Congenital cataract
(Redirected from Cataract, total congenital)
Editor-In-Chief: Prab R Tumpati, MD
Obesity, Sleep & Internal medicine
Founder, WikiMD Wellnesspedia &
W8MD medical weight loss NYC and sleep center NYC
| Congenital cataract | |
|---|---|
| |
| Synonyms | N/A |
| Pronounce | N/A |
| Specialty | N/A |
| Symptoms | Cloudy vision, blurred vision, nystagmus, strabismus |
| Complications | Amblyopia, glaucoma, blindness |
| Onset | At birth |
| Duration | Lifelong |
| Types | N/A |
| Causes | Genetic disorders, intrauterine infections, metabolic disorders |
| Risks | Family history, maternal infections during pregnancy |
| Diagnosis | Ophthalmic examination, slit lamp examination, ultrasound |
| Differential diagnosis | Retinoblastoma, persistent fetal vasculature, retinopathy of prematurity |
| Prevention | N/A |
| Treatment | Surgery, corrective lenses, patching therapy |
| Medication | N/A |
| Prognosis | Variable, depends on severity and treatment |
| Frequency | 1-6 per 10,000 live births |
| Deaths | N/A |
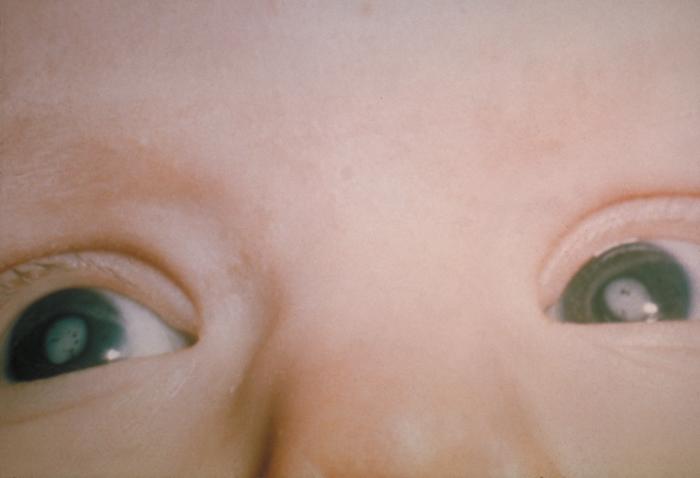
File:Fetal cataract.ogv Congenital cataract is a condition that is present at birth, where the lens of the eye is clouded, causing vision problems. This condition can affect one or both eyes.
Causes[edit | edit source]
Congenital cataracts are often caused by genetic mutations. Other causes can include infections during pregnancy, such as rubella, toxoplasmosis, or cytomegalovirus. Certain metabolic disorders, such as galactosemia, can also cause congenital cataracts.
Symptoms[edit | edit source]
The primary symptom of a congenital cataract is a white or gray cloudiness in the pupil of the eye. This can be present at birth or develop shortly after. Other symptoms can include nystagmus (involuntary eye movements), strabismus (crossed eyes), and vision problems.
Diagnosis[edit | edit source]
Congenital cataracts can be diagnosed through a comprehensive eye exam. This can include a visual acuity test, a dilated eye exam, and tonometry. Genetic testing may also be done to determine if the cataract is due to a genetic mutation.
Treatment[edit | edit source]
Treatment for congenital cataracts often involves surgery to remove the cataract. This is usually followed by the use of glasses or contact lenses to correct vision. In some cases, an artificial lens may be implanted during surgery.
Prognosis[edit | edit source]
The prognosis for congenital cataracts is generally good, especially if the cataract is detected and treated early. However, some children may have permanent vision loss if the cataract is not treated promptly.
See also[edit | edit source]
Search WikiMD
Ad.Tired of being Overweight? Try W8MD's NYC physician weight loss.
Semaglutide (Ozempic / Wegovy and Tirzepatide (Mounjaro / Zepbound) available. Call 718 946 5500.
Advertise on WikiMD
|
WikiMD's Wellness Encyclopedia |
| Let Food Be Thy Medicine Medicine Thy Food - Hippocrates |
Translate this page: - East Asian
中文,
日本,
한국어,
South Asian
हिन्दी,
தமிழ்,
తెలుగు,
Urdu,
ಕನ್ನಡ,
Southeast Asian
Indonesian,
Vietnamese,
Thai,
မြန်မာဘာသာ,
বাংলা
European
español,
Deutsch,
français,
Greek,
português do Brasil,
polski,
română,
русский,
Nederlands,
norsk,
svenska,
suomi,
Italian
Middle Eastern & African
عربى,
Turkish,
Persian,
Hebrew,
Afrikaans,
isiZulu,
Kiswahili,
Other
Bulgarian,
Hungarian,
Czech,
Swedish,
മലയാളം,
मराठी,
ਪੰਜਾਬੀ,
ગુજરાતી,
Portuguese,
Ukrainian
Medical Disclaimer: WikiMD is not a substitute for professional medical advice. The information on WikiMD is provided as an information resource only, may be incorrect, outdated or misleading, and is not to be used or relied on for any diagnostic or treatment purposes. Please consult your health care provider before making any healthcare decisions or for guidance about a specific medical condition. WikiMD expressly disclaims responsibility, and shall have no liability, for any damages, loss, injury, or liability whatsoever suffered as a result of your reliance on the information contained in this site. By visiting this site you agree to the foregoing terms and conditions, which may from time to time be changed or supplemented by WikiMD. If you do not agree to the foregoing terms and conditions, you should not enter or use this site. See full disclaimer.
Credits:Most images are courtesy of Wikimedia commons, and templates, categories Wikipedia, licensed under CC BY SA or similar.
Contributors: Prab R. Tumpati, MD


