Bearing (mechanical)
Bearing (mechanical)
A bearing is a machine element that constrains relative motion to only the desired motion and reduces friction between moving parts. The design of the bearing may, for example, provide for free linear movement of the moving part or for free rotation around a fixed axis; it may also prevent a motion by controlling the vectors of normal forces that bear on the moving parts.
Types of Bearings[edit | edit source]
Bearings are classified broadly according to the type of operation, the motions allowed, or to the directions of the loads (forces) applied to the parts. The most common types include:
Plain Bearings[edit | edit source]
Plain bearings, also known as bushings, journal bearings, or sleeve bearings, are the simplest type of bearing, comprising just a bearing surface and no rolling elements. They are used in a wide variety of applications.
Rolling-Element Bearings[edit | edit source]
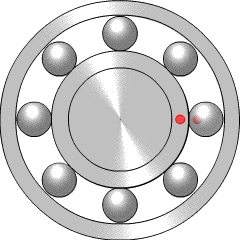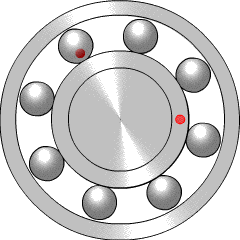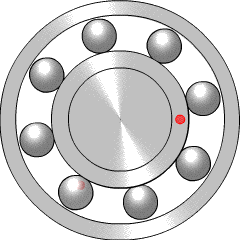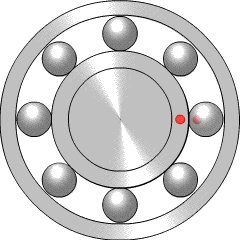
Rolling-element bearings, such as ball bearings and roller bearings, use rolling elements placed between the races, or journals, of the bearing assembly. The rolling elements can be balls, cylindrical rollers, spherical rollers, tapered rollers, or needle rollers.
Jewel Bearings[edit | edit source]
Jewel bearings are plain bearings in which a metal spindle turns in a jewel-lined pivot hole. They are used in precision instruments, such as watches, because they have very low and predictable friction.
Fluid Bearings[edit | edit source]
Fluid bearings are bearings that support their loads solely on a thin layer of liquid or gas. They are used in high-speed applications where ordinary ball bearings would have a short life or cause too much noise.
Magnetic Bearings[edit | edit source]
Magnetic bearings support moving parts without physical contact. They are used in applications where very high speeds or very low friction are required.
Flexure Bearings[edit | edit source]
Flexure bearings are designed to allow motion by bending a load element. They are used in applications requiring precise positioning and low friction.
Applications[edit | edit source]
Bearings are used in a wide range of applications, from household appliances to industrial machinery. Some common applications include:
Maintenance[edit | edit source]
Proper maintenance of bearings is crucial for the longevity and performance of machinery. This includes regular lubrication, cleaning, and inspection for wear and damage.
Related Pages[edit | edit source]
Search WikiMD
Ad.Tired of being Overweight? Try W8MD's physician weight loss program.
Semaglutide (Ozempic / Wegovy and Tirzepatide (Mounjaro / Zepbound) available.
Advertise on WikiMD
|
WikiMD's Wellness Encyclopedia |
| Let Food Be Thy Medicine Medicine Thy Food - Hippocrates |
Translate this page: - East Asian
中文,
日本,
한국어,
South Asian
हिन्दी,
தமிழ்,
తెలుగు,
Urdu,
ಕನ್ನಡ,
Southeast Asian
Indonesian,
Vietnamese,
Thai,
မြန်မာဘာသာ,
বাংলা
European
español,
Deutsch,
français,
Greek,
português do Brasil,
polski,
română,
русский,
Nederlands,
norsk,
svenska,
suomi,
Italian
Middle Eastern & African
عربى,
Turkish,
Persian,
Hebrew,
Afrikaans,
isiZulu,
Kiswahili,
Other
Bulgarian,
Hungarian,
Czech,
Swedish,
മലയാളം,
मराठी,
ਪੰਜਾਬੀ,
ગુજરાતી,
Portuguese,
Ukrainian
Medical Disclaimer: WikiMD is not a substitute for professional medical advice. The information on WikiMD is provided as an information resource only, may be incorrect, outdated or misleading, and is not to be used or relied on for any diagnostic or treatment purposes. Please consult your health care provider before making any healthcare decisions or for guidance about a specific medical condition. WikiMD expressly disclaims responsibility, and shall have no liability, for any damages, loss, injury, or liability whatsoever suffered as a result of your reliance on the information contained in this site. By visiting this site you agree to the foregoing terms and conditions, which may from time to time be changed or supplemented by WikiMD. If you do not agree to the foregoing terms and conditions, you should not enter or use this site. See full disclaimer.
Credits:Most images are courtesy of Wikimedia commons, and templates, categories Wikipedia, licensed under CC BY SA or similar.
Contributors: Prab R. Tumpati, MD