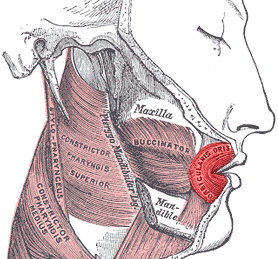
Orbicularis oris muscle
(Redirected from Musculus orbicularis oris)
==Orbicularis Oris Muscle ==
The orbicularis oris muscle is a complex of muscles in the lips that encircles the mouth. It is sometimes referred to as the "kissing muscle" because it is used to pucker the lips. The orbicularis oris muscle is a critical component in the function of the mouth and is involved in various activities such as speaking, eating, and facial expressions.
Anatomy[edit | edit source]
The orbicularis oris muscle is composed of four quadrants that interlace and form a circular muscle around the mouth. These quadrants are divided into the upper right, upper left, lower right, and lower left sections. Each quadrant is further divided into deep and superficial layers.
The muscle fibers of the orbicularis oris originate from the maxilla (upper jaw) and mandible (lower jaw) and insert into the skin around the lips. The muscle is innervated by the facial nerve, specifically the buccal and mandibular branches.
Function[edit | edit source]
The primary function of the orbicularis oris muscle is to control the movements of the mouth and lips. It is responsible for actions such as:
- **Puckering the lips**: Essential for actions like kissing and whistling.
- **Closing the mouth**: Helps in keeping the mouth closed.
- **Articulation**: Plays a crucial role in speech by controlling the movements necessary for pronouncing certain sounds.
- **Facial expressions**: Contributes to expressions such as frowning and smiling.
Clinical Significance[edit | edit source]
Damage or dysfunction of the orbicularis oris muscle can lead to difficulties in speech, eating, and facial expressions. Conditions that may affect this muscle include:
- **Bell's palsy**: A condition that causes temporary weakness or paralysis of the muscles on one side of the face.
- **Stroke**: Can lead to muscle weakness or paralysis, affecting the orbicularis oris muscle.
- **Facial trauma**: Injuries to the face can damage the muscle and impair its function.
Related Muscles[edit | edit source]
The orbicularis oris muscle works in conjunction with several other muscles of facial expression, including:
- Buccinator muscle
- Zygomaticus major muscle
- Zygomaticus minor muscle
- Levator labii superioris muscle
- Depressor anguli oris muscle
See Also[edit | edit source]
Search WikiMD
Ad.Tired of being Overweight? Try W8MD's physician weight loss program.
Semaglutide (Ozempic / Wegovy and Tirzepatide (Mounjaro / Zepbound) available.
Advertise on WikiMD
|
WikiMD's Wellness Encyclopedia |
| Let Food Be Thy Medicine Medicine Thy Food - Hippocrates |
Translate this page: - East Asian
中文,
日本,
한국어,
South Asian
हिन्दी,
தமிழ்,
తెలుగు,
Urdu,
ಕನ್ನಡ,
Southeast Asian
Indonesian,
Vietnamese,
Thai,
မြန်မာဘာသာ,
বাংলা
European
español,
Deutsch,
français,
Greek,
português do Brasil,
polski,
română,
русский,
Nederlands,
norsk,
svenska,
suomi,
Italian
Middle Eastern & African
عربى,
Turkish,
Persian,
Hebrew,
Afrikaans,
isiZulu,
Kiswahili,
Other
Bulgarian,
Hungarian,
Czech,
Swedish,
മലയാളം,
मराठी,
ਪੰਜਾਬੀ,
ગુજરાતી,
Portuguese,
Ukrainian
Medical Disclaimer: WikiMD is not a substitute for professional medical advice. The information on WikiMD is provided as an information resource only, may be incorrect, outdated or misleading, and is not to be used or relied on for any diagnostic or treatment purposes. Please consult your health care provider before making any healthcare decisions or for guidance about a specific medical condition. WikiMD expressly disclaims responsibility, and shall have no liability, for any damages, loss, injury, or liability whatsoever suffered as a result of your reliance on the information contained in this site. By visiting this site you agree to the foregoing terms and conditions, which may from time to time be changed or supplemented by WikiMD. If you do not agree to the foregoing terms and conditions, you should not enter or use this site. See full disclaimer.
Credits:Most images are courtesy of Wikimedia commons, and templates, categories Wikipedia, licensed under CC BY SA or similar.
Contributors: Prab R. Tumpati, MD