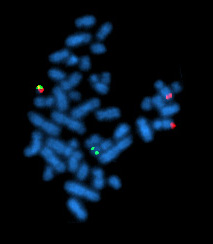
Molecular cytogenetics
Molecular Cytogenetics[edit | edit source]
Molecular cytogenetics is a branch of cytogenetics that combines the techniques of molecular biology and cytogenetics to study the structure and function of chromosomes. This field has revolutionized the ability to detect chromosomal abnormalities and has applications in genetic research, cancer diagnosis, and prenatal diagnosis.
Techniques[edit | edit source]
Molecular cytogenetics employs several advanced techniques to analyze chromosomes at a molecular level. Some of the key techniques include:
Fluorescence In Situ Hybridization (FISH)[edit | edit source]
Fluorescence in situ hybridization (FISH) is a technique used to detect and localize the presence or absence of specific DNA sequences on chromosomes. It uses fluorescent probes that bind to only those parts of the chromosome with which they show a high degree of sequence complementarity.
Comparative Genomic Hybridization (CGH)[edit | edit source]
Comparative genomic hybridization (CGH) is a molecular cytogenetic method for analyzing copy number variations (CNVs) in the DNA content of a cell. It allows for the detection of genomic imbalances such as deletions and duplications across the entire genome.
Spectral Karyotyping (SKY)[edit | edit source]
Spectral karyotyping (SKY) is a technique that uses multiple fluorescent dyes to paint each chromosome in a different color. This allows for the visualization of chromosomal rearrangements and abnormalities.
Applications[edit | edit source]
Molecular cytogenetics has a wide range of applications in various fields of medicine and biology.
Cancer Diagnosis[edit | edit source]
In oncology, molecular cytogenetics is used to identify chromosomal abnormalities associated with different types of cancer. For example, the Philadelphia chromosome, a result of a translocation between chromosomes 9 and 22, is detected using FISH in patients with chronic myeloid leukemia.
Prenatal Diagnosis[edit | edit source]
Molecular cytogenetics is also used in prenatal diagnosis to detect chromosomal abnormalities such as Down syndrome, Edwards syndrome, and Patau syndrome. Techniques like FISH can be applied to amniotic fluid or chorionic villus sampling to provide early diagnosis.
Genetic Research[edit | edit source]
In genetic research, molecular cytogenetics is used to study the genome organization and to map genes to specific locations on chromosomes. This helps in understanding the genetic basis of diseases and in identifying potential targets for gene therapy.
Future Directions[edit | edit source]
The field of molecular cytogenetics continues to evolve with advancements in technology. The development of next-generation sequencing (NGS) and CRISPR-Cas9 gene editing are expected to further enhance the capabilities of molecular cytogenetics in diagnosing and treating genetic disorders.
Related Pages[edit | edit source]
Search WikiMD
Ad.Tired of being Overweight? Try W8MD's physician weight loss program.
Semaglutide (Ozempic / Wegovy and Tirzepatide (Mounjaro / Zepbound) available.
Advertise on WikiMD
|
WikiMD's Wellness Encyclopedia |
| Let Food Be Thy Medicine Medicine Thy Food - Hippocrates |
Translate this page: - East Asian
中文,
日本,
한국어,
South Asian
हिन्दी,
தமிழ்,
తెలుగు,
Urdu,
ಕನ್ನಡ,
Southeast Asian
Indonesian,
Vietnamese,
Thai,
မြန်မာဘာသာ,
বাংলা
European
español,
Deutsch,
français,
Greek,
português do Brasil,
polski,
română,
русский,
Nederlands,
norsk,
svenska,
suomi,
Italian
Middle Eastern & African
عربى,
Turkish,
Persian,
Hebrew,
Afrikaans,
isiZulu,
Kiswahili,
Other
Bulgarian,
Hungarian,
Czech,
Swedish,
മലയാളം,
मराठी,
ਪੰਜਾਬੀ,
ગુજરાતી,
Portuguese,
Ukrainian
Medical Disclaimer: WikiMD is not a substitute for professional medical advice. The information on WikiMD is provided as an information resource only, may be incorrect, outdated or misleading, and is not to be used or relied on for any diagnostic or treatment purposes. Please consult your health care provider before making any healthcare decisions or for guidance about a specific medical condition. WikiMD expressly disclaims responsibility, and shall have no liability, for any damages, loss, injury, or liability whatsoever suffered as a result of your reliance on the information contained in this site. By visiting this site you agree to the foregoing terms and conditions, which may from time to time be changed or supplemented by WikiMD. If you do not agree to the foregoing terms and conditions, you should not enter or use this site. See full disclaimer.
Credits:Most images are courtesy of Wikimedia commons, and templates, categories Wikipedia, licensed under CC BY SA or similar.
Contributors: Prab R. Tumpati, MD