ALPSA lesion
| ALPSA lesion | |
|---|---|
[[File: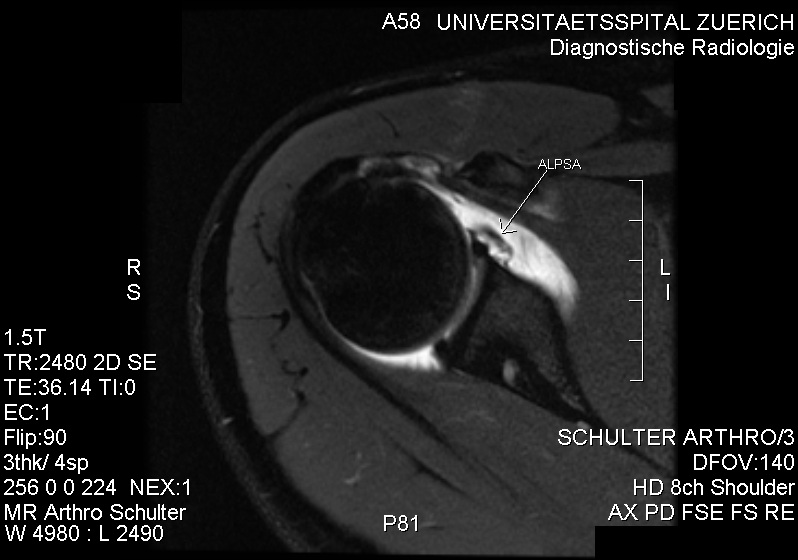 |250px|alt=|MRI showing an ALPSA lesion]] |250px|alt=|MRI showing an ALPSA lesion]]
| |
| Synonyms | Anterior Labroligamentous Periosteal Sleeve Avulsion |
| Pronounce | N/A |
| Field | N/A |
| Symptoms | Shoulder instability, pain |
| Complications | Recurrent shoulder dislocation |
| Onset | Often after shoulder trauma |
| Duration | Chronic if untreated |
| Types | N/A |
| Causes | Shoulder dislocation, trauma |
| Risks | Contact sports, previous shoulder injuries |
| Diagnosis | MRI, arthroscopy |
| Differential diagnosis | Bankart lesion, Hill-Sachs lesion |
| Prevention | N/A |
| Treatment | Physical therapy, arthroscopic surgery |
| Medication | N/A |
| Prognosis | Good with treatment |
| Frequency | Common in athletes |
| Deaths | N/A |
An ALPSA lesion (Anterior Labroligamentous Periosteal Sleeve Avulsion) is a specific type of shoulder injury that involves the detachment of the anterior labrum from the glenoid rim, with the periosteum remaining intact. This condition is often associated with shoulder dislocation and can lead to shoulder instability.
Anatomy and Pathophysiology[edit | edit source]
The shoulder joint is a complex structure that allows for a wide range of motion. It is stabilized by the glenoid labrum, a fibrocartilaginous rim attached to the margin of the glenoid cavity. In an ALPSA lesion, the anterior labrum is avulsed from the glenoid, but the periosteum remains attached, allowing the labrum to displace medially and inferiorly. This displacement can compromise the stability of the shoulder joint, leading to recurrent dislocations.
Clinical Presentation[edit | edit source]
Patients with an ALPSA lesion typically present with symptoms of shoulder instability, such as a feeling of the shoulder "slipping" or "giving way," especially during activities that involve overhead motion. There may also be pain, particularly with movements that stress the anterior shoulder structures.
Diagnosis[edit | edit source]
Diagnosis of an ALPSA lesion is primarily made through imaging studies. Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) is the preferred modality as it provides detailed images of the soft tissues, including the labrum and periosteum. The MRI image of an ALPSA lesion shows the characteristic medial and inferior displacement of the labrum.
Treatment[edit | edit source]
The treatment of an ALPSA lesion depends on the severity of the instability and the patient's activity level. Conservative management may include physical therapy to strengthen the rotator cuff muscles and improve shoulder stability. However, surgical intervention is often required to reattach the labrum to the glenoid and restore normal anatomy. Arthroscopic surgery is commonly performed, where anchors and sutures are used to secure the labrum back to the bone.
Prognosis[edit | edit source]
With appropriate treatment, the prognosis for patients with an ALPSA lesion is generally good. Surgical repair typically results in a stable shoulder with a low risk of recurrent dislocation. Rehabilitation plays a crucial role in recovery, focusing on restoring range of motion and strengthening the shoulder muscles.
Related Pages[edit | edit source]
Search WikiMD
Ad.Tired of being Overweight? Try W8MD's physician weight loss program.
Semaglutide (Ozempic / Wegovy and Tirzepatide (Mounjaro / Zepbound) available.
Advertise on WikiMD
|
WikiMD's Wellness Encyclopedia |
| Let Food Be Thy Medicine Medicine Thy Food - Hippocrates |
Translate this page: - East Asian
中文,
日本,
한국어,
South Asian
हिन्दी,
தமிழ்,
తెలుగు,
Urdu,
ಕನ್ನಡ,
Southeast Asian
Indonesian,
Vietnamese,
Thai,
မြန်မာဘာသာ,
বাংলা
European
español,
Deutsch,
français,
Greek,
português do Brasil,
polski,
română,
русский,
Nederlands,
norsk,
svenska,
suomi,
Italian
Middle Eastern & African
عربى,
Turkish,
Persian,
Hebrew,
Afrikaans,
isiZulu,
Kiswahili,
Other
Bulgarian,
Hungarian,
Czech,
Swedish,
മലയാളം,
मराठी,
ਪੰਜਾਬੀ,
ગુજરાતી,
Portuguese,
Ukrainian
Medical Disclaimer: WikiMD is not a substitute for professional medical advice. The information on WikiMD is provided as an information resource only, may be incorrect, outdated or misleading, and is not to be used or relied on for any diagnostic or treatment purposes. Please consult your health care provider before making any healthcare decisions or for guidance about a specific medical condition. WikiMD expressly disclaims responsibility, and shall have no liability, for any damages, loss, injury, or liability whatsoever suffered as a result of your reliance on the information contained in this site. By visiting this site you agree to the foregoing terms and conditions, which may from time to time be changed or supplemented by WikiMD. If you do not agree to the foregoing terms and conditions, you should not enter or use this site. See full disclaimer.
Credits:Most images are courtesy of Wikimedia commons, and templates, categories Wikipedia, licensed under CC BY SA or similar.
Contributors: Prab R. Tumpati, MD, Prabhudeva
