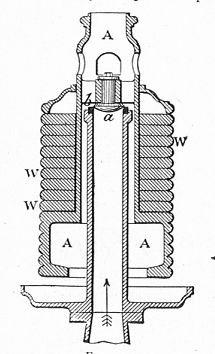
Safety valve
Safety valve is a critical component in various systems where pressure can build up to dangerous levels. It is designed to automatically release substances from a boiler, pressure vessel, or other system when the pressure or temperature exceeds preset limits. By doing so, safety valves ensure the safety of the equipment and the people operating it, preventing potential explosions or system failures.
Overview[edit | edit source]
A safety valve operates by opening at a predetermined set pressure, allowing the excess pressure to be vented out of the system, thereby preventing the pressure from escalating to a point where it could cause damage or failure. Once the pressure drops to a safe level, the valve closes, ensuring the system can continue to operate without interruption. The design of safety valves varies depending on the application, including the type of fluid (gas, steam, or liquid), operating environment, and the specific safety standards that need to be met.
Types of Safety Valves[edit | edit source]
There are several types of safety valves, each designed for specific applications and operating conditions:
- Pop-type safety valve: This is the most common type, which opens rapidly (pops open) when the set pressure is reached.
- Pilot-operated safety valve: Uses system pressure to seal the valve and opens when pressure under the pilot piston exceeds the set value.
- Relief valve: Gradually opens in proportion to the increase in pressure, used where precise control of the release is required.
- Temperature and pressure (T&P) relief valve: Specifically designed for water heaters to release water if either the temperature or pressure becomes too high.
Applications[edit | edit source]
Safety valves are used in a wide range of applications, including:
- Boilers and steam generators in power plants and industrial facilities
- Pressure vessels and tanks in chemical processing plants
- Gas storage facilities
- Oil and gas production and processing facilities
- Water heaters and domestic heating systems
Standards and Regulations[edit | edit source]
The design, installation, and maintenance of safety valves are governed by international and national standards and regulations to ensure they perform effectively in preventing overpressure conditions. Some of the key standards include:
- ASME (American Society of Mechanical Engineers) Boiler and Pressure Vessel Code
- API (American Petroleum Institute) standards
- EN (European Norm) standards
Maintenance[edit | edit source]
Regular maintenance and testing are crucial for the reliable operation of safety valves. This includes periodic inspection, testing for correct opening pressure, seat leakage, and reseating after operation. Maintenance ensures that the valve will operate as intended when required, providing protection against overpressure events.
Conclusion[edit | edit source]
Safety valves are an essential safety component in many industrial and domestic systems, providing a critical defense against the dangers of overpressure. By understanding the different types of safety valves, their applications, and the importance of regular maintenance, operators can ensure the safety and reliability of their systems.
Search WikiMD
Ad.Tired of being Overweight? Try W8MD's physician weight loss program.
Semaglutide (Ozempic / Wegovy and Tirzepatide (Mounjaro / Zepbound) available.
Advertise on WikiMD
|
WikiMD's Wellness Encyclopedia |
| Let Food Be Thy Medicine Medicine Thy Food - Hippocrates |
Translate this page: - East Asian
中文,
日本,
한국어,
South Asian
हिन्दी,
தமிழ்,
తెలుగు,
Urdu,
ಕನ್ನಡ,
Southeast Asian
Indonesian,
Vietnamese,
Thai,
မြန်မာဘာသာ,
বাংলা
European
español,
Deutsch,
français,
Greek,
português do Brasil,
polski,
română,
русский,
Nederlands,
norsk,
svenska,
suomi,
Italian
Middle Eastern & African
عربى,
Turkish,
Persian,
Hebrew,
Afrikaans,
isiZulu,
Kiswahili,
Other
Bulgarian,
Hungarian,
Czech,
Swedish,
മലയാളം,
मराठी,
ਪੰਜਾਬੀ,
ગુજરાતી,
Portuguese,
Ukrainian
Medical Disclaimer: WikiMD is not a substitute for professional medical advice. The information on WikiMD is provided as an information resource only, may be incorrect, outdated or misleading, and is not to be used or relied on for any diagnostic or treatment purposes. Please consult your health care provider before making any healthcare decisions or for guidance about a specific medical condition. WikiMD expressly disclaims responsibility, and shall have no liability, for any damages, loss, injury, or liability whatsoever suffered as a result of your reliance on the information contained in this site. By visiting this site you agree to the foregoing terms and conditions, which may from time to time be changed or supplemented by WikiMD. If you do not agree to the foregoing terms and conditions, you should not enter or use this site. See full disclaimer.
Credits:Most images are courtesy of Wikimedia commons, and templates, categories Wikipedia, licensed under CC BY SA or similar.
Contributors: Prab R. Tumpati, MD