Autobiographical memory
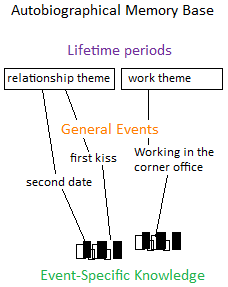
Autobiographical memory refers to a type of memory system that consists of episodes recollected from an individual's life, based on a combination of episodic (memory of events) and semantic (general knowledge and facts about the world) memory. These memories are distinctive because they relate to the self and include contextual details such as when and where an event occurred, along with emotional and sensory experiences. Autobiographical memory plays a crucial role in the development of personal identity, allowing individuals to construct a narrative of their life.
Characteristics[edit | edit source]
Autobiographical memories are complex and multifaceted. They are not just mere recollections of past events but are imbued with personal significance and emotional depth. These memories can be triggered spontaneously or through intentional recall efforts. The vividness and accuracy of autobiographical memories can vary greatly, influenced by factors such as the emotional intensity of the event, the passage of time, and cognitive processes like rehearsal and reconstruction.
Formation and Retrieval[edit | edit source]
The formation of autobiographical memories is a dynamic process that involves encoding, storage, and retrieval. During encoding, sensory information and emotional experiences associated with an event are integrated with existing knowledge and stored in the brain. Over time, the specifics of a memory may fade, but the gist or the emotional essence often remains. Retrieval of autobiographical memories can be influenced by cues in the environment, current mood, and the relevance of the memory to the self.
The Role of the Brain[edit | edit source]
Research in neuroscience has identified several brain regions involved in the processing of autobiographical memories, including the hippocampus, prefrontal cortex, and amygdala. The hippocampus is crucial for the encoding and retrieval of episodic details, while the prefrontal cortex is involved in organizing and integrating the components of autobiographical memories. The amygdala plays a key role in processing emotional aspects of these memories.
Functions[edit | edit source]
Autobiographical memory serves several important functions. It helps individuals make sense of their past, understand their identity, and navigate social relationships. These memories also play a role in guiding future behavior and decision-making, allowing individuals to learn from past experiences. Furthermore, sharing autobiographical memories can foster intimacy and social bonds.
Development[edit | edit source]
The development of autobiographical memory in children is closely linked to language acquisition and the understanding of self. Young children's autobiographical memories are often fragmented and lack coherence, but as they grow older and their cognitive and linguistic abilities mature, they begin to construct more complex and detailed narratives of their past experiences.
Memory Distortions[edit | edit source]
Autobiographical memories are susceptible to distortions and inaccuracies. Factors such as misinformation, bias, and the reconstructive nature of memory can lead to changes in how a memory is recalled. People may also unconsciously alter their memories to fit their current beliefs or attitudes.
Clinical Relevance[edit | edit source]
Autobiographical memory has implications for mental health. Disorders such as depression and post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD) can affect how autobiographical memories are processed and recalled. For instance, individuals with depression may recall negative memories more readily than positive ones, while those with PTSD may experience intrusive and distressing recollections of traumatic events.
Conclusion[edit | edit source]
Autobiographical memory is a fundamental aspect of human cognition, intricately linked to the sense of self and personal history. It encompasses the rich and varied tapestry of personal experiences that define an individual's life story. Understanding the mechanisms and functions of autobiographical memory not only sheds light on how people remember their past but also provides insights into the nature of memory itself.
This article is a psychology-related stub. You can help WikiMD by expanding it!
Search WikiMD
Ad.Tired of being Overweight? Try W8MD's physician weight loss program.
Semaglutide (Ozempic / Wegovy and Tirzepatide (Mounjaro / Zepbound) available.
Advertise on WikiMD
|
WikiMD's Wellness Encyclopedia |
| Let Food Be Thy Medicine Medicine Thy Food - Hippocrates |
Translate this page: - East Asian
中文,
日本,
한국어,
South Asian
हिन्दी,
தமிழ்,
తెలుగు,
Urdu,
ಕನ್ನಡ,
Southeast Asian
Indonesian,
Vietnamese,
Thai,
မြန်မာဘာသာ,
বাংলা
European
español,
Deutsch,
français,
Greek,
português do Brasil,
polski,
română,
русский,
Nederlands,
norsk,
svenska,
suomi,
Italian
Middle Eastern & African
عربى,
Turkish,
Persian,
Hebrew,
Afrikaans,
isiZulu,
Kiswahili,
Other
Bulgarian,
Hungarian,
Czech,
Swedish,
മലയാളം,
मराठी,
ਪੰਜਾਬੀ,
ગુજરાતી,
Portuguese,
Ukrainian
Medical Disclaimer: WikiMD is not a substitute for professional medical advice. The information on WikiMD is provided as an information resource only, may be incorrect, outdated or misleading, and is not to be used or relied on for any diagnostic or treatment purposes. Please consult your health care provider before making any healthcare decisions or for guidance about a specific medical condition. WikiMD expressly disclaims responsibility, and shall have no liability, for any damages, loss, injury, or liability whatsoever suffered as a result of your reliance on the information contained in this site. By visiting this site you agree to the foregoing terms and conditions, which may from time to time be changed or supplemented by WikiMD. If you do not agree to the foregoing terms and conditions, you should not enter or use this site. See full disclaimer.
Credits:Most images are courtesy of Wikimedia commons, and templates, categories Wikipedia, licensed under CC BY SA or similar.
Contributors: Prab R. Tumpati, MD