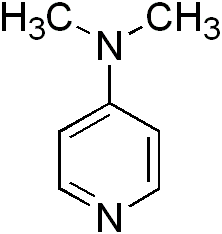
4-dimethylaminopyridine
4-Dimethylaminopyridine (4-DMAP) is a chemical compound that belongs to the class of organic compounds known as pyridines. It is used as a catalyst and a reagent in organic synthesis, particularly in the synthesis of peptides, esters, and amides. 4-DMAP is valued for its ability to increase the speed and efficiency of certain chemical reactions, making it a useful tool in both research and industrial applications.
Properties[edit | edit source]
4-Dimethylaminopyridine is a white crystalline powder with the chemical formula C7H10N2. It has a melting point of 109-112 °C and is soluble in a variety of organic solvents, including ethanol, methanol, and chloroform. Its basicity, attributed to the dimethylamino group attached to the pyridine ring, is a key feature that enables its role as a catalyst in acylation reactions.
Applications[edit | edit source]
The primary application of 4-DMAP is in the field of organic synthesis, where it serves as a powerful catalyst for the formation of amides, esters, and peptide bonds. It is particularly useful in the synthesis of complex molecules due to its ability to promote the activation of carboxylic acids and their derivatives, facilitating their reaction with amines and alcohols.
Peptide Synthesis[edit | edit source]
In peptide synthesis, 4-DMAP is used to enhance the coupling of amino acids, a critical step in the formation of peptide chains. Its efficiency in catalyzing the formation of peptide bonds makes it a valuable tool in the production of both simple and complex peptides.
Esterification and Amidation[edit | edit source]
4-DMAP is also widely used in the esterification and amidation reactions, where it acts as a catalyst to promote the formation of esters and amides from acids and alcohols or amines, respectively. This application is crucial in the synthesis of a wide range of organic compounds, including pharmaceuticals, agrochemicals, and polymers.
Safety and Handling[edit | edit source]
While 4-DMAP is a useful catalyst in organic synthesis, it must be handled with care due to its toxic and irritant properties. It can cause skin, eye, and respiratory irritation, and appropriate safety measures, including the use of personal protective equipment (PPE), should be taken when handling this chemical.
Environmental Impact[edit | edit source]
The environmental impact of 4-DMAP is not well-documented, but as with many chemical compounds, care should be taken to prevent its release into the environment. Proper disposal methods should be followed to minimize its potential impact on ecosystems.
Search WikiMD
Ad.Tired of being Overweight? Try W8MD's physician weight loss program.
Semaglutide (Ozempic / Wegovy and Tirzepatide (Mounjaro / Zepbound) available.
Advertise on WikiMD
|
WikiMD's Wellness Encyclopedia |
| Let Food Be Thy Medicine Medicine Thy Food - Hippocrates |
Translate this page: - East Asian
中文,
日本,
한국어,
South Asian
हिन्दी,
தமிழ்,
తెలుగు,
Urdu,
ಕನ್ನಡ,
Southeast Asian
Indonesian,
Vietnamese,
Thai,
မြန်မာဘာသာ,
বাংলা
European
español,
Deutsch,
français,
Greek,
português do Brasil,
polski,
română,
русский,
Nederlands,
norsk,
svenska,
suomi,
Italian
Middle Eastern & African
عربى,
Turkish,
Persian,
Hebrew,
Afrikaans,
isiZulu,
Kiswahili,
Other
Bulgarian,
Hungarian,
Czech,
Swedish,
മലയാളം,
मराठी,
ਪੰਜਾਬੀ,
ગુજરાતી,
Portuguese,
Ukrainian
Medical Disclaimer: WikiMD is not a substitute for professional medical advice. The information on WikiMD is provided as an information resource only, may be incorrect, outdated or misleading, and is not to be used or relied on for any diagnostic or treatment purposes. Please consult your health care provider before making any healthcare decisions or for guidance about a specific medical condition. WikiMD expressly disclaims responsibility, and shall have no liability, for any damages, loss, injury, or liability whatsoever suffered as a result of your reliance on the information contained in this site. By visiting this site you agree to the foregoing terms and conditions, which may from time to time be changed or supplemented by WikiMD. If you do not agree to the foregoing terms and conditions, you should not enter or use this site. See full disclaimer.
Credits:Most images are courtesy of Wikimedia commons, and templates Wikipedia, licensed under CC BY SA or similar.
Contributors: Prab R. Tumpati, MD