised learning, where the model is trained on labeled data, unsupervised learning works with unlabeled data.
Overview[edit | edit source]
Unsupervised learning is used to draw inferences from datasets consisting of input data without labeled responses. The most common unsupervised learning tasks are clustering and association.
- Clustering: This involves grouping a set of objects in such a way that objects in the same group (or cluster) are more similar to each other than to those in other groups. K-means clustering and hierarchical clustering are popular clustering algorithms.
- Association: This involves discovering interesting relations between variables in large databases. A common example is market basket analysis, which is used to identify sets of products that frequently co-occur in transactions.
Techniques[edit | edit source]
Several techniques are used in unsupervised learning, including:
- Neural networks: These are computational models inspired by the human brain, consisting of interconnected groups of artificial neurons. They are used in various unsupervised learning tasks.
- Dimensionality reduction: Techniques such as Principal Component Analysis (PCA) and t-distributed Stochastic Neighbor Embedding (t-SNE) are used to reduce the number of random variables under consideration.
- Anomaly detection: This involves identifying rare items, events, or observations that raise suspicions by differing significantly from the majority of the data.
Applications[edit | edit source]
Unsupervised learning is applied in various fields, including:
- Image recognition: Identifying patterns and features in images without prior labeling.
- Genomics: Analyzing genetic data to find patterns and relationships.
- Natural language processing: Understanding and processing human language data.
Related pages[edit | edit source]
Gallery[edit | edit source]
References[edit | edit source]
- Ian,
Deep Learning, MIT Press, 2016, ISBN 978-0262035613,
- LeCun, Yann,
Unsupervised Learning: Foundations of Neural Computation, MIT Press, 1998,
Helmholtz Machine
Search WikiMD
Ad.Tired of being Overweight? Try W8MD's physician weight loss program.
Semaglutide (Ozempic / Wegovy and Tirzepatide (Mounjaro / Zepbound) available.
Advertise on WikiMD
|
WikiMD's Wellness Encyclopedia |
| Let Food Be Thy Medicine Medicine Thy Food - Hippocrates |
Translate this page: - East Asian
中文,
日本,
한국어,
South Asian
हिन्दी,
தமிழ்,
తెలుగు,
Urdu,
ಕನ್ನಡ,
Southeast Asian
Indonesian,
Vietnamese,
Thai,
မြန်မာဘာသာ,
বাংলা
European
español,
Deutsch,
français,
Greek,
português do Brasil,
polski,
română,
русский,
Nederlands,
norsk,
svenska,
suomi,
Italian
Middle Eastern & African
عربى,
Turkish,
Persian,
Hebrew,
Afrikaans,
isiZulu,
Kiswahili,
Other
Bulgarian,
Hungarian,
Czech,
Swedish,
മലയാളം,
मराठी,
ਪੰਜਾਬੀ,
ગુજરાતી,
Portuguese,
Ukrainian
Medical Disclaimer: WikiMD is not a substitute for professional medical advice. The information on WikiMD is provided as an information resource only, may be incorrect, outdated or misleading, and is not to be used or relied on for any diagnostic or treatment purposes. Please consult your health care provider before making any healthcare decisions or for guidance about a specific medical condition. WikiMD expressly disclaims responsibility, and shall have no liability, for any damages, loss, injury, or liability whatsoever suffered as a result of your reliance on the information contained in this site. By visiting this site you agree to the foregoing terms and conditions, which may from time to time be changed or supplemented by WikiMD. If you do not agree to the foregoing terms and conditions, you should not enter or use this site. See full disclaimer.
Credits:Most images are courtesy of Wikimedia commons, and templates, categories Wikipedia, licensed under CC BY SA or similar.
Contributors: Prab R. Tumpati, MD