Neuropeptide
(Redirected from Dense core vesicle)
Neuropeptide Y[edit | edit source]
Neuropeptide Y (NPY) is a 36-amino acid peptide neurotransmitter found in the brain and autonomic nervous system. It is one of the most abundant neuropeptides in the central nervous system and plays a significant role in various physiological processes, including energy balance, memory, and emotion.
Structure[edit | edit source]
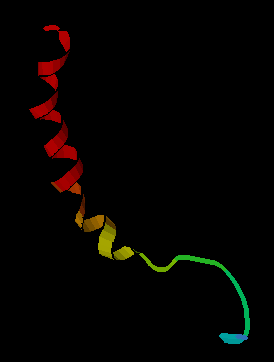
Neuropeptide Y is composed of 36 amino acids and has a highly conserved structure across different species. The peptide is characterized by its ability to form a helical structure, which is crucial for its interaction with receptors. The structure of NPY allows it to bind effectively to its receptors, which are part of the G-protein coupled receptor family.
Function[edit | edit source]
Neuropeptide Y is involved in several key physiological functions:
- Appetite Regulation: NPY is a potent stimulator of food intake. It is released in the hypothalamus, where it promotes feeding behavior and increases energy storage.
- Stress Response: NPY modulates the body's response to stress. It has anxiolytic effects, meaning it can reduce anxiety and stress levels.
- Cardiovascular System: NPY influences cardiovascular function by affecting blood pressure and heart rate.
- Memory and Learning: NPY is involved in the regulation of memory and learning processes. It can enhance memory retention and cognitive function.
Receptors[edit | edit source]
Neuropeptide Y exerts its effects through interaction with specific receptors, known as Y receptors. There are several subtypes of Y receptors, including Y1, Y2, Y4, and Y5, each with distinct functions and tissue distributions. These receptors are G-protein coupled receptors that mediate the physiological actions of NPY.
Clinical Significance[edit | edit source]
Neuropeptide Y has been implicated in various clinical conditions:
- Obesity: Due to its role in appetite regulation, NPY is a target for obesity research. Modulating NPY activity could help in developing treatments for obesity and related metabolic disorders.
- Anxiety and Depression: Alterations in NPY levels have been associated with anxiety and depression. Therapeutic strategies targeting NPY pathways are being explored for these conditions.
- Cardiovascular Diseases: NPY's role in the cardiovascular system makes it a potential target for treating hypertension and other cardiovascular disorders.
Related Pages[edit | edit source]
Search WikiMD
Ad.Tired of being Overweight? Try W8MD's physician weight loss program.
Semaglutide (Ozempic / Wegovy and Tirzepatide (Mounjaro / Zepbound) available.
Advertise on WikiMD
|
WikiMD's Wellness Encyclopedia |
| Let Food Be Thy Medicine Medicine Thy Food - Hippocrates |
Translate this page: - East Asian
中文,
日本,
한국어,
South Asian
हिन्दी,
தமிழ்,
తెలుగు,
Urdu,
ಕನ್ನಡ,
Southeast Asian
Indonesian,
Vietnamese,
Thai,
မြန်မာဘာသာ,
বাংলা
European
español,
Deutsch,
français,
Greek,
português do Brasil,
polski,
română,
русский,
Nederlands,
norsk,
svenska,
suomi,
Italian
Middle Eastern & African
عربى,
Turkish,
Persian,
Hebrew,
Afrikaans,
isiZulu,
Kiswahili,
Other
Bulgarian,
Hungarian,
Czech,
Swedish,
മലയാളം,
मराठी,
ਪੰਜਾਬੀ,
ગુજરાતી,
Portuguese,
Ukrainian
Medical Disclaimer: WikiMD is not a substitute for professional medical advice. The information on WikiMD is provided as an information resource only, may be incorrect, outdated or misleading, and is not to be used or relied on for any diagnostic or treatment purposes. Please consult your health care provider before making any healthcare decisions or for guidance about a specific medical condition. WikiMD expressly disclaims responsibility, and shall have no liability, for any damages, loss, injury, or liability whatsoever suffered as a result of your reliance on the information contained in this site. By visiting this site you agree to the foregoing terms and conditions, which may from time to time be changed or supplemented by WikiMD. If you do not agree to the foregoing terms and conditions, you should not enter or use this site. See full disclaimer.
Credits:Most images are courtesy of Wikimedia commons, and templates, categories Wikipedia, licensed under CC BY SA or similar.
Contributors: Prab R. Tumpati, MD