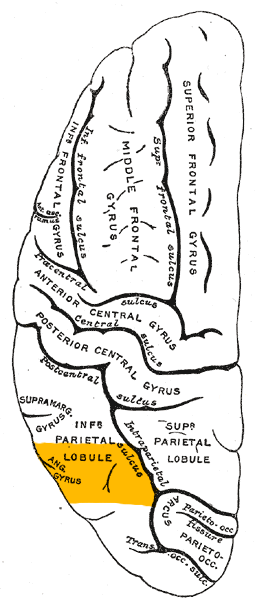
Angular gyrus
The angular gyrus is a region of the brain located in the parietal lobe. It lies near the superior edge of the temporal lobe, immediately posterior to the supramarginal gyrus. The angular gyrus is involved in a number of processes related to language, number processing, spatial cognition, memory retrieval, attention, and theory of mind.
Anatomy[edit | edit source]
The angular gyrus is part of the parietal lobe and is situated at the posterior end of the sylvian fissure. It is bounded anteriorly by the supramarginal gyrus, inferiorly by the superior temporal gyrus, and posteriorly by the occipital lobe. The angular gyrus is supplied by the middle cerebral artery.
Functions[edit | edit source]
The angular gyrus plays a crucial role in various cognitive functions. It is involved in:
- Language processing: The angular gyrus is essential for the comprehension of written language. It is involved in the process of reading and converting written words into an internal monologue.
- Number processing: This region is also implicated in arithmetic and number comprehension.
- Spatial cognition: The angular gyrus helps in understanding spatial relationships and in the perception of spatial orientation.
- Memory retrieval: It is involved in the retrieval of episodic memories.
- Attention: The angular gyrus contributes to the allocation of attention to different stimuli.
- Theory of mind: This region is associated with the ability to understand the mental states of others.
Clinical significance[edit | edit source]
Damage to the angular gyrus can result in various neurological conditions, including:
- Gerstmann syndrome: A neurological disorder characterized by agraphia, acalculia, finger agnosia, and left-right disorientation.
- Alexia: The inability to read, often due to damage in the angular gyrus.
- Agraphia: The inability to write, which can also be associated with damage to this region.
Related pages[edit | edit source]
- Parietal lobe
- Supramarginal gyrus
- Superior temporal gyrus
- Occipital lobe
- Middle cerebral artery
- Gerstmann syndrome
- Alexia
- Agraphia
This article is a neuroanatomy stub. You can help WikiMD by expanding it!
Search WikiMD
Ad.Tired of being Overweight? Try W8MD's physician weight loss program.
Semaglutide (Ozempic / Wegovy and Tirzepatide (Mounjaro / Zepbound) available.
Advertise on WikiMD
|
WikiMD's Wellness Encyclopedia |
| Let Food Be Thy Medicine Medicine Thy Food - Hippocrates |
Translate this page: - East Asian
中文,
日本,
한국어,
South Asian
हिन्दी,
தமிழ்,
తెలుగు,
Urdu,
ಕನ್ನಡ,
Southeast Asian
Indonesian,
Vietnamese,
Thai,
မြန်မာဘာသာ,
বাংলা
European
español,
Deutsch,
français,
Greek,
português do Brasil,
polski,
română,
русский,
Nederlands,
norsk,
svenska,
suomi,
Italian
Middle Eastern & African
عربى,
Turkish,
Persian,
Hebrew,
Afrikaans,
isiZulu,
Kiswahili,
Other
Bulgarian,
Hungarian,
Czech,
Swedish,
മലയാളം,
मराठी,
ਪੰਜਾਬੀ,
ગુજરાતી,
Portuguese,
Ukrainian
Medical Disclaimer: WikiMD is not a substitute for professional medical advice. The information on WikiMD is provided as an information resource only, may be incorrect, outdated or misleading, and is not to be used or relied on for any diagnostic or treatment purposes. Please consult your health care provider before making any healthcare decisions or for guidance about a specific medical condition. WikiMD expressly disclaims responsibility, and shall have no liability, for any damages, loss, injury, or liability whatsoever suffered as a result of your reliance on the information contained in this site. By visiting this site you agree to the foregoing terms and conditions, which may from time to time be changed or supplemented by WikiMD. If you do not agree to the foregoing terms and conditions, you should not enter or use this site. See full disclaimer.
Credits:Most images are courtesy of Wikimedia commons, and templates, categories Wikipedia, licensed under CC BY SA or similar.
Contributors: Kondreddy Naveen