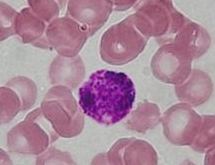
Basophilic
Basophilic refers to the affinity of cellular structures for basic dyes in histological staining. This property is indicative of the presence of nucleic acids and other acidic substances within cells that bind to basic (alkaline) dyes. Basophilic structures are crucial in various biological and medical contexts, particularly in the study of blood cells, tissue samples, and the identification of cellular components under a microscope.
Overview[edit | edit source]
In histology, the term "basophilic" is used to describe cells or structures within cells that stain readily with basic dyes. This staining property is due to the presence of phosphate groups in the cellular components, which have a negative charge and attract the positively charged basic dyes. The most common basic dye used in histology is hematoxylin, which stains basophilic structures a deep blue or purple color. This contrasts with "eosinophilic" or "acidophilic" structures, which stain with acidic dyes such as eosin.
Basophilic Structures[edit | edit source]
Several key cellular components are basophilic, including:
- Nucleus: The nucleus is highly basophilic due to its rich content of DNA and RNA, which contain phosphate groups. This makes the nucleus one of the most prominently stained parts of a cell in histological sections. - Ribosomes and Rough ER: Ribosomes, whether free in the cytoplasm or attached to the rough ER, are basophilic because of their RNA content. This gives the cytoplasm of cells with high protein synthesis activity, such as plasma cells, a basophilic appearance. - Nucleolus: The nucleolus, found within the nucleus, is particularly basophilic due to its function in ribosome synthesis, involving high concentrations of RNA.
Clinical Significance[edit | edit source]
In clinical medicine, the basophilic staining properties of cells and tissues can aid in diagnosis. For example:
- Leukemia: Certain types of leukemia can be identified by the presence of abnormal, basophilic blast cells in the blood or bone marrow. - Infectious diseases: The identification of basophilic inclusion bodies within cells can be a hallmark of specific viral infections. - Anemia: Basophilic stippling of red blood cells can indicate certain types of anemia or lead poisoning.
Basophils[edit | edit source]
While the term "basophilic" refers broadly to the staining properties of cells and structures, it is also specifically associated with basophils, a type of white blood cell. Basophils are characterized by their basophilic granules, which contain histamine and heparin, and play a role in immune responses, particularly allergic reactions and parasitic infections.
Conclusion[edit | edit source]
Understanding the basophilic properties of cells and tissues is fundamental in histology, providing insights into cellular composition, function, and pathology. The ability to distinguish basophilic structures under the microscope is a key skill in the diagnosis and study of diseases.
Search WikiMD
Ad.Tired of being Overweight? Try W8MD's physician weight loss program.
Semaglutide (Ozempic / Wegovy and Tirzepatide (Mounjaro / Zepbound) available.
Advertise on WikiMD
|
WikiMD's Wellness Encyclopedia |
| Let Food Be Thy Medicine Medicine Thy Food - Hippocrates |
Translate this page: - East Asian
中文,
日本,
한국어,
South Asian
हिन्दी,
தமிழ்,
తెలుగు,
Urdu,
ಕನ್ನಡ,
Southeast Asian
Indonesian,
Vietnamese,
Thai,
မြန်မာဘာသာ,
বাংলা
European
español,
Deutsch,
français,
Greek,
português do Brasil,
polski,
română,
русский,
Nederlands,
norsk,
svenska,
suomi,
Italian
Middle Eastern & African
عربى,
Turkish,
Persian,
Hebrew,
Afrikaans,
isiZulu,
Kiswahili,
Other
Bulgarian,
Hungarian,
Czech,
Swedish,
മലയാളം,
मराठी,
ਪੰਜਾਬੀ,
ગુજરાતી,
Portuguese,
Ukrainian
Medical Disclaimer: WikiMD is not a substitute for professional medical advice. The information on WikiMD is provided as an information resource only, may be incorrect, outdated or misleading, and is not to be used or relied on for any diagnostic or treatment purposes. Please consult your health care provider before making any healthcare decisions or for guidance about a specific medical condition. WikiMD expressly disclaims responsibility, and shall have no liability, for any damages, loss, injury, or liability whatsoever suffered as a result of your reliance on the information contained in this site. By visiting this site you agree to the foregoing terms and conditions, which may from time to time be changed or supplemented by WikiMD. If you do not agree to the foregoing terms and conditions, you should not enter or use this site. See full disclaimer.
Credits:Most images are courtesy of Wikimedia commons, and templates, categories Wikipedia, licensed under CC BY SA or similar.
Contributors: Prab R. Tumpati, MD