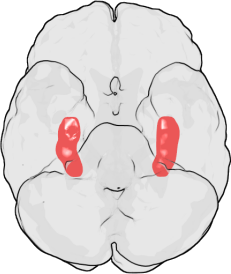
Amygdalohippocampectomy
Surgical procedure involving the removal of the amygdala and hippocampus
Amygdalohippocampectomy[edit | edit source]
Amygdalohippocampectomy is a surgical procedure that involves the removal of the amygdala and the hippocampus, two critical structures located in the temporal lobe of the brain. This procedure is primarily performed to treat certain types of epilepsy, particularly temporal lobe epilepsy, when seizures are not controlled by medication.
Anatomy and Function[edit | edit source]
The amygdala is an almond-shaped set of neurons located deep within the temporal lobe. It is involved in the processing of emotions such as fear, anger, and pleasure. The hippocampus, on the other hand, is a seahorse-shaped structure that plays a crucial role in the formation of new memories and is also associated with learning and emotions.
Indications[edit | edit source]
Amygdalohippocampectomy is indicated in patients with drug-resistant temporal lobe epilepsy. This type of epilepsy is characterized by seizures that originate in the temporal lobe and are often associated with mesial temporal sclerosis, a condition where there is scarring in the inner part of the temporal lobe.
Procedure[edit | edit source]
The procedure is typically performed under general anesthesia. A neurosurgeon makes an incision in the scalp and removes a portion of the skull to access the brain. Using advanced imaging techniques, the surgeon identifies the amygdala and hippocampus and carefully removes them while preserving surrounding brain tissue. The goal is to eliminate the seizure focus while minimizing damage to critical brain functions.
Outcomes[edit | edit source]
The success of an amygdalohippocampectomy is measured by the reduction or elimination of seizures. Many patients experience significant improvement in seizure control, and some may become seizure-free. However, the procedure carries risks, including memory impairment, changes in emotional processing, and other cognitive effects due to the removal of these important brain structures.
Complications[edit | edit source]
Potential complications of the surgery include infection, bleeding, and neurological deficits. Memory problems are a common concern, as the hippocampus is integral to memory formation. Emotional changes may also occur due to the removal of the amygdala.
Related pages[edit | edit source]
Search WikiMD
Ad.Tired of being Overweight? Try W8MD's physician weight loss program.
Semaglutide (Ozempic / Wegovy and Tirzepatide (Mounjaro / Zepbound) available.
Advertise on WikiMD
|
WikiMD's Wellness Encyclopedia |
| Let Food Be Thy Medicine Medicine Thy Food - Hippocrates |
Translate this page: - East Asian
中文,
日本,
한국어,
South Asian
हिन्दी,
தமிழ்,
తెలుగు,
Urdu,
ಕನ್ನಡ,
Southeast Asian
Indonesian,
Vietnamese,
Thai,
မြန်မာဘာသာ,
বাংলা
European
español,
Deutsch,
français,
Greek,
português do Brasil,
polski,
română,
русский,
Nederlands,
norsk,
svenska,
suomi,
Italian
Middle Eastern & African
عربى,
Turkish,
Persian,
Hebrew,
Afrikaans,
isiZulu,
Kiswahili,
Other
Bulgarian,
Hungarian,
Czech,
Swedish,
മലയാളം,
मराठी,
ਪੰਜਾਬੀ,
ગુજરાતી,
Portuguese,
Ukrainian
Medical Disclaimer: WikiMD is not a substitute for professional medical advice. The information on WikiMD is provided as an information resource only, may be incorrect, outdated or misleading, and is not to be used or relied on for any diagnostic or treatment purposes. Please consult your health care provider before making any healthcare decisions or for guidance about a specific medical condition. WikiMD expressly disclaims responsibility, and shall have no liability, for any damages, loss, injury, or liability whatsoever suffered as a result of your reliance on the information contained in this site. By visiting this site you agree to the foregoing terms and conditions, which may from time to time be changed or supplemented by WikiMD. If you do not agree to the foregoing terms and conditions, you should not enter or use this site. See full disclaimer.
Credits:Most images are courtesy of Wikimedia commons, and templates, categories Wikipedia, licensed under CC BY SA or similar.
Contributors: Prab R. Tumpati, MD