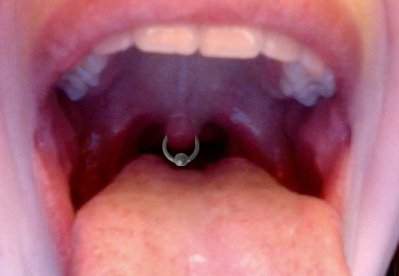
Uvula piercing
Uvula Piercing is a type of body modification that involves the insertion of jewelry through the uvula, the fleshy extension at the back of the soft palate that hangs above the throat. This form of piercing is considered rare and unusual due to the uvula's sensitive nature and the potential risks involved.
Procedure[edit | edit source]
The process of uvula piercing must be carried out by an experienced and professional piercer. It typically involves the use of a sterilized needle to create a hole through the uvula, through which a piece of jewelry is inserted. The most common types of jewelry used for this piercing are small barbells or rings. Due to the uvula's sensitivity and the piercing's proximity to the throat, the procedure can induce a gag reflex, making it more complex than other oral piercings.
Risks and Complications[edit | edit source]
Uvula piercing carries several health risks and potential complications. These include:
- Infection: The mouth is full of bacteria, and despite the uvula's relatively isolated position, there is a risk of infection.
- Swelling: Swelling is a common response to any piercing, but in the case of the uvula, it can potentially interfere with breathing or swallowing.
- Damage: There is a risk of damaging the uvula or surrounding tissues during the piercing process.
- Aspiration: There is a small risk that the jewelry could become dislodged and inhaled into the lungs.
Due to these risks, it is crucial for individuals considering this piercing to consult with professionals and weigh the potential complications against their desire for the piercing.
Aftercare[edit | edit source]
Proper aftercare is vital to minimize the risks associated with uvula piercing. Recommendations include:
- Regularly rinsing the mouth with saline solution or an alcohol-free antimicrobial mouthwash to prevent infection.
- Avoiding spicy or hot foods that can irritate the piercing.
- Not touching or playing with the jewelry to avoid irritation and promote healing.
Cultural and Historical Context[edit | edit source]
Uvula piercing does not have a significant presence in historical or cultural practices compared to other forms of body modification. Its emergence is a relatively recent phenomenon within the body modification community, often seen as a form of self-expression or a way to achieve a unique look.
Legal and Ethical Considerations[edit | edit source]
Given the risks involved, not all countries or regions may have piercers willing or legally able to perform uvula piercings. It is essential to research local laws and regulations regarding body modification before pursuing a uvula piercing.
See Also[edit | edit source]
Search WikiMD
Ad.Tired of being Overweight? Try W8MD's physician weight loss program.
Semaglutide (Ozempic / Wegovy and Tirzepatide (Mounjaro / Zepbound) available.
Advertise on WikiMD
|
WikiMD's Wellness Encyclopedia |
| Let Food Be Thy Medicine Medicine Thy Food - Hippocrates |
Translate this page: - East Asian
中文,
日本,
한국어,
South Asian
हिन्दी,
தமிழ்,
తెలుగు,
Urdu,
ಕನ್ನಡ,
Southeast Asian
Indonesian,
Vietnamese,
Thai,
မြန်မာဘာသာ,
বাংলা
European
español,
Deutsch,
français,
Greek,
português do Brasil,
polski,
română,
русский,
Nederlands,
norsk,
svenska,
suomi,
Italian
Middle Eastern & African
عربى,
Turkish,
Persian,
Hebrew,
Afrikaans,
isiZulu,
Kiswahili,
Other
Bulgarian,
Hungarian,
Czech,
Swedish,
മലയാളം,
मराठी,
ਪੰਜਾਬੀ,
ગુજરાતી,
Portuguese,
Ukrainian
Medical Disclaimer: WikiMD is not a substitute for professional medical advice. The information on WikiMD is provided as an information resource only, may be incorrect, outdated or misleading, and is not to be used or relied on for any diagnostic or treatment purposes. Please consult your health care provider before making any healthcare decisions or for guidance about a specific medical condition. WikiMD expressly disclaims responsibility, and shall have no liability, for any damages, loss, injury, or liability whatsoever suffered as a result of your reliance on the information contained in this site. By visiting this site you agree to the foregoing terms and conditions, which may from time to time be changed or supplemented by WikiMD. If you do not agree to the foregoing terms and conditions, you should not enter or use this site. See full disclaimer.
Credits:Most images are courtesy of Wikimedia commons, and templates, categories Wikipedia, licensed under CC BY SA or similar.
Contributors: Prab R. Tumpati, MD