Benign paroxysmal positional vertigo
(Redirected from Benign positional vertigo)
Editor-In-Chief: Prab R Tumpati, MD
Obesity, Sleep & Internal medicine
Founder, WikiMD Wellnesspedia &
W8MD medical weight loss NYC and sleep center NYC
| Benign paroxysmal positional vertigo | |
|---|---|
| |
| Synonyms | BPPV, Benign positional vertigo |
| Pronounce | N/A |
| Specialty | N/A |
| Symptoms | Vertigo, nausea, vomiting, nystagmus |
| Complications | N/A |
| Onset | Sudden |
| Duration | Episodes last seconds to minutes |
| Types | N/A |
| Causes | Calcium crystals in the inner ear |
| Risks | Head injury, ear surgery, prolonged bed rest |
| Diagnosis | Dix–Hallpike test, supine roll test |
| Differential diagnosis | Meniere's disease, vestibular neuritis, migraine-associated vertigo |
| Prevention | N/A |
| Treatment | Epley maneuver, Semont maneuver, Brandt-Daroff exercises |
| Medication | N/A |
| Prognosis | N/A |
| Frequency | 2.4% of people at some point in their life |
| Deaths | N/A |
Benign Paroxysmal Positional Vertigo (BPPV) is a common inner ear disorder characterized by brief, episodic feelings of vertigo (a spinning sensation), which are triggered by specific changes in the position of the head. It's typically provoked by maneuvers such as turning over in bed, tilting the head upward, or transitioning from lying down to standing.
Symptoms[edit | edit source]
The primary symptom of BPPV is a sensation of spinning or vertigo, which occurs in response to changes in head position. This sensation typically lasts less than a minute but can be quite intense. Accompanying symptoms can include:
- Nausea, often associated with the vertigo
- Unsteadiness or loss of balance, particularly when moving
- Rarely, a sense of faintness or lightheadedness
Causes[edit | edit source]
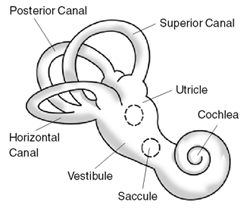
BPPV is caused by displacement of small calcium carbonate crystals, known as otoconia, within the inner ear. These crystals can migrate into the semi-circular canals, where they are not typically found. When the head moves, these crystals shift, resulting in an abnormal sensation of motion.
Diagnosis[edit | edit source]
Diagnosis of BPPV is primarily based on the individual's history of vertigo episodes and the findings of specific physical examination maneuvers, such as the Dix-Hallpike test or the roll test. These tests involve reproducing vertigo and observing characteristic eye movements, known as nystagmus, that accompany the sensation of vertigo in BPPV.
Treatment[edit | edit source]
Treatment for BPPV usually involves a series of physical maneuvers performed by a trained healthcare professional. These maneuvers, such as the Epley or Semont maneuver, aim to move the displaced otoconia out of the semi-circular canals and into an area of the inner ear where they will not cause vertigo. In most cases, these procedures are successful in relieving symptoms. In rare cases where these maneuvers are not effective, surgical treatments may be considered.
Prognosis[edit | edit source]
BPPV generally has a good prognosis. Most people recover with treatment, but some may experience recurrent episodes over time. Regular follow-up with a healthcare provider is recommended for people with BPPV to monitor for recurrence and manage any ongoing symptoms.
References[edit | edit source]
See also[edit | edit source]
Search WikiMD
Ad.Tired of being Overweight? Try W8MD's physician weight loss program.
Semaglutide (Ozempic / Wegovy and Tirzepatide (Mounjaro / Zepbound) available.
Advertise on WikiMD
|
WikiMD's Wellness Encyclopedia |
| Let Food Be Thy Medicine Medicine Thy Food - Hippocrates |
Translate this page: - East Asian
中文,
日本,
한국어,
South Asian
हिन्दी,
தமிழ்,
తెలుగు,
Urdu,
ಕನ್ನಡ,
Southeast Asian
Indonesian,
Vietnamese,
Thai,
မြန်မာဘာသာ,
বাংলা
European
español,
Deutsch,
français,
Greek,
português do Brasil,
polski,
română,
русский,
Nederlands,
norsk,
svenska,
suomi,
Italian
Middle Eastern & African
عربى,
Turkish,
Persian,
Hebrew,
Afrikaans,
isiZulu,
Kiswahili,
Other
Bulgarian,
Hungarian,
Czech,
Swedish,
മലയാളം,
मराठी,
ਪੰਜਾਬੀ,
ગુજરાતી,
Portuguese,
Ukrainian
Medical Disclaimer: WikiMD is not a substitute for professional medical advice. The information on WikiMD is provided as an information resource only, may be incorrect, outdated or misleading, and is not to be used or relied on for any diagnostic or treatment purposes. Please consult your health care provider before making any healthcare decisions or for guidance about a specific medical condition. WikiMD expressly disclaims responsibility, and shall have no liability, for any damages, loss, injury, or liability whatsoever suffered as a result of your reliance on the information contained in this site. By visiting this site you agree to the foregoing terms and conditions, which may from time to time be changed or supplemented by WikiMD. If you do not agree to the foregoing terms and conditions, you should not enter or use this site. See full disclaimer.
Credits:Most images are courtesy of Wikimedia commons, and templates, categories Wikipedia, licensed under CC BY SA or similar.
Contributors: Prab R. Tumpati, MD

