Diseases of the foot
Overview of diseases affecting the foot
Overview[edit | edit source]
The human foot is a complex structure composed of bones, muscles, tendons, and ligaments, all working together to support the body and enable movement. Diseases of the foot can affect any of these components, leading to pain, discomfort, and impaired mobility. This article provides an overview of common foot diseases, their causes, symptoms, and potential treatments.
Common Foot Diseases[edit | edit source]
Flatfoot[edit | edit source]
Flatfoot, or pes planus, is a condition where the arch of the foot collapses, resulting in the entire sole coming into complete or near-complete contact with the ground. It can be congenital or acquired, often due to posterior tibial tendon dysfunction. Symptoms may include pain, swelling, and difficulty walking.
Ischemia[edit | edit source]
Ischemia of the foot occurs when there is insufficient blood flow to the tissues, often due to peripheral artery disease. This can lead to pain, ulcers, and in severe cases, gangrene. Management includes improving circulation through lifestyle changes, medication, or surgical intervention.
Chilblains[edit | edit source]
Chilblains, or pernio, are small, itchy, and painful swellings on the skin that occur as a reaction to cold temperatures. They typically affect the toes and can be managed by keeping the feet warm and dry.
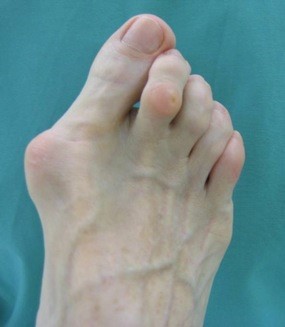
Hallux Valgus[edit | edit source]
Hallux valgus, commonly known as a bunion, is a deformity of the big toe joint, causing the toe to deviate towards the other toes. It can lead to pain and difficulty wearing shoes. Treatment options include orthotics, physical therapy, and surgery.
Athlete's Foot[edit | edit source]
Athlete's foot, or tinea pedis, is a fungal infection that affects the skin of the feet, particularly between the toes. It is characterized by itching, scaling, and redness. Antifungal treatments are effective in managing the condition.
Leprosy[edit | edit source]
Leprosy, caused by the bacterium Mycobacterium leprae, can lead to nerve damage and deformities in the feet. Early diagnosis and treatment with antibiotics can prevent severe complications.
Prevention and Management[edit | edit source]
Preventing foot diseases involves maintaining good foot hygiene, wearing appropriate footwear, and managing underlying health conditions such as diabetes and vascular disease. Regular check-ups with a healthcare provider can help in early detection and management of foot problems.
Related Pages[edit | edit source]
Search WikiMD
Ad.Tired of being Overweight? Try W8MD's physician weight loss program.
Semaglutide (Ozempic / Wegovy and Tirzepatide (Mounjaro / Zepbound) available.
Advertise on WikiMD
|
WikiMD's Wellness Encyclopedia |
| Let Food Be Thy Medicine Medicine Thy Food - Hippocrates |
Translate this page: - East Asian
中文,
日本,
한국어,
South Asian
हिन्दी,
தமிழ்,
తెలుగు,
Urdu,
ಕನ್ನಡ,
Southeast Asian
Indonesian,
Vietnamese,
Thai,
မြန်မာဘာသာ,
বাংলা
European
español,
Deutsch,
français,
Greek,
português do Brasil,
polski,
română,
русский,
Nederlands,
norsk,
svenska,
suomi,
Italian
Middle Eastern & African
عربى,
Turkish,
Persian,
Hebrew,
Afrikaans,
isiZulu,
Kiswahili,
Other
Bulgarian,
Hungarian,
Czech,
Swedish,
മലയാളം,
मराठी,
ਪੰਜਾਬੀ,
ગુજરાતી,
Portuguese,
Ukrainian
Medical Disclaimer: WikiMD is not a substitute for professional medical advice. The information on WikiMD is provided as an information resource only, may be incorrect, outdated or misleading, and is not to be used or relied on for any diagnostic or treatment purposes. Please consult your health care provider before making any healthcare decisions or for guidance about a specific medical condition. WikiMD expressly disclaims responsibility, and shall have no liability, for any damages, loss, injury, or liability whatsoever suffered as a result of your reliance on the information contained in this site. By visiting this site you agree to the foregoing terms and conditions, which may from time to time be changed or supplemented by WikiMD. If you do not agree to the foregoing terms and conditions, you should not enter or use this site. See full disclaimer.
Credits:Most images are courtesy of Wikimedia commons, and templates, categories Wikipedia, licensed under CC BY SA or similar.
Contributors: Prab R. Tumpati, MD