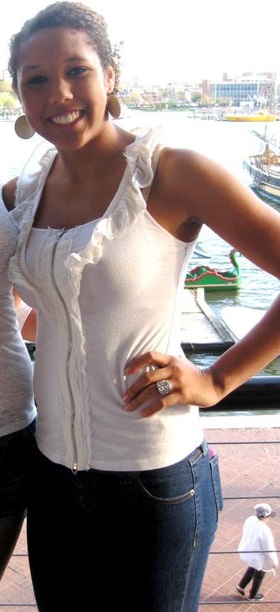Blouse
Blouse is an upper garment that varies in style and fit, traditionally worn by women and girls. The term can also refer to some men's garments of similar appearance, especially in historical contexts and in some modern folk costumes. Blouses are typically made from cotton, silk, or synthetic fibers and may be adorned with embroidery, lace, or other decorative elements. They are a staple in both casual and formal attire, offering versatility in fashion and function.
History[edit | edit source]
The history of the blouse begins in the early 19th century, where it was initially a loose-fitting garment worn by peasants, workers, and artists in Europe. It was considered informal wear and was not part of the high fashion of the time. However, by the late 19th century, the blouse had evolved into a more fashionable garment for women, incorporating various styles, fabrics, and decorations. This evolution continued throughout the 20th century, with the blouse adapting to changes in fashion trends, including the introduction of the Peter Pan collar, puff sleeves, and the peplum waist.
Styles and Variations[edit | edit source]
Blouses come in numerous styles, each with its own distinct characteristics. Some common styles include:
- Button-down blouses: Feature buttons down the front and are often made of cotton or silk.
- Peasant blouses: Characterized by their loose fit, embroidery, and sometimes elasticated or smocked necklines and cuffs.
- Wrap blouses: Cross over the front and tie or button at the side or back, creating a V-neckline.
- Sleeveless blouses: Lack sleeves and are ideal for warm weather or as layering pieces.
Each style serves different aesthetic and practical purposes, making the blouse a versatile component of women's fashion.
Materials[edit | edit source]
Blouses are made from a wide range of materials, each offering different textures, drapes, and levels of formality. Common materials include:
- Cotton: Breathable and comfortable, ideal for casual wear.
- Silk: Luxurious and smooth, often used for formal or evening blouses.
- Polyester and other synthetic fibers: Affordable and easy to care for, with a wide range of textures.
Cultural Significance[edit | edit source]
In many cultures, the blouse has significance beyond its function as clothing. For example, in Indian culture, the sari is traditionally paired with a blouse (choli), which is as much a subject of fashion as the sari itself. The design, cut, and fit of the blouse are integral to the overall look of the sari ensemble.
Modern Trends[edit | edit source]
Today, blouses are a common garment in women's fashion worldwide, with designs that range from the traditional and simple to the modern and complex. They can be dressed up or down, depending on the occasion, and are often paired with skirts, trousers, or jeans. The modern blouse combines elements from its rich history with contemporary fashion trends, making it a timeless piece that evolves with the changing tastes and styles of society.
Search WikiMD
Ad.Tired of being Overweight? Try W8MD's physician weight loss program.
Semaglutide (Ozempic / Wegovy and Tirzepatide (Mounjaro / Zepbound) available.
Advertise on WikiMD
|
WikiMD's Wellness Encyclopedia |
| Let Food Be Thy Medicine Medicine Thy Food - Hippocrates |
Translate this page: - East Asian
中文,
日本,
한국어,
South Asian
हिन्दी,
தமிழ்,
తెలుగు,
Urdu,
ಕನ್ನಡ,
Southeast Asian
Indonesian,
Vietnamese,
Thai,
မြန်မာဘာသာ,
বাংলা
European
español,
Deutsch,
français,
Greek,
português do Brasil,
polski,
română,
русский,
Nederlands,
norsk,
svenska,
suomi,
Italian
Middle Eastern & African
عربى,
Turkish,
Persian,
Hebrew,
Afrikaans,
isiZulu,
Kiswahili,
Other
Bulgarian,
Hungarian,
Czech,
Swedish,
മലയാളം,
मराठी,
ਪੰਜਾਬੀ,
ગુજરાતી,
Portuguese,
Ukrainian
Medical Disclaimer: WikiMD is not a substitute for professional medical advice. The information on WikiMD is provided as an information resource only, may be incorrect, outdated or misleading, and is not to be used or relied on for any diagnostic or treatment purposes. Please consult your health care provider before making any healthcare decisions or for guidance about a specific medical condition. WikiMD expressly disclaims responsibility, and shall have no liability, for any damages, loss, injury, or liability whatsoever suffered as a result of your reliance on the information contained in this site. By visiting this site you agree to the foregoing terms and conditions, which may from time to time be changed or supplemented by WikiMD. If you do not agree to the foregoing terms and conditions, you should not enter or use this site. See full disclaimer.
Credits:Most images are courtesy of Wikimedia commons, and templates, categories Wikipedia, licensed under CC BY SA or similar.
Contributors: Prab R. Tumpati, MD