Electrometer
Instrument for measuring electric charge or electrical potential difference
An electrometer is a scientific instrument used for measuring electric charge or electrical potential difference. Electrometers are capable of measuring extremely small amounts of charge, down to a single electron in some cases. They are highly sensitive and are used in various fields such as physics, chemistry, and biology.
History[edit | edit source]
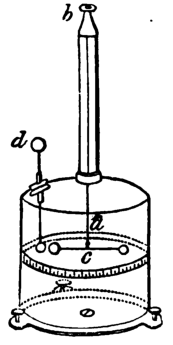
The development of electrometers dates back to the 18th century. Early electrometers were simple devices, such as the gold-leaf electroscope, which could detect the presence of electric charge. Over time, more sophisticated electrometers were developed, including the quadrant electrometer invented by Lord Kelvin in the 19th century.
Types of Electrometers[edit | edit source]
There are several types of electrometers, each with its own specific applications and advantages:
- Gold-leaf Electroscope: One of the earliest types of electrometers, it consists of a pair of thin gold leaves suspended from a metal rod. When a charge is applied, the leaves repel each other, and the degree of separation indicates the amount of charge.
- Quadrant Electrometer: Invented by Lord Kelvin, this device uses a needle suspended between four quadrants. The movement of the needle in response to an electric charge is measured to determine the potential difference.
- Vibrating Reed Electrometer: This type uses a vibrating reed mechanism to measure charge. It is highly sensitive and can measure very small charges.
- Solid-State Electrometer: Modern electrometers often use solid-state components, such as field-effect transistors (FETs), to achieve high sensitivity and accuracy.
Applications[edit | edit source]
Electrometers are used in a variety of scientific and industrial applications:
- Nuclear Physics: Measuring the charge of particles in particle accelerators and detectors.
- Electrochemistry: Studying the properties of electrolytes and electrochemical cells.
- Medical Physics: Used in radiation therapy to measure the dose of radiation.
- Environmental Science: Monitoring ionizing radiation in the environment.
Operation[edit | edit source]
The operation of an electrometer involves the detection and measurement of electric charge. The device typically consists of an input stage that collects the charge, a measurement stage that quantifies the charge, and a display stage that shows the result. Modern electrometers often include digital displays and computer interfaces for data logging and analysis.
See Also[edit | edit source]
References[edit | edit source]
Search WikiMD
Ad.Tired of being Overweight? Try W8MD's physician weight loss program.
Semaglutide (Ozempic / Wegovy and Tirzepatide (Mounjaro / Zepbound) available.
Advertise on WikiMD
|
WikiMD's Wellness Encyclopedia |
| Let Food Be Thy Medicine Medicine Thy Food - Hippocrates |
Translate this page: - East Asian
中文,
日本,
한국어,
South Asian
हिन्दी,
தமிழ்,
తెలుగు,
Urdu,
ಕನ್ನಡ,
Southeast Asian
Indonesian,
Vietnamese,
Thai,
မြန်မာဘာသာ,
বাংলা
European
español,
Deutsch,
français,
Greek,
português do Brasil,
polski,
română,
русский,
Nederlands,
norsk,
svenska,
suomi,
Italian
Middle Eastern & African
عربى,
Turkish,
Persian,
Hebrew,
Afrikaans,
isiZulu,
Kiswahili,
Other
Bulgarian,
Hungarian,
Czech,
Swedish,
മലയാളം,
मराठी,
ਪੰਜਾਬੀ,
ગુજરાતી,
Portuguese,
Ukrainian
Medical Disclaimer: WikiMD is not a substitute for professional medical advice. The information on WikiMD is provided as an information resource only, may be incorrect, outdated or misleading, and is not to be used or relied on for any diagnostic or treatment purposes. Please consult your health care provider before making any healthcare decisions or for guidance about a specific medical condition. WikiMD expressly disclaims responsibility, and shall have no liability, for any damages, loss, injury, or liability whatsoever suffered as a result of your reliance on the information contained in this site. By visiting this site you agree to the foregoing terms and conditions, which may from time to time be changed or supplemented by WikiMD. If you do not agree to the foregoing terms and conditions, you should not enter or use this site. See full disclaimer.
Credits:Most images are courtesy of Wikimedia commons, and templates, categories Wikipedia, licensed under CC BY SA or similar.
Contributors: Prab R. Tumpati, MD